Solar panel installations in Indiana require permits from local building departments, with fees typically ranging from $150 to $400 for residential systems under 10 kilowatts. The complete permitting process takes between 6 to 16 weeks from design approval to system activation, including permit approval, installation, inspections, and utility connection.
Indiana homeowners must obtain both building permits and electrical permits before installing solar panels. Building permits verify roof structural integrity can support panel weight, while electrical permits ensure wiring and inverters meet National Electrical Code standards. Most Indiana jurisdictions follow International Residential Code (IRC) requirements, though local amendments may apply.
The permitting process involves six key steps: system design development, application submission with fees, jurisdiction review and approval, licensed contractor installation, local authority inspections, and obtaining Permission to Operate (PTO) from utility companies. Systems qualifying for simplified review can receive approval within days, while complex installations may take several weeks.
Indiana law requires all solar installations be performed by licensed contractors. The state transitioned from traditional net metering to an Excess Distributed Generation (EDG) net billing policy in 2022, where utilities purchase excess solar energy at reduced wholesale rates rather than full retail prices. Solar owners receive a 30% federal tax credit on total installation costs including permits, plus property tax exemptions and sales tax exemptions on qualifying equipment components.
Understanding the Solar Permitting System
Permitting refers to the official approval required by local government authorities to install a solar energy system. The process ensures installations comply with safety regulations, building codes, and electrical standards while confirming the system can integrate seamlessly with the local electrical grid.
In Indiana, the permitting process varies by city and county, with each jurisdiction maintaining its own specific requirements. Most municipalities follow the International Residential Code (IRC) and National Electrical Code (NEC) standards, though local amendments may apply.
The Critical Role of Solar Permits
Permitting serves as a critical step in ensuring solar installations remain safe, legal, and compliant with local and state building codes. This protection extends to property owners, the surrounding community, and the environment. Obtaining proper permits ensures solar systems qualify for utility grid connection and any available incentives or rebates.
Without proper permits, installations risk fines, project delays, and potential system removal. Securing appropriate permits represents more than a formality; it stands as an essential component for successful solar projects.
Navigating Indiana’s Solar Permit Process
The solar permitting process in Indiana follows several key stages.
Step 1: Develop Solar System Design
The permitting process begins with preparing a design for the solar panel system. This involves working with a licensed solar contractor who assesses the property and develops an installation plan. Designs must adhere to local building codes, the International Residential Code, and electrical requirements.
Key Considerations:
Roof strength: The roof structure must support the weight of solar panels and mounting equipment.
Energy requirements: System size should align with energy consumption patterns.
Safety codes: Indiana enforces specific safety rules regarding solar installations, particularly concerning equipment placement, setbacks, and fire access pathways.
Step 2: Submit Application and Pay Fees
Once the design is finalized, contractors submit necessary documents to the local building department for review. Applications typically include:
Structural plans: Verifying the roof can safely support the panels.
Electrical plans: Detailing wiring, inverters, and other electrical components.
Fees: Permitting fees vary by jurisdiction, typically ranging from $150 to $400 for residential systems under 10 kilowatts.
Initial responses from local authorities generally arrive within a few days to several weeks. Factors such as application completeness, system complexity, and seasonal workload can influence processing times.
Step 3: Review and Approval
Local jurisdictions review permit applications to ensure compliance with all local, state, and national standards. Processing times range from a few days for simplified reviews to several weeks for more complex installations.
During review, authorities may request additional documentation or plan modifications to meet specific code requirements. Addressing these requests promptly helps avoid unnecessary delays.
Step 4: Installation
Installation begins once permits receive approval. Licensed contractors install solar panels, inverters, and other necessary components. Installation typically takes one to three days, depending on system size and complexity.
Throughout this stage, contractors ensure everything is installed according to approved plans while maintaining strict adherence to safety protocols.
Step 5: Inspections
Following installation, solar systems undergo one or more inspections by local building authorities. These inspections verify installations meet all safety and building code requirements.
Common inspection areas include:
Structural integrity: Confirming mounting systems are properly secured.
Electrical connections: Verifying all wiring meets National Electrical Code standards.
Fire safety compliance: Ensuring proper setbacks and access pathways.
Step 6: Permission to Operate (PTO)
The final step involves obtaining Permission to Operate (PTO) from the utility company. This authorization allows the solar system to connect to the grid and begin generating power. Utilities may conduct their own inspection or system review before granting PTO.
Once PTO is secured, the solar system becomes fully operational, providing clean, renewable energy.
Solar Permit Solutions
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
Essential Permit Categories for Indiana Solar Projects
Indiana solar installations typically require two main permit types for residential projects:
- Building Permits
Building permits verify the structural integrity of properties can handle additional loads from solar panels. Key considerations include:
Roof Load Capacity: Roofs must safely support solar panels and their mounting systems.
Mounting System Integrity: Solar panels require secure mounting to withstand wind loads and potential seismic activity.
Building permits apply to both rooftop and ground-mounted installations, though requirements may vary.
- Electrical Permits
Electrical permits ensure wiring, inverters, and electrical connections meet safety standards. Coverage includes:
Wiring and Connections: Ensuring compliance with the National Electrical Code.
Inverter and Battery Compliance: Confirming inverters and batteries follow safety regulations.
Some jurisdictions issue electrical permits separately, while others combine them with building permits. Cities like Lafayette provide specific checklists to streamline the process.
Fast-Track Permitting Options in Indiana
Many Indiana jurisdictions offer streamlined permitting processes for smaller residential solar systems. Simplified review procedures typically apply to straightforward installations meeting specific criteria:
Roof-mounted systems on permitted structures
Systems using standard mounting equipment
Installations meeting basic structural requirements
Roof slopes of 6:12 or less
Systems under specific size thresholds
Simplified applications can receive approval within days rather than weeks, making solar adoption more accessible for homeowners eager to begin generating clean energy. Solar Permit Solutions specializes in expediting these approvals.
Larger systems, ground-mounted installations, or systems with battery storage may require standard review processes with more detailed documentation and longer processing times. Commercial solar projects typically need more comprehensive reviews than residential installations. Planning resources like MACOG’s pollinator guide help optimize solar development strategies.

What to Expect: Permit Fees and Expenses
Solar permitting costs in Indiana vary based on location, system size, and required permit types. Homeowners typically pay between $150 and $400 for residential systems under 10 kilowatts.
Additional factors affecting costs include:
Combined versus separate building and electrical permits
Ground-mounted versus rooftop installations
System complexity and customization
Commercial installations generally incur higher permitting fees
These costs represent a small portion of total solar installation expenses but remain essential for ensuring compliance and safety.
Avoiding Common Permit Application Mistakes
While Indiana’s permitting process is generally straightforward, several common challenges can arise:
Incomplete Applications: Submitting all required documents completely helps prevent delays.
Overlooking Local Codes: Local jurisdictions maintain specific requirements. Checking with city or county offices before submission ensures compliance.
Using Unlicensed Contractors: Indiana law requires solar installations be performed by licensed contractors to ensure safety and compliance.
Missing Documentation: Manufacturer specifications, structural calculations, and electrical diagrams must be complete and accurate.
Navigating Homeowners Association Requirements
Homeowners associations present unique challenges for solar installations in Indiana. Under Indiana House Bill 1196 (passed in 2022), HOAs may require screening and preapproval procedures before installation. Homeowners must petition fellow association members and obtain signatures from either the number required to amend governing documents or 65% of unit owners, whichever is less.
The approval process requires submitting detailed information including site plans, solar system specifications, screening details for non-roof installations, and vendor information. HOA boards cannot deny requests once proper signatures are obtained and requirements are met. However, failing to follow these procedures can result in installation denials, legal disputes, and project delays.
Homeowners in HOA-governed communities should begin the approval process early, review governing documents carefully, and consider working with solar contractors experienced in HOA requirements. Starting HOA communications before permit applications prevents timeline disruptions and ensures smoother project completion.
Staying proactive, addressing issues early, and working with qualified professionals helps avoid these common obstacles. Professional services can navigate complex requirements efficiently.

Working with Licensed Contractors
Indiana requires solar installations be completed by properly licensed contractors. Licensed professionals understand local permitting requirements, building codes, and safety standards necessary for successful projects.
Qualified contractors typically handle:
Permit application preparation and submission
Coordination with local building departments
Scheduling required inspections
Obtaining Permission to Operate from utility companies
Ensuring all work meets current code requirements
Selecting experienced contractors familiar with Indiana’s permitting landscape significantly streamlines the process. Resources from Indiana University and Purdue Extension provide additional guidance for community solar development.
Grid Connection and Net Billing
Indiana transitioned from traditional net metering to an Excess Distributed Generation (EDG) net billing policy in 2022. Under this system, solar owners can still sell excess electricity back to the grid, but the compensation structure differs significantly from true net metering.
Key aspects of Indiana’s EDG policy:
Solar owners receive credits at reduced rates compared to retail electricity prices, meaning excess energy is purchased by utilities at a discount.
Investor-owned utilities and electric cooperatives offer net billing programs for systems under 1 megawatt.
Each utility company maintains its own specific rates and program guidelines, so compensation varies by service provider. Cities like South Bend and Indianapolis provide local solar resources.
Interconnection agreements require approval from the Indiana Utility Regulatory Commission (IURC) before connecting systems to the grid.
Unlike traditional net metering where credits match retail electricity rates, Indiana’s net billing approach provides partial credit for each kilowatt-hour sold back to the grid. Solar owners essentially sell electricity to utilities at wholesale rates but buy it back later at retail rates, reducing overall bill savings compared to states with true net metering programs.
Understanding these policies helps set realistic expectations for energy bill savings and return on investment calculations when planning solar installations in Indiana.
Indiana Solar Incentives and Tax Benefits
Several financial incentives make solar more affordable in Indiana:
Federal Solar Tax Credit: The Residential Clean Energy Credit provides a 30% tax credit on total system costs, including equipment, labor, permitting, and sales tax. Systems must be installed by December 31, 2025, to qualify.
Property Tax Exemption: Solar installations do not increase property taxes despite adding value to homes. Form 18865 must be filed with the county auditor.
Sales Tax Exemption: Many solar system components qualify for sales tax exemptions under Indiana’s electrical generating equipment exemption.
Utility Rebates: Some utility companies offer additional incentives for solar adoption. Checking with local providers reveals available programs. Communities like Bloomington and Allen County offer specific solar resources.
These incentives significantly reduce upfront costs and improve long-term return on investment. The Indiana Office of Energy Development provides additional information on commercial solar programs.

Timeline Expectations
Understanding typical timelines helps plan solar projects effectively:
Design and Planning: 1-3 weeks
Permit Submission to Approval: 1-8 weeks
Installation: 1-3 days
Inspections: 1-2 weeks
Permission to Operate: 1-4 weeks
Total project timelines typically range from 6 to 16 weeks from initial design to system activation. Timelines vary based on jurisdiction workload, application completeness, and seasonal demand.
Conclusion
Understanding the solar panel permitting process in Indiana proves crucial for smooth and successful installations. With proper preparation, timely document submission, and careful attention to local regulations, solar systems can become operational without unnecessary delays. Working with qualified professionals and understanding all requirements ensures solar installations remain compliant and positioned for long-term success. For expert assistance with your solar project, contact Solar Permit Solutions or explore additional resources on solar permitting best practices.
FAQs
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, permits are required for solar panel installations in Indiana. Most jurisdictions require both building permits to verify structural integrity and electrical permits to ensure safe wiring and connections. Ground-mounted systems may need additional permits compared to rooftop installations. Permit requirements vary by city and county, so checking with local building departments before starting any solar project is essential.
Permit approval timelines in Indiana typically range from a few days to eight weeks depending on the jurisdiction and application complexity. Simplified review processes for straightforward residential installations can receive approval within days, while more complex systems requiring standard review may take several weeks. Application completeness, local department workload, and seasonal demand all influence processing times. Working with installers familiar with local permitting offices often speeds up the process.
Solar permit fees in Indiana typically range from $150 to $400 for residential systems under 10 kilowatts. Actual costs vary based on location, system size, and whether building and electrical permits are issued separately or combined. Some jurisdictions charge additional fees for ground-mounted installations or systems with battery storage. Commercial installations generally incur higher permitting costs. These fees represent a small portion of total installation expenses but are necessary for legal compliance.
No, installing solar panels without proper permits is illegal in Indiana and carries significant risks. Unpermitted installations can result in fines, mandatory system removal, inability to connect to the utility grid, and invalidated insurance coverage. Permits ensure installations meet safety standards and building codes, protecting property owners and the community. Additionally, unpermitted systems typically cannot qualify for federal tax credits, state incentives, or net billing programs.
If a solar permit application receives denial, the local building department provides specific reasons for the rejection. Common issues include incomplete documentation, plans not meeting structural requirements, electrical code violations, or zoning conflicts. Applicants can address these concerns by revising plans, providing additional documentation, or working with engineers to resolve technical issues. Once corrections are made, resubmitting the application typically moves forward without starting the process from scratch. Licensed contractors experienced in Indiana permitting can help navigate revisions efficiently.
Yes, Indiana law requires solar installations to be performed by properly licensed contractors. Licensed professionals understand local building codes, electrical requirements, and permitting procedures necessary for compliant installations. They handle permit applications, coordinate inspections, and ensure all work meets current standards. Using unlicensed contractors can result in permit denials, failed inspections, safety hazards, and potential legal liability. Homeowners should verify contractor licenses and insurance coverage before beginning any solar project.
After installation, Indiana solar systems undergo inspections by local building authorities to verify compliance with safety and building codes. Typical inspections cover structural integrity of mounting systems, electrical connections and wiring compliance with National Electrical Code standards, and fire safety requirements including proper setbacks. Some jurisdictions conduct single comprehensive inspections while others require separate building and electrical inspections. Utility companies may also perform their own inspection before granting Permission to Operate and connecting the system to the grid.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
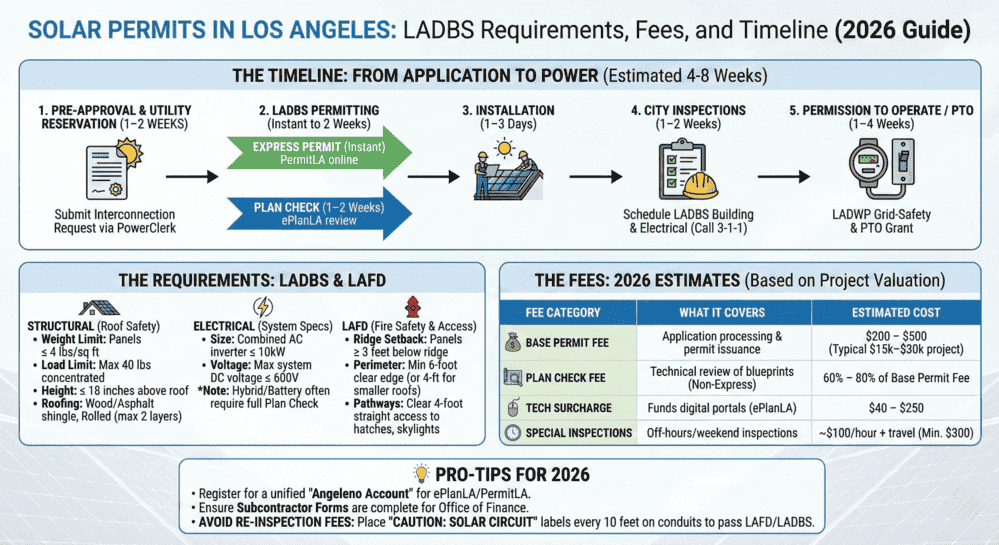
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...
