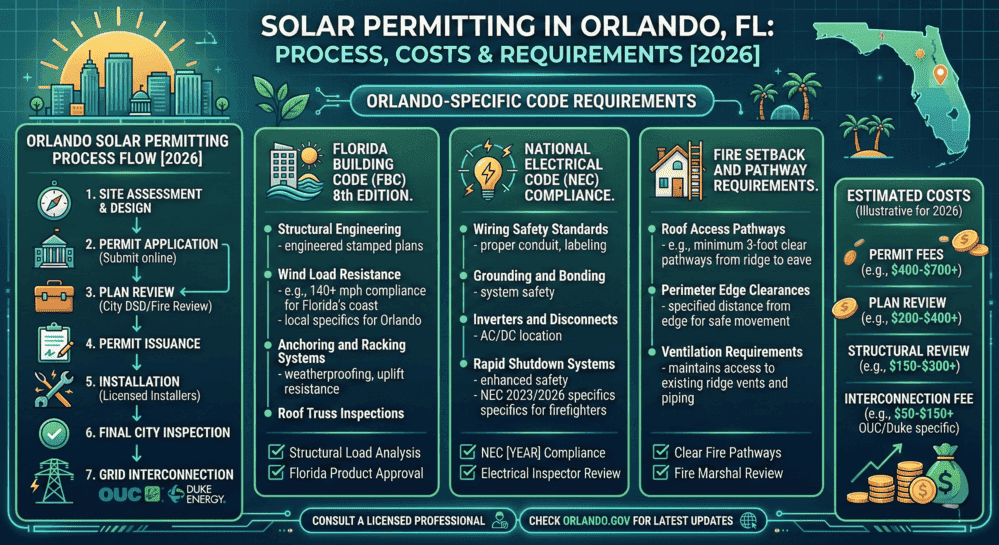
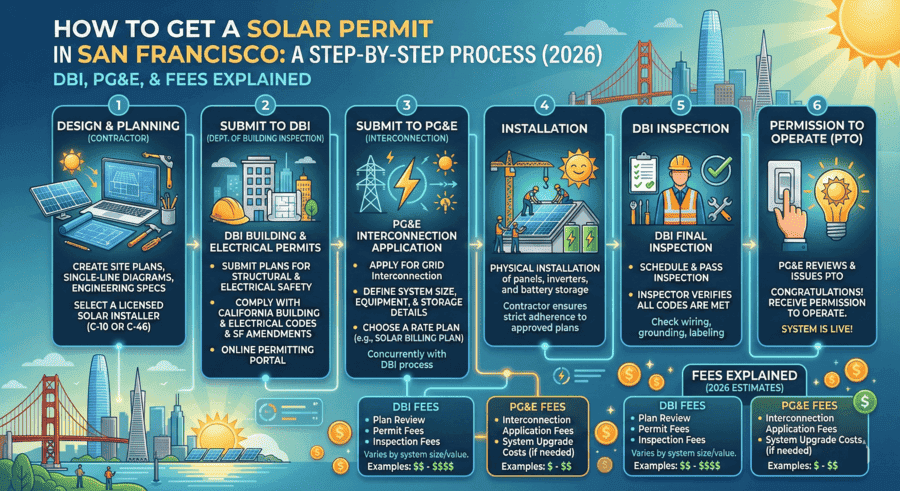
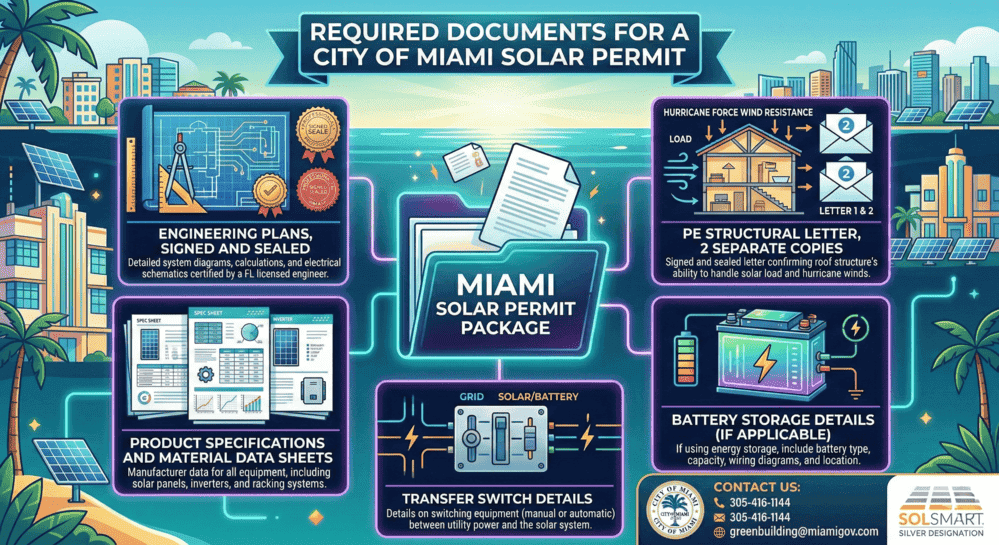
Solar energy storage systems are battery-based or alternative technologies that store excess electricity generated by solar panels for later use during nighttime, cloudy periods, or power outages. These systems have become essential for homeowners and businesses seeking energy independence, with the market experiencing significant growth as the 30% federal solar tax credit phases out after 2025.
Three main types of solar energy storage systems exist:
- Electrical Storage – Lithium-ion batteries (LFP and NMC chemistries) and lead-acid batteries that store electricity directly
- Chemical Energy Storage – Hydrogen-based systems that store energy in molecular bonds through electrolysis
- Thermal Energy Storage – Systems using molten salts, water, or sand to store heat energy
The primary difference between AC-coupled and DC-coupled solar storage systems lies in how they connect to solar panels. AC-coupled systems include built-in inverters and work with existing solar installations, offering easier retrofitting. DC-coupled systems require hybrid inverters but may provide better efficiency for new installations.
Key factors when selecting solar energy storage systems include:
- Battery capacity (most homes need 10-15 kWh)
- Chemistry type (LFP offers longer lifespan and safety; NMC provides higher energy density)
- Cost ($8,000-$15,000 for residential installations)
- Lifespan (10-15 years for lithium-ion systems)
- Inverter compatibility (AC-coupled or DC-coupled configuration)
States offering additional incentives beyond federal tax credits include California, Hawaii, Illinois, Maryland, Massachusetts, and Oregon. Installation professionals report unprecedented demand growth, positioning 2025 as a pivotal year for solar energy storage adoption. Understanding solar permit requirements proves essential before installation begins.
This comprehensive guide explores each solar energy storage system type, compares lithium-ion battery chemistries (LFP vs NMC), explains AC-coupled versus DC-coupled configurations, and provides selection criteria to identify optimal solutions for residential installations and commercial applications.
What Are Solar Energy Storage Systems?
Solar energy storage maximizes value and reliability within solar power installations. Solar energy generation occurs only during daylight, making storage systems necessary for capturing excess production for nighttime use or grid outage scenarios.
Off-grid installations require batteries for continuous 24/7 power supply. Grid-connected solar energy storage systems with hybrid configurations allow property owners to maintain power during blackouts and strategically shift energy consumption based on cost structures and requirements.
Areas with time-of-use (TOU) electricity pricing benefit from solar energy storage solutions that store energy during low-rate periods and discharge when rates peak. This load-shifting function substantially reduces system payback timelines while enhancing energy independence.
The Critical Role Of Storage In Energy Resilience
Aging electrical infrastructure and increasing extreme weather incidents contribute to more frequent power disruptions. Wildfire-prone areas experience planned Public Safety Power Shutoffs (PSPS) implemented by utilities to minimize fire risk, leaving properties without electricity for extended periods.
Gas-powered backup generators provide temporary solutions but depend on fossil fuels, produce noise pollution, and release carbon emissions. Solar energy storage systems present clean, silent, and increasingly economical alternatives. These systems capture surplus solar electricity for future use, delivering solar power backup during grid failures and supporting broader grid stability through supply-demand balancing.
Regions with high solar penetration face midday excess solar energy that often results in curtailment or wasted generation. Solar energy storage resolves this challenge by storing unused power during low-demand windows and releasing it during demand surges, improving overall grid efficiency and minimizing waste.
Breaking Down Solar Storage Technology Types
Installation professionals should recognize different solar energy storage system types available, each designed for specific applications based on scale, duration requirements, and spatial constraints.
Electrical Storage
Battery technology represents the predominant solar energy storage method currently deployed. Common battery chemistries include:
Lead-Acid Batteries (sealed AGM variants): Budget-friendly options with limited cycle longevity.
Lithium-Ion Batteries: High-efficiency solutions with extended operational lifespans. Two primary chemistries exist:
- Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP): Stable, durable, and optimal for solar power storage applications.
- Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC): Superior energy density, frequently used in space-constrained systems.
These technologies dominate residential and commercial solar energy storage markets, providing versatile solar energy storage solutions for backup power and peak demand management. Proper equipment specifications ensure code compliance during installation.
Chemical Energy Storage Systems
Less prevalent but developing, chemical energy storage captures power within molecular bonds rather than direct electrical form. Hydrogen energy storage exemplifies this approach, utilizing electricity to produce hydrogen through electrolysis. The hydrogen remains stored and converts back to electricity via fuel cells, suitable for extended-duration solar energy storage applications or remote and off-grid scenarios.
Thermal Energy Storage
These energy storage systems employ materials like water, molten salts, or sand within insulated tanks to retain heat. This stored energy either generates electricity or provides thermal energy directly. Thermal storage proves valuable for concentrated solar thermal power (CSP) facilities that concentrate sunlight to heat fluids.
Solar thermal water heaters represent a widespread application, using solar collectors to heat water in storage tanks. The heated water serves as domestic hot water or provides building heat through heat exchangers or radiant floor heating systems. Researchers continue exploring advanced thermal storage using next-generation materials.
Solar Permit Solutions
Affordable Solar Permit Plans
Don't let permit costs slow your project. Professional plan sets at competitive prices — all 50 states, fast turnaround.
How To Select The Best Solar Storage Solution
Evaluating solar energy storage systems requires consideration of multiple factors: power rating, usable storage capacity, round-trip efficiency, warranties, cost, and battery lifespan. Lead-acid and lithium-ion constitute the two most frequently deployed battery types for solar energy storage, though solid-state battery technology advances rapidly and will reach mass production soon.
Lead-acid batteries offer lower upfront costs but typically provide shorter lifespans and warranty coverage. As lithium-ion battery pricing continues declining, these batteries gain popularity in residential and commercial solar applications due to extended lifespans and superior overall performance. Understanding common application mistakes helps avoid delays during system approval.
LFP Or NMC: Evaluating Lithium-Ion Battery Chemistries
Two primary lithium-ion battery chemistries dominate solar energy storage systems: Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP or LiFePO₄) and Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC). Both deliver distinct advantages, and understanding these differences remains critical when selecting appropriate energy storage solutions for projects.
Popular LFP and NMC Solar Energy Storage Products
NMC batteries see widespread use in solar energy storage applications. LFP solar energy storage systems also maintain strong market presence with various product offerings available.
Why Choose LiFePO4 Battery Systems
LiFePO4 batteries deliver multiple advantages for solar energy storage systems, combining safety features, longevity, stability, and environmental considerations.
Safety: LiFePO4 batteries demonstrate excellent safety characteristics. These batteries show lower susceptibility to thermal runaway and maintain greater stability at elevated temperatures compared to NMC solar energy storage batteries.
Extended Cycle Life: LiFePO4 batteries typically achieve longer cycle life versus NMC solar energy storage systems. These batteries endure more charge-discharge cycles before experiencing meaningful degradation.
Stability: LiFePO4 chemistry exhibits inherent stability, contributing to decreased thermal runaway risk and enhanced overall solar storage system safety.
High-Temperature Performance: LiFePO4 batteries operate effectively in high-temperature conditions, making them appropriate for applications where elevated temperatures present concerns.
Flat Discharge Curve: LiFePO4 batteries display relatively flat discharge curves, delivering consistent voltage output across broad state-of-charge ranges. This characteristic benefits specific applications.
Environmental Impact: LiFePO4 batteries offer more environmentally friendly profiles than NMC solar energy storage, containing fewer rare and toxic materials.
Why Choose NMC Battery Systems
NMC batteries provide several advantages to solar energy storage systems, particularly where space, weight, and cost efficiency matter most.
Energy Density: NMC batteries generally achieve higher energy density than LiFePO4 batteries, storing more energy within given volume or weight parameters. This makes them appropriate for applications where space or weight constitutes critical factors.
Cost: NMC solar energy storage batteries can offer more cost-effective manufacturing, making them popular choices for various applications where cost considerations dominate.
Wider Voltage Range: NMC batteries often provide broader voltage ranges, offering flexibility when designing battery packs for specific voltage requirements.
Application Flexibility: Due to superior energy density, NMC batteries commonly appear in electric vehicles and applications requiring maximum energy storage in limited space.
Final Verdict: Which Chemistry Performs Better?
Typically, LFP solar energy storage systems deliver longer operational lifespans and enhanced safety profiles. Conversely, NMC batteries usually cost slightly less, provide higher energy density, and tolerate colder temperatures marginally better. However, NMC solar energy storage systems do not necessarily deliver better cost-effectiveness than LFP batteries due to potentially shorter lifespans.
AC-Coupled Vs. DC-Coupled: Understanding The Key Differences
Selecting solar energy storage systems also involves considering inverter compatibility. Some solar energy storage batteries feature AC-coupling with integrated battery inverters. AC-coupled solar systems eliminate hybrid inverter requirements, functioning with microinverters and string inverters.
DC-coupled solar energy batteries require hybrid inverters for operation. Professional installation services ensure proper system configuration and AC-coupled batteries include various models available in the market.
Finding Your Ideal Solar Storage Match
Choosing appropriate solar energy storage systems proves essential for successful project outcomes. While numerous options exist in the market, certain systems suit specific applications or configurations better than others. Understanding project objectives and budget parameters remains key to selecting optimal solutions.
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional support for all types of solar energy system projects. Whether planning residential installations or commercial deployments, expert guidance ensures code-compliant designs that meet local requirements and maximize system performance.
Conclusion
Solar energy storage systems have become essential infrastructure for maximizing solar investments and achieving energy independence. Lithium-ion batteries dominate the market, with LFP systems offering superior safety and longevity, while NMC batteries provide higher energy density for compact installations. System architecture matters significantly—AC-coupled configurations excel in retrofit applications, whereas DC-coupled systems may deliver efficiency advantages in new projects.
Federal tax incentives expire after 2025, creating urgency for property owners to act now. Understanding permit approval timelines, reviewing state-level policies, and following EPA guidelines ensures compliant installations. Avoiding DIY installation mistakes prevents costly project delays.
Contact solar experts to explore design services and access helpful resources that streamline solar storage installations from planning through final approval.