Commercial solar requirements include structural and electrical code compliance (NEC and IBC), solar permit design submission, energy efficiency verification, fire safety clearances (3 feet from roof ridges, 18 inches from hip/valley lines), inverter manufacturer installation standards, regular inspections, tax filing documentation, and utility interconnection coordination. The installation process spans 3-6 months across six phases: site evaluation, custom design, permit approval, financing selection, installation execution, and final inspection with utility interconnection.
Business leaders across the United States face mounting pressure to address climate change, navigate energy market instability, and meet stakeholder sustainability expectations. Commercial solar power delivers a proven path forward, offering measurable cost reductions and environmental benefits for organizations spanning industrial, agricultural, and commercial sectors.
Adopting solar energy extends beyond panel installation. Successfully navigating commercial solar requirements, including permitting protocols, design specifications, code compliance, and utility interconnection, requires strategic planning. Property owners who underestimate these critical components encounter project delays, regulatory setbacks, or inefficient systems that fail to deliver expected returns.
Federal incentives include the 30% Investment Tax Credit (ITC) and Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), allowing five-year depreciation. A $1,000,000 commercial solar system generates $850,000 in depreciation deductions after ITC adjustments while reducing operating expenses by approximately $1,400 annually per average facility, according to Department of Energy data.
This comprehensive resource equips you with actionable knowledge for your solar project. Discover how to address building codes, execute proper solar permit design, and capitalize on federal tax incentives while ensuring full compliance and optimal system performance.

Understanding Commercial Solar Requirements
Every commercial solar project must satisfy specific technical, legal, and procedural standards before installation commences. While commercial solar requirements vary by jurisdiction, expect to address these fundamental elements:
- Structural and Electrical Code Compliance: Align your installation with National Electric Code (NEC) and International Building Code (IBC) mandates. The IBC establishes roof attachment protocols in Section 1503, defines fire classifications for photovoltaic systems relative to roofing materials in Section 1509, and outlines structural load requirements in Section 3403.
- Solar Permit Design and Application Package: Compile a comprehensive permit submission featuring electrical schematics, load calculations, structural engineering reports, roof layout plans, and anchoring specifications.
- Energy Efficiency Standards Verification: Demonstrate compliance through either the prescriptive method (which establishes fixed component requirements) or the performance method (which permits customized energy modeling to meet efficiency targets).
- Fire Safety and Emergency Access Planning: Establish adequate clearances around rooftop equipment for fire safety and emergency responder access. Standard specifications require minimum clearances of 3 feet from roof ridges and 18 inches from hip or valley lines.
- Inverter Manufacturer Installation Protocol: Follow manufacturer installation guidelines precisely to maintain system performance and preserve warranty validity. Most inverter manufacturers extend warranties beyond the standard 10- to 12-year industry benchmark.
- Inspection and Testing Schedules: Implement routine inspection procedures to verify safe and efficient system operation. Inspectors confirm proper installation according to manufacturer specifications, including equipment sizing, grounding integrity, and wiring configurations.
- Tax Filing Documentation: Maintain complete records of system components and warranty documentation for tax submissions and incentive claim processing.
- Utility Company Coordination: Submit an interconnection application to your utility provider containing system capacity details, installation location information, and technical specifications.
Meeting these requirements positions your system for legal compliance, operational safety, lasting durability, and maximum solar incentive eligibility.
The Solar Installation Process: Planning Through Activation
Understanding your installation timeline and procedural workflow helps you manage expectations and minimize business disruptions. A structured methodology ensures smooth progression through each phase, from initial planning to final inspection.
1. Site Evaluation and Energy Assessment
Start with a comprehensive evaluation of your commercial facility or installation site. Professional solar contractors examine:
- Historical Energy Consumption and Demand Patterns: Analyze usage data to determine appropriate system sizing for your operational needs.
- Available Installation Space: Evaluate roof or ground space to confirm sufficient area for panel deployment.
- Structural Load Capacity: Assess building structural integrity to ensure adequate support for solar system weight.
- Shading Analysis and Solar Access: Document potential shading issues using solar radiation mapping data that could impact system productivity.
- Energy Storage and Backup Power Options: Consider battery storage solutions for enhanced energy security and independence.
This evaluation phase establishes your energy requirements and defines your system’s power generation capacity and savings potential.
2. Custom Solar System Design
Once you’ve clarified project objectives and site constraints, your solar provider develops a tailored system design. Critical design elements include:
- Panel Positioning and Angle Optimization: Configure panel orientation and tilt to maximize solar exposure.
- Inverter Selection and Configuration: Match inverter specifications to your interconnection voltage requirements.
- Equipment Layout Strategy: Position junction boxes, inverters, and safety disconnects for optimal performance and access.
- Compliance and Safety Integration: Incorporate pathways for annual maintenance access and emergency responder requirements.
This design phase ensures your solar installation maximizes energy production while maintaining code compliance and integrating seamlessly with your facility infrastructure.
3. Permit Application and Regulatory Approval
Secure necessary approvals by submitting a complete solar permit design package to your local building authority. Your submission package typically includes:
- Electrical system diagrams
- Load calculation worksheets
- Structural engineering assessments
- Roof layout and attachment details
- Interconnection documentation
Your application must demonstrate energy standard compliance using either the prescriptive approach (fixed requirements) or the performance approach (custom modeling). Anticipate review periods ranging from several weeks to multiple months depending on local authority workload.
4. Financing Strategy Selection
After completing the design and securing approvals, choose the financing structure that aligns with your business objectives. Available financing options include:
- Solar Lease Programs: Pay fixed monthly fees to access solar power without ownership obligations.
- Solar Loan Financing: Finance upfront costs while retaining system ownership and complete tax benefit access.
- Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Purchase electricity at predetermined rates per kilowatt-hour.
- Direct Purchase: Pay the full system cost upfront for immediate ownership.
Your financing choice impacts long-term return on investment, operational expenses, and tax planning strategies. Understanding insurance and liability considerations also helps protect your investment.
5. System Installation Execution
With financing secured and permits approved, installation work begins. Your solar installation contractor manages the complete process, including:
- High-efficiency solar panel deployment
- Commercial-grade equipment installation
- Inverter and electrical wiring integration
- Racking and ballast system assembly
- Optional energy storage installation for backup power capability
Experienced solar installers adhere strictly to safety protocols, code requirements, and manufacturer specifications to ensure reliable system performance.
6. Final Inspection, Interconnection and System Activation
Before energizing your system, it must pass inspection by the Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ). Simultaneously, complete the utility interconnection procedure.
Final completion tasks include:
- Comprehensive structural and electrical verification
- Solar interconnection diagram and inverter setting review
- Safety disconnection point confirmation
- Interconnection request submission to utility provider
Upon completion, your system connects to the utility grid, delivering clean solar electricity to your facility and often generating excess energy for credit through renewable energy certificates (RECs).

Financial Incentives and Tax Benefits
While solar’s environmental impact drives adoption, financial advantages provide equally compelling motivation. United States businesses access substantial tax incentives and rebates that improve return on investment.
Federal Incentive Programs
- Federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC): Deduct 30% of total system costs, including energy storage and labor expenses, from your federal tax liability.
- Accelerated Depreciation (MACRS): Depreciate solar system value over five years under the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System, reducing taxable income. A $1,000,000 system generates $850,000 in depreciation deductions after accounting for ITC adjustments.
Additional Financial Advantages
- Property Tax Exemptions: Numerous states exempt solar installations from property value assessments, preventing property tax increases. California provides property tax exemptions for added solar system value, maintaining existing tax levels post-installation.
- State and Local Rebate Programs: Access rebates, cash-back incentives, and zero-interest loan programs available in select regions. The Department of Energy’s Home Energy Rebates Program provides rebates for energy efficiency improvements that combine effectively with solar installations.
- Reduced Operating Expenses: Generate your own electricity to significantly decrease utility bills over time. Department of Energy data indicates solar systems save average U.S. households approximately $1,400 annually on electricity costs.
- Enhanced Property Valuation: Solar installations increase property value and attract environmentally conscious tenants. Research demonstrates homes with photovoltaic systems sell for 4.1% more on average compared to similar properties without solar.
- Renewable Energy Certificate (REC) Revenue: Generate and sell RECs for additional income streams. These certificates represent renewable energy generation’s environmental benefits and can be sold to utilities or other organizations meeting renewable energy requirements.
Combined, these financial benefits transform solar into a strategic asset for commercial property owners, rental properties, and qualifying residential projects under business ownership.
Solar Permit Solutions
Commercial Solar Design Services
Professional permit plan sets for commercial installations. PE-stamped, code-compliant, fast delivery.
The Environmental Impact of Commercial Solar
Beyond financial returns, solar power helps businesses decrease carbon emissions, reduce fossil fuel dependency, and advance sustainability objectives. Key environmental benefits include:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Decreased strain on electrical grid infrastructure
- Alignment with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) frameworks
- Enhanced brand reputation through clean energy leadership
- Long-term operational resilience through renewable energy independence
In today’s marketplace, environmental leadership represents a competitive necessity rather than an optional consideration. Commercial customers investing in clean energy solutions demonstrate commitment to innovation, corporate responsibility, and sustainable growth. According to IEEE Power and Energy Society research, renewable energy adoption continues accelerating across commercial sectors.
Selecting the Right Solar Provider
Even exceptional solar planning delivers subpar results with poor execution. Choosing a qualified solar provider proves critical for project success.
Evaluate potential service providers based on these criteria:
- Demonstrated experience with commercial-scale systems and large-scale construction projects
- Comprehensive knowledge of installation procedures, permitting requirements, and code compliance standards
- Proven ability to manage solar service agreements and navigate local utility processes
- Proactive support throughout the interconnection process
- Expert guidance on maximizing solar investment value and accessing available tax credits
Partnering with experienced solar professionals ensures your project moves forward efficiently from initial design through system activation and ongoing maintenance, helping your business reduce energy costs and achieve sustainability objectives. For those interested in expanding their knowledge, essential solar energy resources provide valuable insights into system design and implementation.
Conclusion
Transitioning to commercial solar power represents a significant strategic decision that delivers both immediate and long-term value for your business. While the process involves navigating complex requirements, from code compliance and permit submissions to utility interconnection and tax incentive optimization, the financial and environmental returns justify the investment.
Understanding commercial solar requirements positions your organization to avoid costly delays, ensure regulatory compliance, and maximize system performance. By addressing structural and electrical codes, securing proper permits, selecting appropriate financing options, and partnering with qualified solar professionals, you create a foundation for a successful solar installation that serves your business for decades.
The combination of federal tax credits, accelerated depreciation, reduced operating costs, and environmental benefits makes commercial solar one of the most effective investments available to businesses today. As energy costs continue rising and sustainability expectations intensify, organizations that adopt solar power gain competitive advantages through lower overhead, enhanced brand reputation, and demonstrated commitment to environmental stewardship.
Take action now to evaluate your facility’s solar potential, engage qualified solar providers, and begin your journey toward energy independence and operational cost reduction. Your commercial solar system awaits, delivering clean, reliable, and cost-effective power for years to come.
FAQs
What happens if my commercial building’s roof cannot support the weight of solar panels?
If your roof structure lacks adequate load-bearing capacity for solar panel installation, you have several alternatives. Ground-mounted solar arrays provide an excellent solution when available land space exists, offering easier maintenance access and flexible panel orientation. Carport or parking structure solar installations serve dual purposes by generating power while providing covered parking for employees or customers. Roof reinforcement represents another option, though you must weigh structural upgrade costs against overall project economics. Your solar provider should conduct thorough structural engineering assessments during the site evaluation phase to identify load capacity limitations early and recommend the most cost-effective solution for your specific situation.
Commercial Solar Design Services
Professional permit plan sets for commercial installations. PE-stamped, code-compliant, fast delivery.
Frequently Asked Questions
Commercial solar installation timelines typically range from three to six months, though complex projects may extend longer. The timeline breaks down into distinct phases: site evaluation and system design (2 to 4 weeks), permit application and approval (4 to 12 weeks depending on local authority workload), financing finalization (2 to 4 weeks), physical installation (2 to 6 weeks based on system size), and final inspection and utility interconnection (2 to 4 weeks). Factors affecting your timeline include local permitting authority efficiency, utility interconnection requirements, weather conditions, and system complexity. Working with experienced solar contractors who understand local requirements helps minimize delays and keeps your project on schedule.
If your roof structure lacks adequate load-bearing capacity for solar panel installation, you have several alternatives. Ground-mounted solar arrays provide an excellent solution when available land space exists, offering easier maintenance access and flexible panel orientation. Carport or parking structure solar installations serve dual purposes by generating power while providing covered parking for employees or customers. Roof reinforcement represents another option, though you must weigh structural upgrade costs against overall project economics. Your solar provider should conduct thorough structural engineering assessments during the site evaluation phase to identify load capacity limitations early and recommend the most cost-effective solution for your specific situation.
Yes, off-grid commercial solar systems are technically feasible but require significant battery storage capacity to maintain power during nighttime hours and periods of low solar production. Off-grid installations prove most practical for remote facilities without existing utility access or businesses seeking complete energy independence. However, most commercial properties benefit more from grid-connected systems that use net metering—selling excess power back to the utility during peak production and drawing power when needed. Grid-connected systems cost less than off-grid alternatives since they require less battery storage, provide backup power from the utility during extended cloudy periods, and generate additional revenue through renewable energy certificates. Evaluate your specific operational needs, location, and budget to determine whether a grid-connected or off-grid configuration better serves your business objectives.
Commercial solar requirements typically involve more stringent standards than residential installations due to larger system sizes, higher voltages, and increased structural loads. Commercial projects require more detailed engineering documentation, including comprehensive load calculations, structural assessments certified by licensed engineers, and more extensive electrical diagrams showing three-phase power configurations. Commercial installations must comply with additional fire safety requirements, including wider equipment spacing and enhanced emergency responder access pathways. The permitting process for commercial systems takes longer and involves more review layers, often requiring approval from building departments, fire marshals, and utility engineering departments. Commercial projects also qualify for different financial incentives, including accelerated depreciation and larger federal tax credits that residential systems cannot access. Despite these added complexities, commercial installations offer superior returns on investment due to higher energy consumption, better tax benefits, and economies of scale.
Commercial solar systems require minimal maintenance compared to other business equipment, but regular upkeep ensures optimal performance and longevity. Annual maintenance tasks include visual inspections of panels, racking, and wiring for damage or degradation; inverter performance verification; electrical connection testing; and panel cleaning to remove dirt, debris, or snow accumulation that reduces efficiency. Most commercial systems benefit from professional maintenance visits one to two times annually, costing approximately $200 to $500 per visit depending on system size. Panel cleaning frequency depends on your location—dusty or industrial areas require more frequent cleaning than regions with regular rainfall. Monitor your system's production data regularly to identify performance drops that may indicate maintenance needs. Many solar providers offer maintenance agreements bundling inspections, cleaning, and repairs for predictable annual costs. Budget approximately 0.5 to 1% of your total system cost annually for maintenance and repairs to keep your installation operating at peak efficiency throughout its 25 to 30 year lifespan.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
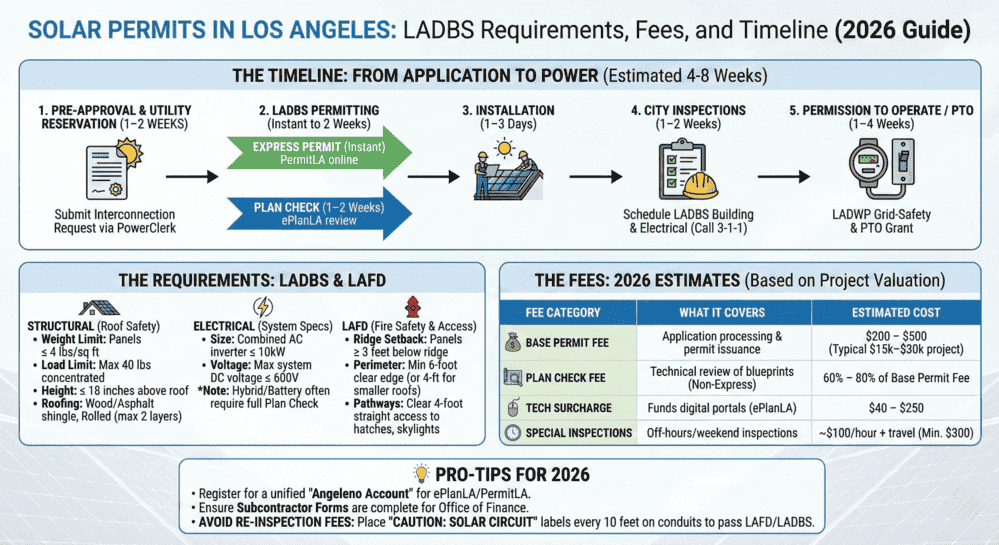
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...
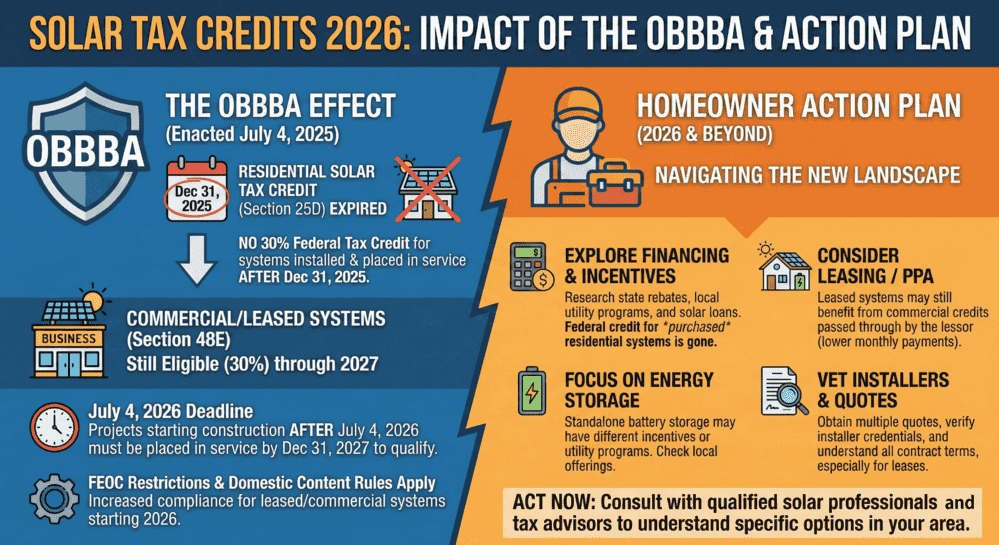
Solar Tax Credits 2026: What Changed After OBBBA and What Homeowners Can Do Now
Summary: The federal residential solar tax credit (Section 25D) expired December...
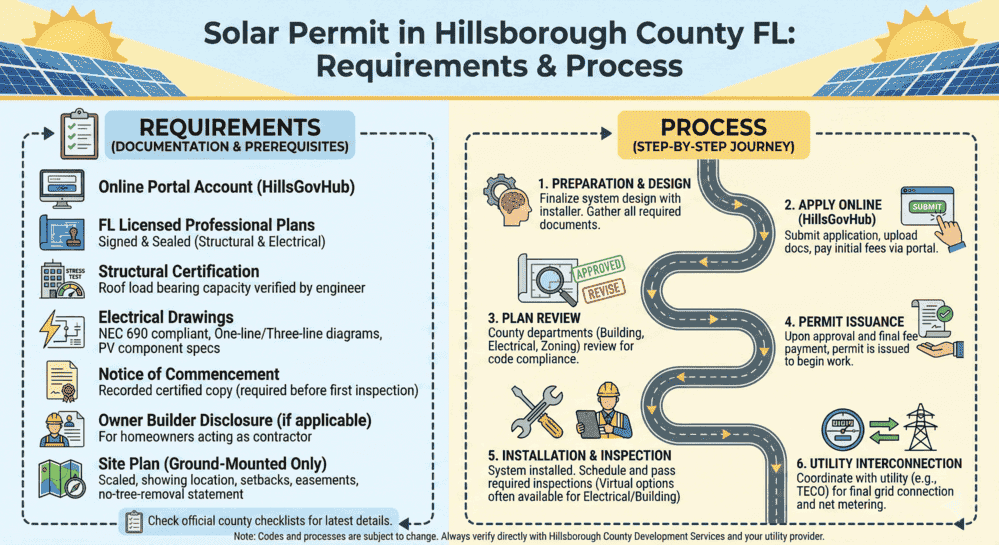
Solar Permit in Hillsborough County FL: Requirements & Process
Hillsborough County solar permits require either an Electrical Trade permit for ...
