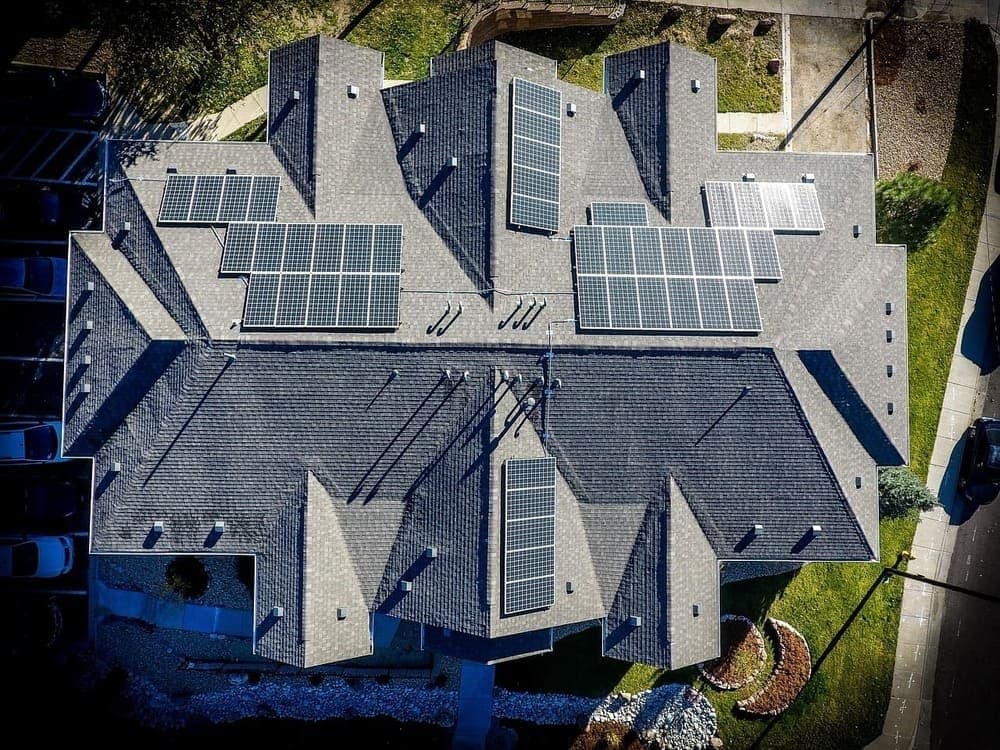
Solar panel setback requirements mandate specific spacing distances between solar arrays and roof elements to ensure fire safety and emergency access. Most jurisdictions require 3-foot clearances from roof ridges, 18-inch spacing from hip and valley lines, and designated firefighter access pathways across residential rooftops. These setback regulations serve three primary purposes: enabling safe emergency responder access during fires, preventing rapid fire spread across solar installations, and maintaining proper ventilation around panels. Typical residential solar setback requirements include a minimum 3-foot perimeter clearance from all roof edges, 3-foot clearance from ridge lines, 18-inch clearance from valley and hip areas, and two 3-foot-wide access pathways extending from roof edge to ridge. Homeowners must comply with local building codes that may vary by state and municipality, with some areas allowing reduced setbacks when additional fire suppression equipment is installed. Professional solar installers design systems that maximize energy production within these mandatory safety parameters by using high-efficiency panels, optimizing panel orientation, and strategically positioning arrays in compliant roof zones. Non-compliance with setback requirements can result in failed inspections, mandatory system removal, fines, voided warranties, and increased liability during fire emergencies.

Understanding Roof Setbacks for Solar Fire Safety
What Are Solar Setbacks?
Solar setbacks define the legally required spacing between your panels and certain roof sections or property boundaries. These rules ensure emergency personnel can access critical areas during fires and maintain your solar installation’s structural stability. Consider setbacks as safety margins that create open corridors across your rooftop, usually measuring 3 to 6 feet depending on your municipality’s building regulations.
These spacing rules accomplish more than just fire prevention. They enable proper airflow around panels, reduce how quickly flames can spread, and allow maintenance workers to safely reach your equipment. Many cities and counties enforce specific setback policies through solar permitting processes that dictate the exact distance panels must keep from roof boundaries, peak lines, and other architectural features.
While setbacks might feel like they limit your options, they’re actually a critical safeguard protecting your home and any professionals requiring roof access. Understanding these rules is fundamental when designing your solar project to confirm your installation meets all local safety regulations.
How Proper Roof Setbacks Improve Solar Fire Protection
Fire setbacks serve a vital function in protecting your home and the firefighters who may need to work on your roof during emergencies. These mandatory clear zones around your panels create critical pathways allowing first responders to safely move across your rooftop, carry firefighting equipment, and effectively battle any flames that might emerge.
Think of setbacks as emergency corridors across your roof. They stop fires from spreading quickly by creating gaps in your panel layout, functioning like firebreaks in forest management. These spaces also create ventilation points that allow heat and smoke to escape during fires, helping firefighters gain control more efficiently.
Beyond this, setbacks allow emergency responders to quickly identify and reach structural weak points and ventilation areas on your roof, saving precious seconds during crisis response. This strategic design consideration protects both your renewable energy investment and your home’s overall security.

Essential Setback Guidelines for Safe Solar Installations
Roof Edge Setbacks
Perimeter setbacks are critical safety measures establishing accessible walkways for emergency responders during fires. Most local codes require at least 3 feet of clearance from roof edges, though some areas demand greater distances. These clearances serve several functions: they create safe pathways for maintenance workers, prevent wind from dislodging panels during storms, and maintain proper water runoff from your roof.
Hip roofs with slopes on all sides need setbacks around the entire perimeter. Gable roofs typically require setbacks along eaves, with potentially different rules for rake edges. Some areas allow smaller 18-inch setbacks on compact roofs to increase solar coverage without compromising safety.
Remember that edge setbacks don’t automatically mean reduced solar production. Roof edges typically receive less direct sunlight because gutters and overhangs create shade, making these spots less productive for panel placement anyway. During your solar design phase, work closely with your installer to strategically position panels within these safety boundaries while maximizing your system’s energy output.
Ridge and Valley Setbacks
Peak and valley areas need specific clearance measurements to maintain fire safety and proper ventilation. Most home installations require at least 3 feet of space from the ridge line, giving firefighters safe passage and maintaining adequate airflow. This corridor serves as a crucial pathway for emergency operations and helps prevent flames from jumping across your roof.
Valley sections, the V-shaped channels formed where roof planes intersect, usually need 18 inches of clearance on both sides. These gaps keep panels away from areas where rainwater naturally concentrates and flows, avoiding potential water damage while keeping emergency access routes clear.
Different jurisdictions may enforce varying requirements, particularly in regions experiencing strong winds or heavy snow. Areas with significant snowfall might require wider valley setbacks to handle snow accumulation and removal. Always consult your local building department, as measurements may vary based on your region’s unique solar radiation patterns and climate patterns.
Though these setbacks reduce your available panel space, they’re indispensable for maintaining your home’s safety and ensuring your installation complies with all mandatory regulations.
Access Pathways
Solar arrays must feature clear corridors allowing firefighters safe roof access during emergencies. These emergency access requirements usually call for three-foot-wide pathways along roof edges and between panel groups. These corridors let emergency crews move safely, vent smoke and gases, and reach critical locations during firefighting operations. Most building codes require two clear corridors running from roof edge to ridge, plus adequate space around roof vents and skylights. When designing your solar layout, partner with your installer to integrate these vital access corridors into your plan, balancing safety requirements with effective panel placement for maximum energy production while avoiding common design mistakes.
Optimizing Your Solar Panel Layout for Maximum Efficiency
Roof Design Tips for Optimal Solar Panel Placement
Designing your panel arrangement while respecting setback requirements doesn’t have to be challenging. Start by getting detailed measurements or diagrams of your roof surface. Mark all required setback zones first, typically along ridges, valleys, and edges, then plan panel placement in the remaining space.
Identify large, unshaded rectangular sections available after accounting for setbacks. These areas work best for panel arrays. South-facing sections usually capture the most sunlight in North America, so prioritize these when available. When south-facing areas are limited by setbacks, east and west-facing sections can still deliver strong performance.
Consider installing several smaller arrays instead of one large installation when setbacks create layout challenges. This approach often lets you use more of your available roof space while maintaining all necessary safety clearances. Many homeowners find that dividing panels into two or three separate groups works better with their roof architecture than forcing everything into one large array.
Don’t forget that equipment like inverters and emergency disconnects need proper clearance too. Plan these locations early in your design to ensure they don’t conflict with panel placement or setback zones. Partnering with an experienced installer helps you optimize your design while meeting all safety standards and understanding electrical fundamentals.
Solar Permit Solutions
Homeowner Going Solar?
Get the permit-ready plan set your city requires — delivered fast so your solar project stays on schedule.
Maintaining Solar Panel Efficiency Within Safety Limits
Though following setback rules is non-negotiable, you can still maximize your system’s performance within these safety parameters. Start by partnering with your installer to strategically position panels, using every available compliant roof section. Today’s high-efficiency modules generate more electricity from smaller footprints, helping you make the most of limited space.
Consider split-orientation designs where some modules face south and others face east or west. This configuration maintains strong production throughout the day while respecting setback constraints. Module-level power electronics like microinverters or optimizers help each panel achieve peak performance regardless of roof position.
When roof space becomes severely limited by setbacks, look into alternative installation options. Ground-mount systems offer greater flexibility in placement and tilt angle, while solar canopies or pergola structures serve double duty by generating electricity while creating shade.
Consistent upkeep of your system is essential for peak performance. Keep modules clean and trim nearby trees to eliminate shading. This becomes especially important when working with constrained space from setbacks, since every panel must perform at its best. Whether you’re building your own solar system or want to learn from essential solar resources, understanding these maintenance considerations from the start is crucial.
Keep in mind that setbacks may feel restrictive, but they’re designed to protect your property while enabling effective renewable energy generation. With smart planning and modern equipment, you can achieve outstanding energy production while meeting all mandatory safety standards.
Ensuring Professional Installation and Compliance for Your Solar System
For solar installation, hiring qualified professionals isn’t just advisable; it’s critical for safety and peace of mind. Licensed installers bring deep expertise in local fire regulations, setback standards, and safety protocols to ensure your system meets all mandatory requirements while safeguarding your solar investment.
Professional contractors understand the intricacies of roof engineering, electrical systems, and fire safety codes backed by renewable energy research. They’ll conduct thorough roof assessments, ensuring correct panel positioning with proper setbacks for emergency access. They’ll also verify your installation meets local building requirements and secure all necessary permits.
Quality contractors will:
- Examine your roof’s load-bearing capacity
- Design installations incorporating mandatory setback zones
- Install correct mounting systems and racking
- Ensure proper electrical wiring and grounding systems
- Provide paperwork for building department inspections
- Liaise with local fire departments as needed
Choosing certified professionals means getting more than just an installation, you’re getting expertise ensuring your system is both safe and high-performing. Many contractors also offer warranties and ongoing maintenance services, providing extra assurance about your system’s long-term performance and regulatory compliance. This is particularly important given the liability risks of DIY solar installations.
Always verify your contractor’s credentials, including licenses, certifications, and insurance policies. Ask about their familiarity with local fire codes and request references from past projects in your community. If you’re in California, understanding how to navigate utility-specific requirements can streamline your installation process.
Correct solar setbacks are essential for ensuring your installation’s safety and performance. Following these standards protects your home and loved ones while optimizing system functionality and maintaining positive neighbor relations. Always work with qualified designer who understand local regulations and can design systems meeting all safety requirements. Though setback rules might seem like extra hurdles in your solar transition, they’re a crucial investment in your property’s long-term protection and energy independence. With thoughtful design and proper execution, you can enjoy clean, renewable power while maintaining complete confidence in your installation’s safety and compliance, supported by ongoing research and development in solar technology.
Conclusion
Implementing proper solar setbacks represents far more than just checking boxes on a permit application, it’s about creating a solar installation that protects your home, respects emergency protocols, and delivers reliable renewable energy for decades to come. While setback requirements may initially seem like obstacles that limit your panel placement options, they’re actually carefully designed standards that balance maximum energy production with critical safety considerations. By understanding these spacing requirements and working with experienced solar professionals, you can design an installation that meets all regulatory standards while optimizing your roof’s solar potential. The investment you make in proper setback compliance today pays dividends in enhanced safety, reduced liability, and peace of mind knowing your system can be safely accessed during emergencies. Whether you’re in the early planning stages or ready to move forward with installation, prioritizing setback compliance ensures your solar journey begins on a foundation of safety and professionalism. Remember, the most successful solar installations aren’t those that squeeze every possible panel onto a roof, they’re the ones that strategically balance energy production with safety, longevity, and regulatory compliance. With the right approach, your solar system can deliver clean energy efficiently while maintaining the highest safety standards for your home and community, contributing to the global transition toward renewable energy while ensuring proper end-of-life panel management.
FAQs
What happens if my solar panels don’t meet setback requirements?
Failing to meet setback requirements can result in serious consequences including installation rejection during building inspections, mandatory system removal or reconfiguration, fines from local building departments, voided warranties, and potential liability issues if a fire occurs. More importantly, non-compliant installations put firefighters at risk during emergencies and may prevent them from effectively protecting your home. Insurance companies may also deny claims related to a non-compliant solar installation. Always ensure your installer designs your system to meet all local setback requirements before installation begins. If you discover an existing system doesn’t meet current codes, contact a licensed solar professional to evaluate your options for bringing it into compliance.
How do solar setbacks affect my system’s energy production?
While setbacks do reduce the total roof area available for panel placement, their impact on overall energy production is often less significant than you might expect. Roof edges and areas near ridges and valleys frequently experience shading from roof features, reducing their solar potential anyway. Modern high-efficiency panels can compensate for reduced panel counts by generating more power per square foot. Additionally, strategic panel placement within setback constraints, such as using split orientations or module-level power electronics, can maintain strong energy production. Many homeowners find that a well-designed system respecting all setback requirements still meets 90-100% of their energy needs. Work with your installer to run production modeling that accounts for your specific roof layout and setback requirements to understand your system’s expected performance before installation.
Homeowner Going Solar?
Get the permit-ready plan set your city requires — delivered fast so your solar project stays on schedule.
Frequently Asked Questions
Failing to meet setback requirements can result in serious consequences including installation rejection during building inspections, mandatory system removal or reconfiguration, fines from local building departments, voided warranties, and potential liability issues if a fire occurs. More importantly, non-compliant installations put firefighters at risk during emergencies and may prevent them from effectively protecting your home. Insurance companies may also deny claims related to a non-compliant solar installation. Always ensure your installer designs your system to meet all local setback requirements before installation begins. If you discover an existing system doesn't meet current codes, contact a licensed solar professional to evaluate your options for bringing it into compliance.
Yes, setback requirements can vary significantly between states, counties, and municipalities. While many jurisdictions follow the International Fire Code or National Fire Protection Association guidelines recommending 3-foot pathways and specific clearances, local authorities can adopt stricter requirements based on regional conditions. For example, areas prone to wildfires may enforce larger setbacks, while regions with heavy snowfall might require additional valley clearances. Some municipalities have updated their codes to allow smaller setbacks on smaller roofs or when specific fire suppression equipment is installed. Always check with your local building department or fire marshal to understand the exact requirements for your location. A qualified local solar installer should be intimately familiar with these regional variations and design your system accordingly.
In some jurisdictions, you may be able to reduce certain setback requirements by installing approved fire suppression or rapid shutdown systems. Some building departments allow smaller perimeter setbacks when roof-mounted firefighting equipment or enhanced rapid shutdown devices are installed. However, these alternatives aren't universally accepted and must be specifically approved by your local authority having jurisdiction. The rapid shutdown requirements mandated by the National Electrical Code also help improve firefighter safety by quickly de-energizing solar systems. Before assuming you can reduce setbacks with additional equipment, consult with both your solar installer and local building department to understand what options are available in your area. Keep in mind that any alternative solutions must be documented and approved before installation begins.
While setbacks do reduce the total roof area available for panel placement, their impact on overall energy production is often less significant than you might expect. Roof edges and areas near ridges and valleys frequently experience shading from roof features, reducing their solar potential anyway. Modern high-efficiency panels can compensate for reduced panel counts by generating more power per square foot. Additionally, strategic panel placement within setback constraints, such as using split orientations or module-level power electronics, can maintain strong energy production. Many homeowners find that a well-designed system respecting all setback requirements still meets 90-100% of their energy needs. Work with your installer to run production modeling that accounts for your specific roof layout and setback requirements to understand your system's expected performance before installation.
Ground-mounted solar systems have different setback requirements than rooftop installations, typically focusing on property line distances rather than firefighter access pathways. Most jurisdictions require ground-mounted arrays to maintain specific distances from property boundaries, commonly 5 to 20 feet depending on local zoning regulations. Unlike rooftop systems, ground mounts don't need pathways for firefighter access since emergency responders can easily work around them. However, ground-mounted systems must still comply with height restrictions, setbacks from buildings, easements, and utility lines, and sometimes screening requirements if visible from public roads or neighboring properties. Some homeowner associations also impose additional aesthetic requirements for ground-mounted installations. If you're considering a ground-mount system as an alternative to a setback-constrained roof, consult with your local planning or zoning department to understand all applicable requirements for your property.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
New 2026 North Carolina Solar Permit Guide: Duke Energy & Storage Rules
Learn North Carolina solar panel licensing and permitting requirements. Discover...

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
