Installing a solar system in California requires building permits, electrical permits, and interconnection applications that comply with the California Energy Commission’s Title 24 Building Energy Efficiency Standards. Since January 1, 2020, California’s solar mandate has required all new single-family homes and multi-family buildings up to three stories to include solar photovoltaic systems, making California the only U.S. state with mandatory solar requirements for residential construction. As of 2023, this mandate expanded to include commercial buildings, high-rise residential developments, and specific institutional properties.
Builders, construction professionals, and solar design specialists must now guarantee that each solar panel installation in California aligns with energy production and system capacity standards established by the California Energy Commission (CEC). Mastering these regulations proves crucial, not just for regulatory adherence, but for engineering economical systems that integrate seamlessly with existing interconnection frameworks and battery storage programs.

Understanding California’s Rooftop Solar Requirements
What Does California’s Solar Installation Law Entail?
California’s rooftop solar law represents a state-level regulation mandating that nearly all newly constructed residential properties incorporate solar panel systems. The California Energy Commission (CEC) approved this legislation in 2018, which became operational on January 1, 2020. The regulation covers new single-family residences and multi-unit residential structures up to three levels high. This requirement forms a component of California’s Title 24 Building Energy Efficiency Standards.
The law establishes that construction companies must integrate a photovoltaic energy system capable of offsetting the residence’s projected yearly power consumption. Determining system capacity involves considering factors including square footage, building orientation, local climate classification, and incorporated energy-saving features within the structure’s blueprint. This legislation guarantees that nearly all newly built California residences include solar infrastructure from initial occupancy, transforming solar from an elective feature into a mandatory building component.
Are Energy Storage Systems Mandatory Under California’s Solar Legislation?
The California rooftop solar regulation does not mandate battery storage integration for new residential construction. That said, incorporating an energy storage solution, like the Tesla Powerwall or Enphase IQ Battery, can decrease the necessary solar array capacity by as much as 25% according to California’s Energy Code.
Certain scenarios allow for even greater reductions; pairing storage with energy conservation improvements or demand management tactics can shrink system requirements by up to 40%. Though batteries aren’t compulsory, they provide increased design adaptability when satisfying California’s residential solar specifications, while enabling property owners to optimize solar energy utilization and emergency power capabilities.
How Does California’s Solar Law Apply to Business Properties?
California’s solar installation requirement underwent expansion in 2023 to encompass specific commercial structures and tall residential buildings. The revised solar legislation now mandates that newly built commercial facilities, including office spaces, educational institutions, storage facilities, and residential towers exceeding three stories, must incorporate solar panel systems as part of building code adherence.
Though energy storage isn’t required by the mandate, integrating battery systems can lower necessary solar capacity by up to 25%. When storage is combined with energy efficiency tactics or demand-response initiatives, even more substantial reductions become possible, providing enhanced flexibility for meeting California’s solar installation standards across residential and commercial applications.
These broadened requirements are fueling heightened demand for both rooftop photovoltaic systems and storage technologies statewide, generating significant expansion prospects for solar installation professionals and businesses collaborating with Solar Permit Solutions for permitting and engineering documentation.
How Has California’s Solar Regulation Affected the Industry?
California’s rooftop solar regulation has transformed solar contractors’ approaches to both residential and commercial installations. This state legislation mandates photovoltaic systems on most newly constructed buildings, establishing consistent demand for solar installations throughout California. Whether you’re an engineer developing photovoltaic design documentation or an installation contractor executing projects, comprehending how this regulation influences system capacity calculations, energy storage options, and code compliance requirements is critical.

California’s Solar Installation Standards for Newly Constructed Residences
The California solar installation standards for newly constructed residences mandate that the majority of new single-family residences and low-rise multi-unit structures (three stories or fewer) incorporate rooftop photovoltaic systems. This mandate took effect in 2020 as part of the state’s building energy standards (Title 24). Beginning in 2023, the regulation was broadened to include certain high-rise residential developments.
Newly constructed residences must be designed as “solar-ready,” featuring electrical infrastructure that accommodates future energy storage systems and electric-powered appliances. Although energy storage batteries aren’t mandatory, incorporating them can decrease the minimum mandated system capacity by as much as 25% when combined with demand-response programs and energy-efficient improvements.
Property owners may be eligible for financial incentives through the Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP). The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) designated more than $280 million in 2025 for residential photovoltaic and battery implementation, with additional assistance available for lower-income households and high-wildfire-risk areas.
Financial Implications and Factors Related to California’s Photovoltaic Regulation for New Residences
While environmentally advantageous, California’s photovoltaic regulation has faced opposition due to elevated initial expenses. The California Energy Commission calculates that solar installations increase new home construction costs by approximately $9,500. This results in an estimated $40 monthly rise in mortgage obligations. Nevertheless, the CEC anticipates homeowners will realize roughly $80 in monthly electricity cost reductions, producing positive long-term financial outcomes.
However, the implementation of NEM 3.0 has diminished payment for surplus solar power exported to the grid by approximately 75%, potentially limiting utility bill reductions unless systems incorporate battery storage to optimize on-site energy consumption.

Solar Permit Solutions
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
California’s Photovoltaic Requirement for Commercial Structures and High-Rise Developments
California authorities have revised the Building Energy Efficiency Standard, affecting commercial real estate. According to California’s Photovoltaic Requirement, many new commercial developments, including retail establishments, office buildings, educational institutions, multi-family residential complexes, and healthcare facilities, must incorporate solar installations coupled with energy storage systems.
The CEC projects this will generate 280 MW of additional solar power capacity each year, creating substantial opportunities for solar installation professionals. Furthermore, the requirement is expected to contribute an estimated 480 MWh of battery storage capacity across commercial properties.
California is encouraging energy storage battery installation partially to mitigate the effects of public safety power shutoffs, where electric utility providers disconnect service to help prevent wildfire incidents.
Essential Tools for Meeting California’s 2025 Solar Requirements
The California Energy Commission has authorized specific Solar Assessment Tools for meeting California’s solar compliance standards. Available resources comprise:
The Solar Photovoltaic (PV) Calculator analyzes building energy profiles and calculates the required quantity of photovoltaic panels.
The California Solar Shade Analysis examines solar accessibility at development locations and projects energy conservation benefits from adding shade elements or plant coverage.
The California Utility Allowance Calculator (CUAC) determines utility allowances for affordable housing developments by factoring in photovoltaic system specifications, building energy design elements, and applicable utility pricing structures.
Solar Permit Processing in California
California pioneers nationwide solar panel permit processing efficiency initiatives, transforming the approval workflow for PV installations. Through programs like the Solar Permitting Efficiency Act (AB 2188), California has unified procedures, minimized bureaucratic obstacles, and accelerated assessments. These initiatives encourage widespread solar energy implementation and establish a framework for other states pursuing faster renewable energy deployment.
Notwithstanding California’s solar regulation, obtaining permits for solar installations can prove difficult in California and elsewhere due to building and electrical code stipulations. Regrettably, numerous solar installation professionals face bureaucratic barriers when securing solar permits. Additionally, HOA regulations can impact solar permit approval in certain residential communities. Solar Permit Solutions was established to speed up solar energy adoption by providing solar permit solutions, including PV plan packages, solar engineering certifications, and interconnection submissions.
Conclusion
California’s solar mandate represents a transformative shift in how the state approaches renewable energy integration and residential construction standards. As this regulation continues to evolve and expand from residential properties to commercial developments, understanding compliance requirements, exemptions, and financial implications becomes increasingly critical for all stakeholders involved in California’s building industry.
The state’s commitment to solar energy adoption extends beyond simple installation requirements, it encompasses comprehensive building standards, streamlined permitting processes, and financial incentives designed to make the transition both feasible and economically beneficial. While initial construction costs may increase, the long-term advantages of reduced energy expenses, property tax exemptions, and enhanced energy independence present compelling benefits for property owners and developers alike.
Successfully navigating California’s solar regulations demands more than basic knowledge of the mandate itself. It requires expertise in system capacity calculations, understanding solar-ready infrastructure requirements, and maintaining compliance with constantly evolving building codes. The permitting process, despite California’s efficiency initiatives, still presents challenges that can delay projects and increase costs without proper guidance and documentation.
This is where specialized solar permitting services become invaluable. GreenLancer bridges the gap between regulatory requirements and practical implementation, offering comprehensive solutions that include code-compliant design packages, engineering certifications, and interconnection applications. With over a decade of solar industry experience, GreenLancer helps contractors, builders, and installation professionals overcome bureaucratic barriers and expedite project approvals.
As California continues pioneering renewable energy regulations that other states may eventually adopt, staying informed and partnering with experienced solar permitting specialists ensures your projects meet all compliance standards efficiently. Whether you’re developing a single-family residence or a large-scale commercial installation, expert support in navigating California’s solar mandate requirements proves essential for successful, timely project completion.
FAQs
California’s solar panel legislation has generated numerous inquiries from property owners, builders, prospective buyers, and installation professionals. As this solar requirement continues to influence residential construction practices, understanding its effects on home energy planning, setup procedures, and regulatory adherence remains essential.
Does California’s Solar Requirement Include Any Exemptions?
Certain California properties featuring limited roof space or substantial shade coverage may qualify for exemptions from rooftop solar installation requirements. Additionally, seasonal dwellings can receive exemptions from this solar regulation. To qualify, the property must be without at least one essential utility or feature necessary for year-round residence. Furthermore, multi-family structures located in zones lacking virtual net energy metering qualify for exemption under California’s solar regulation.
An alternative method for meeting these requirements involves residents joining a community solar program rather than installing individual rooftop systems.
Is Solar Installation Mandatory For California’s New Residential Construction?
California’s Energy Code has mandated solar panel installation on newly constructed homes since 2020. This solar regulation specifies that the majority of new residential structures must incorporate solar energy systems, encompassing single-family residences and multi-family developments reaching three stories. Nevertheless, certain exclusions apply to California’s solar stipulation for new construction, including vacation homes, properties with inadequate roof dimensions, and heavily shaded locations.
What Does California’s Solar Panel Legislation Entail?
California’s solar regulation, often referenced as the state’s solar panel legislation, mandates that all new residential structures up to three stories and new commercial developments incorporate solar photovoltaic installations. This legislation seeks to advance renewable energy adoption, decrease greenhouse gas output, and strengthen energy self-sufficiency by ensuring new buildings utilize California’s plentiful solar potential.
What Happens When a Property Fails To Meet California’s Solar Panel Legislation?
Failing to satisfy California’s solar requirement for new construction can trigger substantial setbacks. Properties may experience challenges obtaining construction permits, with local officials potentially withholding final occupancy authorization until solar energy stipulations are met. Given that exemptions under California’s solar regulation apply exclusively to particular circumstances, the majority of properties must incorporate solar energy installations to clear inspection and achieve legal habitability status.
What Tax Advantages Accompany California’s Solar Requirement?
California’s solar benefits, including federal tax credits for both residential and commercial installations, can substantially decrease the overall expense of a solar PV installation. Commercial installations may additionally qualify for accelerated or bonus depreciation.
Furthermore, according to section 73 of California’s revenue and taxation code, solar installations receive property tax exemptions. This provision ensures that solar panel installation won’t raise property taxes while simultaneously enhancing property worth.
Although other states have explored similar legislation, none have enacted such requirements thus far. Organizations like Environment America have advocated for comparable mandates in states such as Colorado, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Texas solar permits.
How Does California’s Solar Requirement Impact Home Construction Companies?
California’s solar regulation requires home construction companies to integrate solar panels into new residential projects, substantially affecting design and building strategies. Builders must designate space for solar energy installations, satisfy specific solar-ready standards, and guarantee electrical infrastructure compatibility with solar systems.
This regulation may elevate initial construction expenses, yet it delivers long-term advantages by enhancing the energy performance of new residences. California home construction companies must remain current with evolving regulations to prevent permit acquisition delays and guarantee adherence to solar standards.
What Solar-Ready Standards Are Included in California’s Solar Panel Requirement?
Under California’s solar regulation, newly built low-rise residential structures must comply with certain solar-ready standards detailed in the Building Energy Efficiency Standards. One critical standard addresses the solar zone minimum area, requiring single-family residential structures to maintain a designated space for solar setup.
This exclusion prevents solar energy system additions from being classified as new construction, thereby preserving the property’s base year valuation for taxation purposes. This ensures property owners and homeowners can incorporate solar panels without facing increased property taxes resulting from the solar addition.
Nevertheless, this exclusion expires on January 1, 2027. Consequently, any operational solar energy systems installed prior to this deadline will retain the exclusion benefits. Beyond this deadline, the exclusion may become unavailable unless additional legislative measures extend it. For properties considering off-grid solar system design, different considerations may apply.
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Certain California properties featuring limited roof space or substantial shade coverage may qualify for exemptions from rooftop solar installation requirements. Additionally, seasonal dwellings can receive exemptions from this solar regulation. To qualify, the property must be without at least one essential utility or feature necessary for year-round residence. Furthermore, multi-family structures located in zones lacking virtual net energy metering qualify for exemption under California's solar regulation. An alternative method for meeting these requirements involves residents joining a community solar program rather than installing individual rooftop systems.
California's Energy Code has mandated solar panel installation on newly constructed homes since 2020. This solar regulation specifies that the majority of new residential structures must incorporate solar energy systems, encompassing single-family residences and multi-family developments reaching three stories. Nevertheless, certain exclusions apply to California's solar stipulation for new construction, including vacation homes, properties with inadequate roof dimensions, and heavily shaded locations.
California's solar regulation, often referenced as the state's solar panel legislation, mandates that all new residential structures up to three stories and new commercial developments incorporate solar photovoltaic installations. This legislation seeks to advance renewable energy adoption, decrease greenhouse gas output, and strengthen energy self-sufficiency by ensuring new buildings utilize California's plentiful solar potential.
Failing to satisfy California's solar requirement for new construction can trigger substantial setbacks. Properties may experience challenges obtaining construction permits, with local officials potentially withholding final occupancy authorization until solar energy stipulations are met. Given that exemptions under California's solar regulation apply exclusively to particular circumstances, the majority of properties must incorporate solar energy installations to clear inspection and achieve legal habitability status.
California's solar benefits, including federal tax credits for both residential and commercial installations, can substantially decrease the overall expense of a solar PV installation. Commercial installations may additionally qualify for accelerated or bonus depreciation. Furthermore, according to section 73 of California's revenue and taxation code, solar installations receive property tax exemptions. This provision ensures that solar panel installation won't raise property taxes while simultaneously enhancing property worth.
Through 2025, California stands alone as the sole state mandating solar installations on new residential construction. In 2018, California established the requirement that new single-family residences and multi-family buildings reaching three stories incorporate solar panels. Although other states have explored similar legislation, none have enacted such requirements thus far. Organizations like Environment America have advocated for comparable mandates in states such as Colorado, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Nevada, New Mexico, North Carolina, Pennsylvania, and Texas.
Under California's solar stipulation for new construction, most newly erected homes and residential complexes must feature solar panels, as directed by California's solar regulation. This directive aims to encourage renewable energy utilization. However, exemptions exist under California's solar regulation for homes encountering conditions inappropriate for solar power production, including excessive shade or insufficient roof area. These exemptions guarantee that solar installations remain sensible and achievable for individual properties.
California maintains the nation's largest solar power capacity, exceeding 51.9 GW installed. This capacity can power approximately 13.9 million residences. Through 2023, solar energy represents roughly 32% of the state's electricity production. California's solar requirement for new construction has substantially accelerated this expansion, reinforcing California's position as a renewable energy frontrunner.
California's solar regulation requires home construction companies to integrate solar panels into new residential projects, substantially affecting design and building strategies. Builders must designate space for solar energy installations, satisfy specific solar-ready standards, and guarantee electrical infrastructure compatibility with solar systems. This regulation may elevate initial construction expenses, yet it delivers long-term advantages by enhancing the energy performance of new residences. California home construction companies must remain current with evolving regulations to prevent permit acquisition delays and guarantee adherence to solar standards.
Section 73 of California's Revenue and Taxation Code establishes a property tax exclusion preventing the solar power installation from affecting property tax assessments for properties equipped with solar panels. Consequently, the solar energy installation doesn't increase the property valuation used for taxation purposes for residential, commercial, and industrial California solar panel installations completed between January 1, 1999, and December 31, 2026. This exclusion prevents solar energy system additions from being classified as new construction, thereby preserving the property's base year valuation for taxation purposes. Nevertheless, this exclusion expires on January 1, 2027.
Under California's solar regulation, newly built low-rise residential structures must comply with certain solar-ready standards detailed in the Building Energy Efficiency Standards. One critical standard addresses the solar zone minimum area, requiring single-family residential structures to maintain a designated space for solar setup. This ensures that new construction is properly prepared for solar installation from the design phase.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
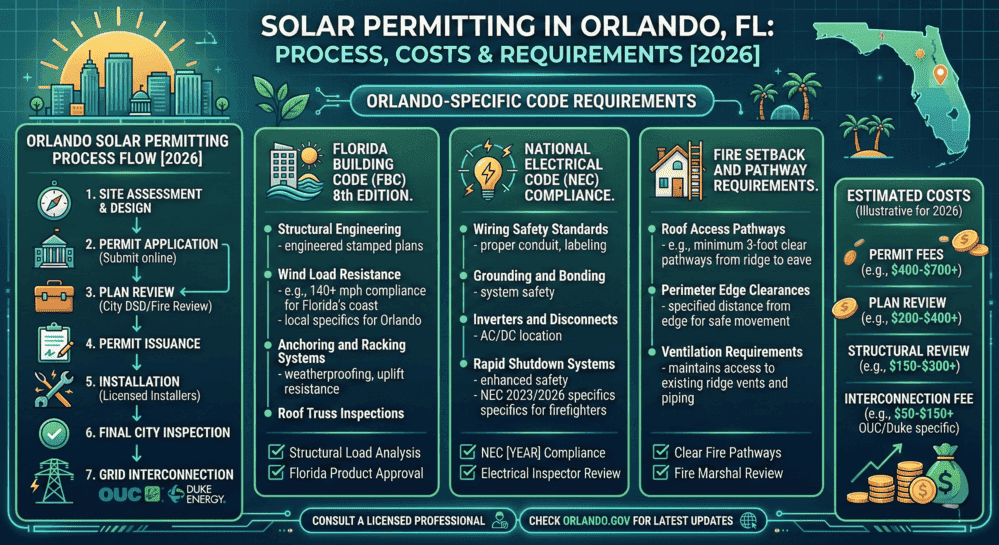
Solar Permitting in Orlando, FL: A Complete Guide for Homeowners & Installers
Solar permitting in Orlando, FL, requires a building permit and an electrical pe...
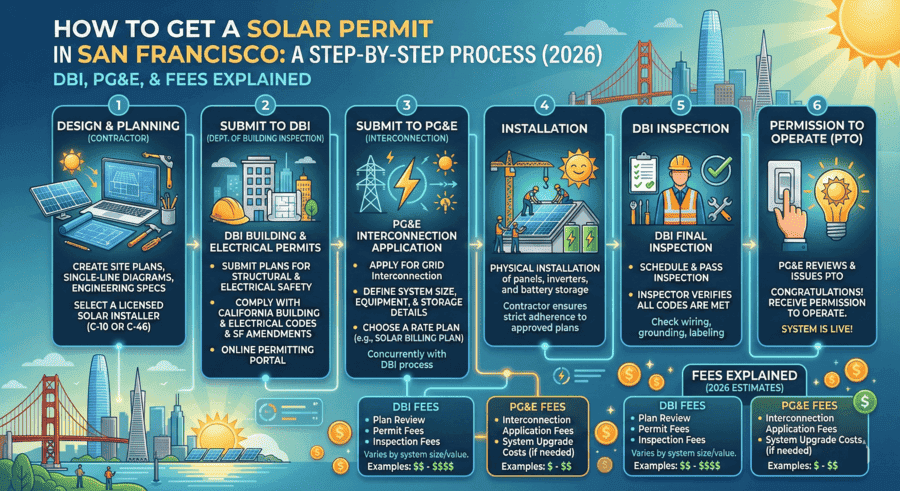
How To Get A Solar Permit In San Francisco: DBI, PG&E And Fees Explained (2026)
San Francisco solar permits require two separate approvals before your system ca...
Bifacial Solar Panel Installation And Permitting Guide
Bifacial solar panels generate 10 to 30 percent more energy than traditional mon...
