A solar inverter converts DC electricity from solar panels into AC power for home use. There are two main types: central inverters (cost $1,000-$3,000, last 10-15 years) and microinverters (last 20-25 years, cost more upfront but offer panel-level optimization). Central inverters work best for unshaded roofs with simple layouts, while microinverters are ideal for complex roofs or partial shade.
Key factors when choosing include: system size, roof shading, budget, warranty length, and whether you plan to add battery storage. Most residential systems are grid-tied, requiring proper inverter capacity matching, typically 1:1 ratio for microinverters or 0.8:1.2 DC-to-AC ratio for central inverters.
When discussing solar power systems, most people immediately picture solar panels on rooftops. However, while panels certainly play a vital role, inverters are equally essential components, particularly for developing sustainable energy solutions for residential and commercial properties worldwide. At Solar Permit Solutions, we understand that choosing the right inverter is crucial for system performance.

Understanding Solar Inverters: Purpose and Function
An inverter serves as a fundamental component in most photovoltaic (PV) systems, where sunlight is captured by panels and converted into electricity you can actually use. The inverter’s primary job is to transform the direct current (DC) generated by your panels into alternating current (AC), which powers your home’s appliances and devices.
Here’s how the conversion process works:
Electricity Generation: Solar panels produce DC electricity when sunlight hits them. Since DC flows in only one direction, it moves straight toward the inverter.
Conversion Process: At the inverter, the solar-generated electricity undergoes rapid switching that converts it into AC, which flows in multiple directions.
Power Delivery: Once converted to alternating current, the electricity can power your home, charge battery systems, or feed back into the utility grid.
Essentially, your inverter functions as your solar system’s core, directing generated power where it’s needed. Since inverter efficiency directly impacts your panels’ overall performance, selecting the appropriate system is vital for optimizing your PV installation. Understanding electrical fundamentals will help you grasp how these components work together seamlessly.
Pure Sine Wave vs. Modified Sine Wave
Not all AC electricity is created equal. The quality of the AC power your inverter produces is measured by its waveform, with pure sine wave being the gold standard for residential solar systems.
Pure Sine Wave Inverters produce smooth, consistent electrical current that perfectly mimics utility grid power. This clean power is essential for:
- Sensitive electronics like computers, televisions, and medical equipment
- Variable-speed motors in appliances like refrigerators and HVAC systems
- Audio equipment that requires clean power to prevent humming or buzzing
- Modern smart home devices and charging systems
Modified Sine Wave Inverters produce a stepped approximation of smooth AC power. While less expensive, these inverters can cause problems including reduced appliance efficiency, motor overheating, audible buzzing in audio equipment, and potential damage to sensitive electronics.
For home solar installations, quality manufacturers use only pure sine wave technology in their residential inverters. This ensures compatibility with all household devices and protects your valuable electronics. When evaluating inverter options, confirm that any system you’re considering produces pure sine wave output – this is a non-negotiable quality indicator that separates professional-grade equipment from budget alternatives.
Safety Features: Fault Detection and Automatic Shutdown
Beyond energy conversion, solar inverters serve as critical safety devices that continuously monitor your system for electrical hazards. These built-in protection mechanisms safeguard both your property and the people who maintain electrical infrastructure in your community.
Ground Fault Protection: Ground faults occur when electrical current escapes its intended path and flows through grounding conductors or other unintended routes. This can happen due to damaged wire insulation, moisture intrusion, or equipment degradation. Your inverter constantly monitors for these dangerous current leaks and will immediately shut down the system if ground fault current exceeds safe thresholds—typically 0.5 to 1.0 amperes. This rapid response prevents potential fire hazards and electrical shock risks.
Arc Fault Detection: Arc faults are particularly dangerous electrical events where current jumps across gaps in damaged connections or degraded components, creating intense heat and potential fire hazards. Modern inverters meeting NEC 2017 and later standards include Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (AFCI) technology that analyzes electrical signatures and detects the characteristic patterns of dangerous arcing. When detected, the inverter interrupts power flow within milliseconds, preventing the arc from escalating into a fire hazard.
Overvoltage and Overcurrent Protection: Inverters continuously monitor voltage and current levels throughout your system. Lightning strikes, utility grid fluctuations, or equipment malfunctions can cause dangerous spikes. Your inverter’s protection circuitry responds instantly to these events, disconnecting affected components before damage occurs. This protects not only the inverter itself but also your solar panels, home electrical system, and connected appliances.
These automated safety systems work silently in the background, providing continuous protection throughout your system’s operational life. When a fault is detected and the system shuts down, your inverter’s monitoring interface will typically display fault codes that help service technicians quickly identify and resolve the underlying issue. This combination of prevention, detection, and diagnostic capability makes modern inverters essential safety components in every properly designed solar installation.
Types of Solar Power Inverters
Four primary inverter technologies dominate today’s residential PV market. Each option effectively produces usable household electricity while offering unique benefits and tradeoffs. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office provides excellent resources for understanding these technologies in greater depth.
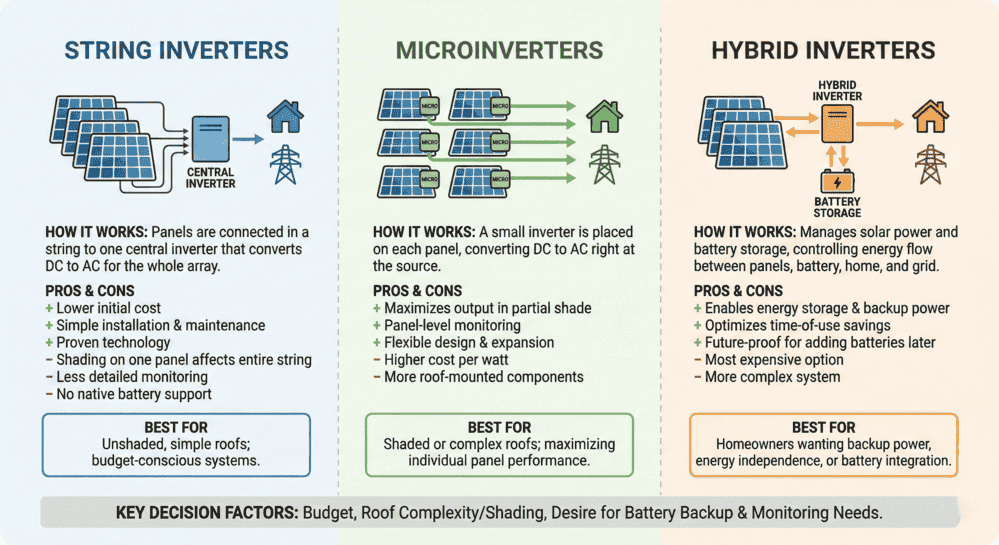
String Inverters (Central Inverters)
String inverters represent the most widely used technology in global PV installations. These units connect multiple panels together in series configurations called “strings,” combining high-voltage DC output before conversion to AC power at a single central unit. The inverter typically mounts on a wall near your main electrical panel or in a garage.
Advantages
String inverter installations typically require the lowest upfront investment of any inverter type, making them attractive for budget-conscious homeowners. These units usually mount in accessible ground-level locations, which simplifies maintenance and reduces the complexity of wire management. The technology is well-proven with decades of real-world performance data, and most licensed electricians are familiar with string inverter installation and troubleshooting.
Drawbacks
The biggest limitation of string inverters is their susceptibility to the “weakest link” effect. When one panel in a string underperforms due to shade, debris, defects, or other issues, it can dramatically reduce the output of every panel in that series. This means a single shaded panel can drag down the production of an entire 10-panel string.
String inverters typically last 10 to 15 years, meaning you will likely need at least one replacement during your solar panels’ 25 to 30 year lifespan. This mid-life replacement adds to total ownership costs, especially if the failure occurs outside warranty coverage. Additionally, since there is only one conversion point, your entire solar system stops producing usable power when the string inverter fails.
Best For: Properties with simple, south-facing roofs that receive consistent, unshaded sunlight throughout the day. Ideal for homeowners seeking the most affordable upfront option.
Microinverters
Microinverters install directly beneath or adjacent to each individual panel in your array. By performing DC-to-AC conversion at the panel level, microinverters allow each panel to operate independently, which eliminates the “weakest link” problem entirely.
Advantages
Microinverters optimize total system efficiency by allowing each panel to produce at its maximum capacity regardless of what neighboring panels are doing. If one panel is shaded while others receive full sun, only the shaded panel’s output decreases. Premium microinverter products include 25-year warranties that match the expected lifespan of your solar panels, exceeding standard string inverter coverage by more than double.
Microinverters also enable detailed, per-panel performance monitoring through smartphone apps and web dashboards. This makes it easy to identify underperforming panels quickly. Future system expansion becomes simpler with microinverters because you can add panels one at a time without needing to upgrade a central unit. The built-in redundancy means that if one microinverter fails, every other panel in your system continues generating electricity normally.
Drawbacks
Microinverter-based installations generally cost more upfront than string inverter systems, typically $200 to $400 per panel. Although failures are uncommon, servicing a microinverter requires roof-level access beneath the panels rather than simple ground-level replacement. This can increase labor costs for repairs.
Best For: Complex roofs with multiple orientations, partial shading, dormers, or other obstructions. Also ideal for homeowners who want panel-level monitoring and plan to expand their system over time.
Power Optimizers
Power optimizers represent a hybrid approach that combines elements of both string inverters and microinverters. Like microinverters, power optimizers are installed at each individual panel. However, instead of converting DC to AC at the panel level, they condition and optimize the DC electricity before sending it to a central string inverter for final conversion.
Advantages
- Maximize individual panel performance similar to microinverters
- Better system efficiency with partial shading compared to basic string inverters
- Lower cost than full microinverter systems (typically $50-$200 per panel)
- Maintain ease of centralized inverter maintenance
- Enable panel-level monitoring and diagnostics
Drawbacks
- More expensive than basic string inverter systems
- Adds complexity with more potential failure points
- Still requires eventual central inverter replacement
- Installation complexity between string and microinverter systems
This configuration offers an excellent compromise for homeowners who want improved performance in partially shaded conditions without the full investment of a microinverter system.
Advantages
Power optimizers solve the “weakest link” problem by allowing each panel to operate at its own maximum power point, similar to microinverters. They provide panel-level performance monitoring while still using a single, accessible string inverter for the actual DC-to-AC conversion. Power optimizers are often less expensive than full microinverter systems while delivering comparable performance improvements in shaded or complex installations.
Drawbacks
Power optimizer systems still rely on a central string inverter, which means you still have a single point of failure for the conversion stage. The total system cost is higher than a standalone string inverter because you are purchasing both the optimizers and the inverter. Since the optimizers mount beneath each panel on the roof, servicing them requires the same roof-level access as microinverters.
Best For: Homeowners who want panel-level optimization and monitoring but prefer to keep costs lower than a full microinverter system. A strong choice for roofs with moderate shading where a basic string inverter would lose too much production.
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters are one of the newest and fastest-growing categories in residential solar technology. A hybrid inverter combines a traditional solar inverter with a battery inverter component in a single unit, allowing it to manage power flow between your solar panels, battery backup system, the utility grid, and sometimes additional sources like backup generators.
Advantages
Hybrid inverters can convert electricity in both directions, from DC to AC for home use and from AC to DC for battery charging. This bidirectional capability makes them the most versatile inverter option available. They integrate solar production, battery storage, and grid connection in one device, simplifying system design and reducing the total number of components needed. If you plan to add battery storage in the future, installing a hybrid inverter now eliminates the need to retrofit your system later. Some hybrid inverters also support direct DC charging of electric vehicles, which is more efficient than AC charging.
Drawbacks
Hybrid inverters carry a higher initial cost than standard grid-tied inverters because of their additional capabilities. The technology is also more complex, which can make installation and troubleshooting slightly more involved. Not all hybrid inverters support every battery brand or chemistry, so compatibility must be verified during the design phase.
Best For: Homeowners who want or plan to add battery storage, need backup power during outages, or are building a comprehensive home energy system that includes EV charging. Also well suited for off-grid installations where grid connection is not available.
Quick Comparison: All Four Inverter Types
|
Feature |
String Inverter |
Microinverter |
Power Optimizer |
Hybrid Inverter |
|
Cost |
$1,000-$2,000 |
$200-$400/panel |
$50-$200/panel + inverter |
$2,000-$4,000+ |
|
Typical Lifespan |
10-15 years |
20-25 years |
20-25 years (optimizer) + 10-15 years (inverter) |
10-15 years |
|
Warranty |
10-15 years |
Up to 25 years |
25 years (optimizer), 12-15 years (inverter) |
10-12 years |
|
Efficiency Range |
96-98% |
95-97% |
96-98% (combined) |
95-97% |
|
Panel-Level Monitoring |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Depends on configuration |
|
Shade Tolerance |
Poor |
Excellent |
Excellent |
Depends on configuration |
|
Battery Compatible |
Requires separate inverter |
AC-coupled solutions |
DC-coupled solutions |
Built-in |
|
System Expansion |
Requires inverter upgrade |
Add panels individually |
Add panels with optimizers |
May require upgrade |
|
Best Roof Type |
Simple, unshaded |
Complex, shaded |
Moderate shade |
Any (with battery plans) |
How Much Does a Solar Inverter Cost?
Inverter costs vary significantly based on the type, capacity, brand, and features you select. As a general guideline, inverters represent approximately 10% of your total solar system cost. Understanding the price ranges helps you budget accurately and evaluate quotes from installers.
- String Inverters: $1,000 to $2,000 for most residential systems. Larger systems or premium brands may push costs slightly higher. This is the most affordable option per watt of capacity.
- Microinverters: $200 to $400 per panel. For a typical 20-panel system, total microinverter costs range from $4,000 to $8,000. The higher upfront cost is offset by longer warranties and better performance in non-ideal conditions.
- Power Optimizers: $50 to $200 per panel, plus the cost of a compatible string inverter ($1,000 to $2,000). Total system cost falls between string-only and microinverter configurations.
- Hybrid Inverters: $2,000 to $4,000 or more, depending on capacity and battery compatibility. While more expensive upfront, a hybrid inverter can save money compared to installing a standard inverter now and retrofitting a battery inverter later.
Solar Permit Solutions
Homeowner Going Solar?
Get the permit-ready plan set your city requires — delivered fast so your solar project stays on schedule.
Selecting Your Inverter System
To maximize electricity generation and lifetime savings, inverter selection represents a critical phase in solar system planning. Finding the optimal inverter configuration requires evaluating specific property characteristics, including power requirements, roof design complexity, and potential shading impacts on system performance. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Solar Energy Technologies Office provides excellent resources for understanding these technical considerations.
Central Inverters or Microinverters?
While central inverters offer lower initial and scaled costs, microinverters frequently provide superior long-term value for home and business solar installations. Quality microinverters are engineered to match your panels’ lifespan and maximize production in systems facing shading or inconsistent panel output.
Ultimately, deciding between central inverters or microinverters should involve consultation with qualified solar professionals. Since this choice depends on your unique situation, it’s worthwhile to evaluate all design possibilities before proceeding with installation.
Determining Appropriate Inverter Capacity
For both central inverter and microinverter configurations, installing properly-sized equipment is crucial for optimizing solar output without unnecessary project expenses.
With microinverters, capacity matching is straightforward since each unit connects to one panel. To capture maximum usable solar energy, your microinverter’s DC input and AC output ratings must align properly to optimize electricity conversion.
Similarly, central inverter capacity follows identical principles but on a larger scale. Your central unit should handle all expected panel generation under normal conditions. While microinverters simplify future panel additions, selecting the correct central inverter capacity before installation is critical, as these systems are purpose-built without expansion capabilities.
Battery Storage, Grid Connection, and Hybrid Configurations
Battery storage plans also affect inverter selection. Most residential and commercial solar installations today connect to the utility grid, using inverters that can export surplus electricity to the power network.
Beyond standard grid-connected inverters, hybrid models can route electricity between your property, battery storage, the utility network, and sometimes alternative power sources like backup generators. For properties completely disconnected from utility infrastructure, off-grid solar system design requires specialized inverter configurations.
Anti-Islanding Protection: Grid Safety During Outages
When utility power fails in your neighborhood, your solar panels may still be generating electricity—and without proper safeguards, this creates a dangerous situation called “islanding.” Anti-islanding protection is a critical inverter feature that protects utility workers and prevents equipment damage during grid outages.
Understanding the Islanding Hazard: During a power outage, utility crews work to repair damaged lines under the assumption that those lines are de-energized. If your solar system continues feeding electricity into the grid during these repairs, it creates a potentially lethal “island” of live electrical current. This energized section could electrocute line workers, damage restoration equipment, or prevent automatic reconnection systems from functioning properly.
How Anti-Islanding Technology Works: Grid-tied solar inverters continuously monitor the utility connection, analyzing voltage, frequency, and other electrical parameters. When the inverter detects that grid power has failed—typically within 0.1 to 2 seconds—it immediately disconnects your solar system from the utility lines and ceases AC power production. This rapid response is mandated by IEEE 1547 and UL 1741 standards, which require certified anti-islanding protection in all grid-connected solar equipment.
The inverter remains disconnected until it detects that stable grid power has been restored for a specified duration (typically 5 minutes). Only after confirming normal grid operation will your inverter automatically reconnect and resume solar power production. This automatic process requires no homeowner intervention and happens seamlessly during everyday grid fluctuations and outage events.
Backup Power During Outages: Standard grid-tied inverters with anti-islanding protection will shut down during outages, meaning your solar panels won’t power your home even on sunny afternoons. However, advanced systems with battery storage and specialized hybrid inverters can provide backup power while maintaining safety. These systems physically isolate your home from the grid during outages, creating a protected “microgrid” that can safely utilize solar production and stored battery energy. When evaluating inverter options, clarify whether backup power capability is important for your situation, as this will influence both equipment selection and system design requirements.
Advanced Monitoring and Performance Tracking
Modern solar inverters function as the communication hub for your entire PV system, providing real-time insights into your energy production and consumption patterns. Most contemporary inverters include built-in monitoring capabilities that connect to your home’s Wi-Fi network, allowing you to track system performance from anywhere using smartphone apps or web-based portals.
What You Can Monitor: Through your inverter’s monitoring interface, you can typically access:
- Real-time energy production (current watts being generated)
- Daily, monthly, and lifetime energy totals
- Individual panel performance (with microinverters or power optimizers)
- System efficiency metrics and performance ratios
- Environmental impact data (CO₂ offset, trees planted equivalent)
- Utility grid interaction and energy export/import levels
Performance Alerts and Diagnostics: Advanced monitoring systems don’t just display data – they actively protect your investment. Your inverter can detect performance anomalies and send alerts when:
- Panel output drops below expected levels (indicating shading, soiling, or equipment issues)
- System efficiency decreases unexpectedly
- Individual components malfunction or fail
- Maintenance is required or warranty events occur
This proactive monitoring allows you to address small issues before they become major problems, maximizing your system’s lifetime energy production. Many installers and service providers can also access your monitoring data remotely, enabling faster diagnosis and service scheduling when maintenance is needed. Understanding your system’s monitoring capabilities helps you stay informed and ensures you’re capturing every available kilowatt-hour from your solar investment.
Moving Forward: Professional Consultation
To ensure system safety and protect your investment, optimal inverter selection and installation should involve certified professionals. In fact, legal requirements typically mandate licensed electrician approval for most PV designs before utilities and building departments grant permits. Understanding the complete solar permit application process is essential for compliance.
Many homeowners don’t realize the serious consequences of installing solar panels without proper permits, including safety hazards, insurance complications, and potential legal issues. The SolSmart permitting and inspection guidelines provide comprehensive information on regulatory requirements.
By consulting multiple local installers, you can identify the ideal solar solution for your property with components specifically chosen to maximize efficiency, performance, and long-term returns. Avoiding common solar permit mistakes can save you significant time and money during the installation process.
For homeowners in California, reviewing the California solar permit guide ensures compliance with state-specific regulations. Additionally, if you live in a planned community, understanding how HOA regulations impact solar approvals is crucial before beginning your project.
Consider using solar permit expediting services if you need faster approval timelines for your installation.
Environmental Impact and End-of-Life Considerations
Solar inverters play a crucial role in clean energy production, and their environmental benefits far outweigh their manufacturing footprint. Most inverter components, including metals, circuit boards, and housing materials, can be recycled at the end of their operational life. Quality manufacturers design inverters with recyclability in mind, allowing up to 95% of materials to be recovered and reused.
When your inverter reaches the end of its 10-25 year lifespan, never dispose of it in regular trash. These devices may contain small amounts of hazardous materials that require proper handling. Instead, contact your original installer or a certified solar service provider who can arrange for safe recycling through specialized e-waste facilities. Many inverter manufacturers also offer take-back programs that ensure responsible disposal and material recovery. By properly recycling your old inverter, you’re completing the sustainability cycle and supporting the circular economy in renewable energy equipment.
Conclusion
Selecting the right solar inverter is a decision that will impact your energy production, savings, and system reliability for decades to come. Whether you choose a central inverter for its cost-effectiveness or opt for microinverters to maximize individual panel performance, understanding the technology behind these essential components empowers you to make informed decisions about your solar investment.
Remember that your inverter isn’t just a technical component, it’s the bridge between your solar panels and the energy independence you’re seeking. The initial investment in quality inverter technology, paired with proper system design, will pay dividends through increased efficiency, reduced maintenance headaches, and optimized energy production throughout your system’s lifetime.
As solar technology continues to evolve, inverter innovations are making renewable energy more accessible, reliable, and efficient than ever before. Resources like the IEEE Power & Energy Society’s renewable energy initiatives and Energy Star’s energy-saving programs demonstrate the industry’s commitment to advancement. For more insights on solar technology and permitting, visit our blog regularly.
By taking the time to research your options, consult with qualified professionals, and consider your property’s unique characteristics, you’re not just installing a solar system, you’re investing in a sustainable energy future that benefits both your household and the environment. Tools like the World Resources Institute’s solar radiation maps can help you understand your location’s solar potential.
The journey to solar energy may seem complex, but with the right inverter system tailored to your needs, you’ll be well-positioned to harness the sun’s power effectively and economically for years to come. Stay informed by following the Department of Energy’s solar blog, EnergySage’s latest updates, and Green Building Advisor’s technical articles for ongoing education about solar technology.
FAQs
Homeowner Going Solar?
Get the permit-ready plan set your city requires — delivered fast so your solar project stays on schedule.
Frequently Asked Questions
Central inverters typically last between 10 and 15 years, which means you'll likely need at least one replacement during your solar panels' 25-30 year lifespan. Microinverters, on the other hand, are generally built to last 20-25 years and often come with warranties matching that timeframe. This longevity difference is an important factor when calculating total cost of ownership, as central inverter replacement costs and potential installation fees should be factored into your long-term budget planning.
Replacement costs vary significantly based on inverter type and system size. Central inverter replacements typically range from $1,000 to $3,000, including equipment and labor, depending on your system's capacity. Microinverter replacements generally cost $200-$400 per unit, though you'll rarely need to replace all units simultaneously. Labor costs for microinverter replacement may be higher due to roof access requirements. Many quality inverters come with warranties that cover replacement costs during the coverage period, so reviewing warranty terms before purchase is essential.
Yes, inverters can be upgraded independently of your solar panels in most cases. This is particularly common when central inverters reach the end of their lifespan or when homeowners want to add battery storage capabilities. However, compatibility is crucial, your new inverter must match your panels' voltage and power specifications. Some homeowners even switch from central inverters to microinverters during upgrades, though this requires installing individual units beneath each panel. Understanding structural considerations for solar installations is important when making equipment changes. Always consult with a licensed solar professional to ensure compatibility and optimal system configuration.
The impact depends on your inverter type. With a central inverter system, your entire solar array stops producing electricity when the inverter fails, leaving you completely dependent on grid power until replacement occurs. With microinverter systems, only the panel connected to the failed microinverter stops producing, the rest of your system continues generating electricity normally. This built-in redundancy is one of the key advantages of microinverter technology, ensuring you maintain at least partial solar production even when maintenance is needed.
Standard grid-tied inverters automatically shut down during power outages for safety reasons, this prevents solar-generated electricity from feeding back into the grid and potentially harming utility workers repairing lines. However, if you have a hybrid inverter paired with battery storage, your system can provide backup power during outages by isolating from the grid and drawing from your batteries. Some advanced systems can also continue charging batteries from solar panels during daylight outages, providing truly independent power. If backup power during outages is important to you, discuss hybrid inverter and battery storage options with your installer during the planning phase. For comprehensive guidance on planning considerations, review Pennsylvania State University's ordinance considerations for solar development.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...