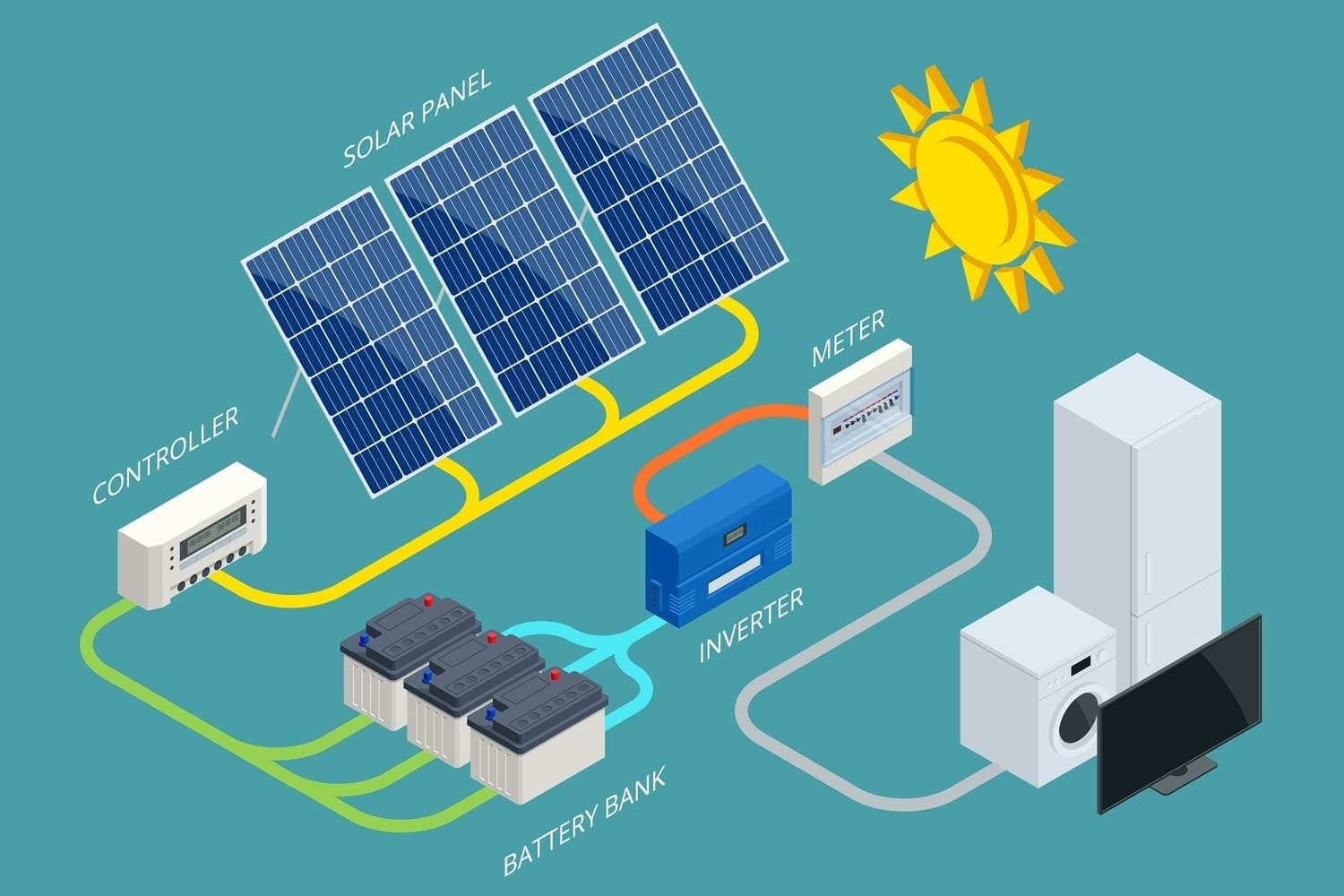
Choosing the right solar battery is essential for maximizing your renewable energy investment and achieving true energy independence. Solar batteries store excess energy generated by your solar panels during the day for use at night or during power outages, with costs ranging from $5,000 to $7,000 after the 30% federal tax credit. The five main types of solar batteries are lead-acid (most affordable at $260/kWh, lasting 5-8 years), lithium-ion (highest efficiency with 4,000-6,000 cycles, lasting up to 15 years), flow batteries (over 10,000 cycles for large-scale use), sodium-nickel chloride (operates in extreme temperatures from -4°F to 140°F), and saltwater batteries (eco-friendly but less energy-dense).
Key factors when selecting a battery include capacity (measured in amp-hours or kWh), round-trip efficiency (aim for 90% or higher), depth of discharge (lithium-ion offers 80% vs. lead-acid’s 60%), lifespan, peak power output (kWp rating), ambient working temperature requirements, and warranty terms. Battery storage becomes especially valuable with time-of-use (TOU) rates and policies like California’s NEM 3.0, enabling energy arbitrage by storing power when rates are low and using it when rates peak. Recent advancements include Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) cathodes for improved safety, AI-powered energy management systems, and modular designs that simplify installation. The federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) provides a 30% tax credit through 2032, plus many utilities offer additional rebates, making solar batteries more affordable than ever with payback periods as short as five years.
Energy storage technology for solar applications represents a cornerstone element of the current renewable power and electrification movement sweeping across the industry. Accessible and dependable battery systems deliver more than just backup power during utility interruptions, they enable the capture and utilization of solar-generated electricity during periods without sunlight. After grasping the advantages of integrating energy storage with your photovoltaic system, the essential next phase involves mastering the selection process for a battery that complements your residential solar design.
Naturally, any comprehensive discussion about energy storage must acknowledge the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which explicitly qualifies battery storage systems for the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), currently standing at 30% through 2032.
Additionally, plug-in electric vehicles, which utilize comparable energy storage solutions, are contributing substantially to the rapid evolution of solar battery innovation, as noted by renewable energy research organizations.
These factors collectively drive remarkable enhancements in battery performance and reductions in energy storage costs. Consequently, an increasing number of property owners are incorporating battery systems into their solar installations. Now, let’s examine the key considerations that guide customers toward selecting the optimal battery solution for their residence.
As previously noted, solar battery systems qualify for a 30% federal solar investment tax credit, and numerous regional utility providers also present battery rebate programs, significantly reducing the overall investment.
Consider the three-fold functionality solar batteries deliver: they serve as emergency backup power sources, contribute to long-term utility bill reduction, and minimize a household’s environmental impact. Taking these factors into account, they frequently represent a worthwhile expenditure for homeowners committed to long-term residency. The return on investment timeline for solar batteries can be as short as five years, with variations of a year or two based on variables including overall system size, configuration details, and accessible rebate programs. Certain advantages of solar batteries (including security and energy independence) hold immeasurable value for specific solar adopters and merit consideration when evaluating whether solar batteries justify the expense.
Certainly, understanding return on investment differs from demonstrating it to potential buyers. Advanced energy storage modeling software enables simulation of battery performance, system setup options, customization features, and additional capabilities for clients. These tools allow customers to clearly visualize the financial and practical advantages of adding battery storage to their solar installation.
NEM 3.0, TOU Rates, and Battery Storage
NEM 3.0, referred to as the Net Billing Tariff, created substantial changes in California’s solar industry following its implementation in 2023. While debates continue regarding CPUC’s objectives with NEM 3.0, the policy reduced immediate returns on solar investments and noticeably slowed market growth.
However, solar installation professionals have consistently demonstrated adaptability, identifying innovative approaches to provide cost savings. A primary method involves leveraging battery storage for self-consumption purposes.
Under time-of-use rates (TOU) and fluctuating export pricing structures, the timing of electricity consumption matters just as much as the total amount used. This reality means that capturing surplus energy in batteries during peak sunlight hours (when rates are comparatively lower) and deploying it during high-rate periods creates an additional savings opportunity with solar-plus-storage systems. There are even practical scenarios where solar energy gets stored in a battery and sold back to the grid when variable export rates reach their highest levels.
This strategy is known as energy arbitrage, and it enables customers to optimize their solar system’s financial performance while decreasing dependence on the conventional electric grid, which can prove unreliable or costly at times. Furthermore, battery storage can help reduce peak demand charges that commercial customers frequently face.
Advancements in Battery Technology
The electrical energy storage sector has experienced remarkable progress over the past ten years, according to recent renewable energy reports. Among the most significant developments is the emergence of modular battery systems. These battery types have transformed energy storage by increasing flexibility, simplifying installation and transportation, and reducing maintenance expenses.
Recent innovations in solar battery technology feature new breakthroughs in lithium iron phosphate (LFP) cathodes for lithium-ion solar batteries. In contrast to conventional cathodes that posed fire risks, LFP cathodes reportedly provide reduced costs, superior performance, and heightened safety standards. These improvements have already demonstrated value in electric vehicle applications.
Furthermore, iron flow batteries (which cost less and offer extended lifespans versus lithium ion) are being deployed to strengthen the electric grid against extreme weather conditions, as documented by global energy organizations.
Battery evolution extends beyond the units themselves to encompass how we utilize them. Recent years have witnessed the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into battery energy storage systems. Through AI technology, we can more effectively monitor solar storage systems by tracking factors like solar production, weather patterns, and seasonal variations. This provides valuable guidance on optimal charging and discharging schedules for solar batteries.
The swift progression in solar battery technology results in newer models reaching the marketplace while previous generations remain available. Moving beyond traditional lead-acid options, today’s solar consumers can choose from an extensive range of battery types, technologies, and capacities. When evaluating battery storage for a solar project, understanding how to select the appropriate system for your specific requirements is the crucial first step.

How to Choose a Battery for Solar Panels
Most individuals, especially residential property owners, begin their solar energy journey with minimal technical expertise. The industry has responded to this reality by standardizing expectations for what buyers should anticipate when purchasing a solar system. However, this information doesn’t always reflect accuracy.
The extensive array of solar battery choices can create an overwhelming selection process. While many consumers opt for a universal solution, this approach may not consistently deliver optimal results.
The Problem with Universal Batteries
Three compelling reasons exist for avoiding universal solar battery solutions:
- The underlying battery technology seldom receives proper emphasis. Many universal batteries have historically relied on lead-acid technology for energy storage. This represents outdated technology compared to current market standards.
- These batteries may appear substantial in physical dimensions, yet they frequently offer limited power storage capacity. The price point rarely aligns with the actual power capacity delivered.
- These standardized solar batteries consistently end up either excessively large or inadequately small. Undersized batteries fail to satisfy power output requirements. Oversized batteries, conversely, rarely achieve full charge status, particularly during winter months.
The universal battery gets promoted as the perfect option for most consumers because the majority of purchasers lack knowledge about essential selection criteria. Nevertheless, it frequently sacrifices various features and performance capabilities to satisfy the baseline requirements across different usage scenarios.
Solar Permit Solutions
Off-Grid Solar System Design
Expert design services for off-grid and battery backup systems. Complete permit packages delivered fast.
Solar Battery Specifications
Solar batteries vary significantly in their manufacturing processes. Some producers utilize robotic assembly lines, while others rely on manual construction methods. The quality control approach can influence battery quality substantially. Certain manufacturers incorporate additional lead and heavier grids, which affects cell performance within the battery. Most critically, some battery brands undergo rigorous safety and performance testing, while others receive minimal evaluation.
Consequently, batteries with comparable specifications often exhibit different performance levels and operational lifespans. Selecting appropriate batteries for your solar installation can determine whether you experience excellent or subpar power system performance. It may also dictate whether you face minimal or extensive maintenance requirements.
Here are the most essential factors to include on your checklist when purchasing a solar battery.

Battery Capacity
Batteries receive ratings in amp-hours, or simply amps. The stated power rating typically represents the fully developed capacity of the battery. This indicates that reaching the advertised full capacity may require tens to hundreds of charging cycles. Put differently, testing your battery after only a few charge cycles can produce misleading results.
Understanding the physics behind electricity is unnecessary for estimating your power needs or properly sizing your batteries. If you currently use grid power, this guide can help you calculate your power consumption using your electricity bills.
As a general guideline, always calculate your peak power requirements using amp-hours. A battery rated at 100 amp-hours, for example, can theoretically deliver 1 ampere of electric energy for 100 hours or 10 amps for 10 hours. When selecting a solar battery, comprehending your power needs is essential to choosing a battery with adequate energy storage, particularly for off-grid solar system design.
Note that batteries with extended warm-up cycles before achieving full capacity typically outlast batteries that advertise high initial capacity.
Flooded vs. Sealed Batteries
Solar batteries fall into two broad categories: flooded and sealed.
Flooded batteries are standard lead-acid batteries used in vehicles and off-grid solar installations. They offer affordability, and because they allow easy cleaning and servicing, they provide longer lifespans. During operation, these batteries produce small amounts of hydrogen gas.
Sealed batteries are also called VRLA (valve regulated lead acid) batteries. They cannot be serviced or maintained due to their sealed construction. A charge controller manages the fluids and plates inside the battery to extend their lifespan. These batteries do not emit hydrogen gas during operation.
Peak Power Output
Solar power batteries can be classified by their kilowatt peak, or kWp. kWp represents the theoretical peak power output of the system under ideal conditions. The peak output serves more as a comparison measure than an absolute unit.
When choosing a solar battery, the kWp rating shows the maximum amount of power it can output at optimal performance: the higher the peak power output rating, the superior the battery.
Round-Trip Efficiency
The round-trip efficiency of a battery measures the amount of energy that can be calculated as a percentage of the energy used to store it. For instance, if 100 kWh of electricity enters a battery, and it can only output 90 kWh, the round-trip efficiency would be 90% (90 kWh / 100 kWh x 100).
Always select batteries with higher round-trip efficiency because they deliver better economic value, as recommended by energy efficiency experts.
Ambient Working Temperature
Ambient temperature refers to the average air temperature surrounding the battery or the temperature of the room where the battery is installed. The rating specifies the optimal temperature under which the battery will operate normally.
The ambient working temperature of a solar battery is a vital rating that frequently gets overlooked. This becomes particularly important for individuals living in regions with extreme temperatures.
Battery Brand and Warranty
Numerous manufacturers compete to develop the optimal solar battery. Their design and manufacturing processes vary, and consequently, the final products differ substantially.
Brand represents an important consideration when choosing solar batteries. Your priorities and budget should determine whether to purchase a battery developed by a new startup or a major automotive company. Regardless of your selection, ensure you examine the warranty details carefully and choose the product offering the most comprehensive guarantee.
Battery Cost
Solar battery prices vary widely and have dropped significantly over the years. The cost of solar batteries ranges between $200 and $750 per kWh. Lead-acid batteries, on average, cost approximately $260 per kWh, and lithium-ion batteries average around $271 per kWh. This brings the total cost of the batteries to between $5,000 and $7,000. Actual prices may fluctuate depending on your location and available brands.
Note that the ITC provides an incentive for installing a solar power system in the US. The tax credit for installing a residential solar system remains at 30% until 2032, thanks to the ITC update. Working with professionals who understand solar permit expediting services can help streamline your installation process and ensure you maximize available incentives.

Battery Lifespan and Charge/Discharge Cycles
Battery lifespan represents a critical factor that manufacturers prioritize when engineering durable solar batteries. The design process typically emphasizes making the battery withstand heat and cold cycles to maintain peak performance over extended periods. The type of solar battery technology also significantly influences its lifespan.
Three factors affect battery longevity that you should verify when shopping:
Depth of discharge: This measures the extent to which the battery is discharged or used, relative to its capacity. Since batteries degrade through usage, their capacity diminishes over time.
Cyclic life: This represents the number of charge and discharge cycles the battery can handle. During typical use, flooded batteries generally last between 300 and 700 cycles. Gel batteries can store and deliver peak power for 500 to 5000 cycles. Lithium batteries can last for up to 2000 cycles.
Temperature: Chemical activity inside batteries accelerates with temperature increases. To maximize the lifespan of your solar batteries, install them in a temperature-controlled environment, following proper wire management and conduit practices.
The Different Types of Solar Batteries
The type, or technology, represents the most critical factor when purchasing a solar battery. Your budget and specific requirements should guide the type of battery you select.
1. Lead-Acid Solar Batteries
Proven and reliable, lead-acid batteries serve as the standard for electrical energy storage. This battery type has existed since its invention in the 17th century, yet it remains the most widely used for power storage. Until five years ago, these were the only viable batteries available for storing electricity in residential or industrial applications.
Pros of Lead-Acid Batteries
The most significant advantage of lead-acid batteries is their affordability. They are frequently installed in rural and remote locations because purchasing them costs less than extending a power mains grid connection.
Lead-acid batteries are deep-cycle batteries, meaning they can deliver steady output over extended periods. Their discharge rate remains consistent. These batteries are available in both flooded and sealed variants. Both operate on the same principle.
Cons of Lead-Acid Batteries
At first glance, lead-acid batteries appear unattractive because they are bulky, unappealing, and heavy. Since they occupy considerable space and their ambient working temperature falls below room temperature, they must be housed in a climate-controlled structure.
Where Lead-Acid Batteries Are Used
Lead-acid batteries are the primary choice for off-grid solar system installations. Their price point and stability make them highly dependable and simple to upgrade or replace. Most emergency power backup systems nationwide still utilize lead-acid batteries.
2. Lithium-Ion Solar Batteries
Li-ion batteries are gaining popularity because they serve as the preferred power storage for electric vehicle manufacturers. The potential of lithium-ion as an energy storage medium remains to be fully realized, but they show promise. However, given the pace of improvements, it is only a matter of time before they become the most popular battery for solar power storage. Popular power storage solutions utilize this technology.
Two types of lithium-ion batteries exist on the market. The first and most popular among electric vehicle manufacturers is the NMC (nickel-manganese-cobalt) chemistry type. The other is a LiFePO₄ (lithium iron phosphate) type battery.
The NMC-type battery offers a high cycle life, making it suitable for off-grid installations. LiFePO₄ batteries perform exceptionally well in extreme temperatures, making them appropriate for regions with temperature extremes.
Pros of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Li-ion batteries require minimal to no maintenance. They possess higher battery energy density. This means a lithium-ion battery can store more energy than a lead-acid battery of identical physical dimensions.
Because they have longer life cycles, they offer extended lifespans and greater depth of discharge. The lithium-ion battery can deliver between 4,000 and 6,000 cycles at an 80% depth of discharge and still function for up to 15 years.
Cons of Lithium-Ion Batteries
The primary disadvantage of lithium-ion batteries is their high cost. They cost approximately double the price of lead-acid batteries with comparable energy storage capacity. These batteries, unlike lead-acid batteries, are also quite fragile and require a stabilizing circuit to ensure safe operation, similar to considerations in understanding solar rapid shutdown systems.
Where Lithium-Ion Batteries Are Used
Lithium-ion batteries have established themselves in the automotive industry. The demand for this battery has reached unprecedented levels as electric vehicle manufacturers compete to secure supplies.
3. Flow Solar Batteries
Also known as redox flow, the flow battery is a recent addition to the solar battery market. These batteries use a water-based zinc and bromine solution and vanadium to store electrical charge. Only a handful of companies manufacture this battery today.
Pros of Flow Batteries
Flow batteries are highly scalable. This means the capacity and outputs of the battery can be increased or reduced proportionally to the battery size. They differ from other batteries on this list in that deep discharge does not affect the performance or lifespan of the battery. They have an extended life cycle and very low self-discharge. It is also worth noting that flow batteries do not heat up during operation.
Cons of Flow Batteries
The fluids used to manufacture flow batteries are prohibitively expensive. While the technology behind them has existed for decades, these batteries remain relatively unknown in the mainstream because few companies produce them commercially.
Due to their chemistry, flow batteries are bulky. The zinc and bromine elements in the battery are also highly corrosive and toxic.
Where Flow Batteries Are Used
Flow batteries are suitable for situations where the batteries undergo multiple charge/discharge cycles daily. They are optimal for large-scale installations.
4. Sodium-Nickel Chloride Solar Batteries
The sodium nickel chloride battery is a strong competitor to the lithium-ion battery. This energy storage solution uses a unique chemistry that makes it fully recyclable. It does not emit toxic chemicals and presents no heating or fire risk. Unlike lithium-ion batteries, sodium-nickel chloride batteries do not require sophisticated cooling systems to operate efficiently.
Pros of Sodium-Nickel Chloride Batteries
Because of its chemistry, the sodium nickel chloride battery is safe and reliable. It can operate optimally even at extreme temperatures between negative 4°F and 140°F. The batteries are fully recyclable because they contain no hazardous or toxic chemicals.
Cons of Sodium-Nickel Chloride Batteries
They have a limited lifespan of approximately 3,000 cycles and only an 80% depth of discharge. This means as much as 20% of the power stored cannot be utilized. These batteries are also quite costly to install, particularly for residential solar systems and large projects.
Where Sodium-Nickel Chloride Batteries Are Used
Sodium nickel chloride batteries are best suited for large installations in solar off-grid power installations and emergency power backup systems.
5. Saltwater Solar Batteries
Saltwater solar batteries, also known as sodium-ion or seawater batteries, are a type of rechargeable battery that uses saltwater as the electrolyte. This makes them a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries since they don’t contain any toxic or hazardous chemicals. While they’re not yet ready for large-scale adoption, they represent an exciting technology worth monitoring, as noted by the American Solar Energy Society.
Pros of Saltwater Batteries
Experts often warn of a lithium-ion shortage, and one advantage of saltwater batteries is that saltwater is abundantly available. In terms of supporting clean energy, you can’t get much cleaner than this. Saltwater batteries are made of eco-friendly materials and are easy to recycle. Additionally, they have a longer lifespan, nearly double that of other batteries on the market, and present less of a fire risk.
Cons of Saltwater Batteries
The biggest disadvantage of saltwater batteries is their lower energy density compared to other battery types, which means they store less energy in the same amount of space. Because larger batteries are required, saltwater batteries are also more expensive to produce compared to other solar batteries, which makes manufacturers less interested in the investment.
Where Saltwater Batteries Are Used
Saltwater batteries are not commonly used for energy storage, mostly due to their high cost and lack of research.
Comparing Solar Battery Types
Lead-Acid Batteries
- The most affordable option in the market
- Easy to maintain; sealed lead-acid batteries require no maintenance
- Highly reliable
- Easily recycled or disposed of
- Bulky, and occupies considerable storage space
- Short lifespan of between 1,000 and 3,000 cycles. On average, a lead-acid battery can last 5 to 8 years
- Shallow discharge depth of approximately 60% and an ambient temperature of 70º
- Good for off-grid solar systems and emergency power backup storage
Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Require minimal to no maintenance
- High battery energy density saves space
- Longer life cycles and lifespans
- Highest depth of discharge
- Relatively expensive
- Relatively fragile and must be enclosed in metal
- Use an electronic circuit to provide stable power output
- Good for electric vehicles, remote cameras, and drones
Flow Batteries
- Can provide over 10,000 cycles with negligible loss of efficiency or storage capacity
- Fast recharge rates
- Little to no heat or fire hazard
- Relatively expensive
- Hard to dispose of and non-recyclable
- Good for large-scale installations
Sodium-Nickel Chloride Batteries
- Safe and reliable
- Can operate normally even in extreme temperatures
- Recyclable
- Short lifespan
- Shallow 80% depth of discharge
- Relatively expensive
- Good for large-scale installations and power backup systems
Saltwater Batteries
- Safe
- Long-lasting
- Recyclable and made of clean, abundant materials
- Lower energy density
- Require more space
- More expensive than most alternatives
- More research is needed
Conclusion
Selecting the right battery for your solar panel system is a critical decision that directly impacts your energy independence, cost savings, and overall system performance. As solar battery technology continues to advance rapidly, homeowners and businesses now have access to more efficient, affordable, and reliable energy storage solutions than ever before.
The key to making an informed choice lies in understanding your specific energy needs, budget constraints, and long-term goals. Whether you opt for the affordability and reliability of lead-acid batteries, the high energy density and longevity of lithium-ion solutions, or explore emerging technologies like flow batteries and saltwater systems, each option offers distinct advantages suited to different applications.
Remember that factors such as battery capacity, lifespan, round-trip efficiency, ambient working temperature, and depth of discharge should all play crucial roles in your decision-making process. Additionally, take advantage of available incentives like the 30% federal Investment Tax Credit, which significantly reduces the upfront investment and improves your return on investment timeline.
As the solar industry continues to evolve with innovations in battery chemistry, modular systems, and AI-powered energy management, the future of solar energy storage looks increasingly promising. Understanding solar supply-side connections becomes essential when integrating battery storage into your system. By carefully evaluating your options and consulting with qualified solar professionals, you can select a battery system that maximizes your solar investment, provides reliable backup power during outages, and contributes to a more sustainable energy future. For more information about solar permit solutions, explore our comprehensive resources.
FAQs
Are solar batteries eligible for tax credits and incentives?
Yes, solar batteries are eligible for the federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which currently offers a 30% tax credit on the total cost of your solar energy system, including battery storage, through 2032. This incentive applies to both new installations and retrofits. Additionally, many local utilities and state governments offer rebate programs and performance incentives specifically for battery storage systems, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. These combined incentives can reduce the overall cost by thousands of dollars, significantly improving
For additional assistance with your solar project, contact our team or visit our blog for more expert insights on solar energy solutions.
Off-Grid Solar System Design
Expert design services for off-grid and battery backup systems. Complete permit packages delivered fast.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar battery lifespan varies significantly depending on the technology used. Lead-acid batteries generally last between 5 and 8 years with 1,000 to 3,000 charge cycles. Lithium-ion batteries offer superior longevity, lasting up to 15 years with 4,000 to 6,000 cycles at 80% depth of discharge. Flow batteries can provide over 10,000 cycles with minimal performance degradation. Proper installation in temperature-controlled environments and following manufacturer maintenance guidelines can help maximize battery lifespan regardless of the type you choose. For DIY enthusiasts interested in building their own home solar power system, understanding battery lifespan is crucial.
The appropriate battery size depends on several factors, including your daily energy consumption, peak power requirements, and backup duration needs. Start by reviewing your electricity bills to determine your average daily usage in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Most residential systems require batteries ranging from 10 kWh to 20 kWh capacity. If you want whole-home backup during outages, you'll need larger capacity. For partial backup covering essential appliances only, a smaller system may suffice. Consulting with a qualified solar installer who can perform a detailed energy audit will help you determine the optimal battery size for your specific needs. Understanding solar interconnection methods is also important when sizing your system.
Absolutely. Adding battery storage to an existing solar panel system is entirely possible and increasingly common, especially in regions with time-of-use rates or unreliable grid power. This process is called a solar retrofit or battery retrofit. However, you may need to install additional equipment, such as a battery-compatible inverter or a separate battery inverter, depending on your current system configuration. Some modern hybrid inverters can manage both solar panels and batteries simultaneously. Consult with your original installer or a qualified solar professional to assess compatibility and determine the most cost-effective approach for integrating battery storage into your existing system. Green building advisors often recommend professional evaluation before retrofitting.
Solar battery performance in extreme weather varies by battery technology and chemistry. Most batteries have optimal operating temperature ranges, typically between 50°F and 85°F. Lead-acid batteries are particularly sensitive to temperature extremes and require climate-controlled installation environments. Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) batteries perform exceptionally well in both hot and cold conditions. Sodium-nickel chloride batteries can operate efficiently in temperatures ranging from negative 4°F to 140°F. To ensure reliable performance regardless of climate, install batteries in temperature-controlled spaces such as garages, basements, or specially designed battery enclosures. Modern battery management systems also include thermal protection features that help maintain optimal operating conditions and prevent damage from temperature extremes. For more technical details, review our guide on understanding solar three-line diagrams and proper system design. The EPA's green power resources also provide valuable information on sustainable energy practices.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
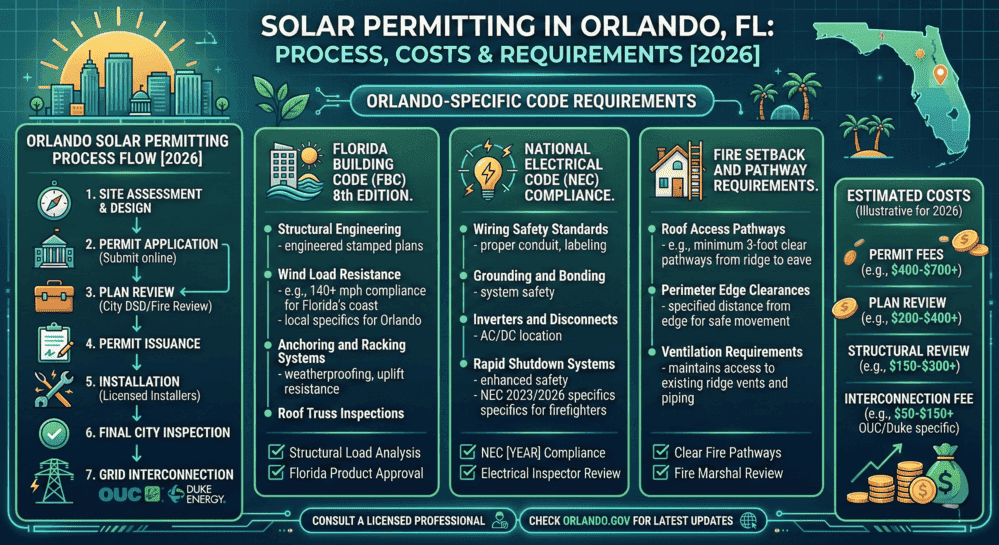
Solar Permitting in Orlando, FL: A Complete Guide for Homeowners & Installers
Solar permitting in Orlando, FL, requires a building permit and an electrical pe...
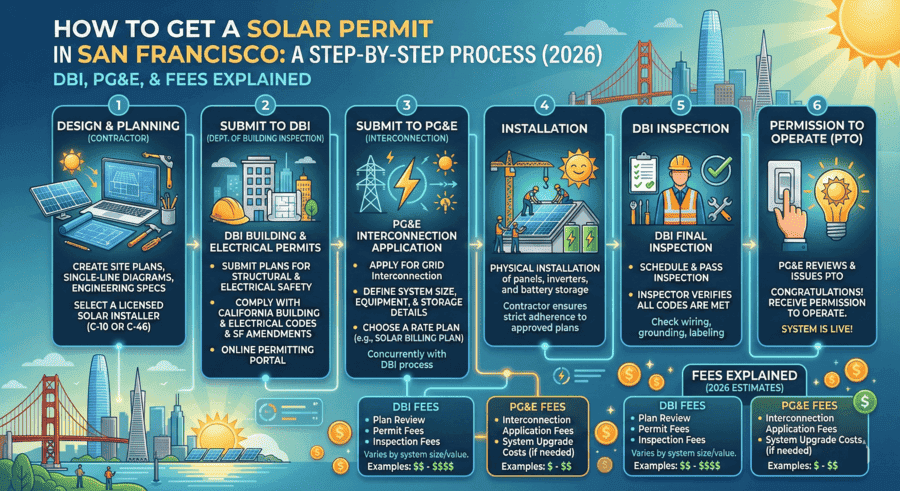
How To Get A Solar Permit In San Francisco: DBI, PG&E And Fees Explained (2026)
San Francisco solar permits require two separate approvals before your system ca...
Bifacial Solar Panel Installation And Permitting Guide
Bifacial solar panels generate 10 to 30 percent more energy than traditional mon...