The 33% rule in solar panels is a fire and building code provision that limits rooftop solar panel coverage to 33% of a roof’s total plan-view area before additional setbacks and clearances are required. This regulation exists in many local jurisdictions to ensure firefighter access, proper roof ventilation, and structural safety during solar installations.
If you’re planning a residential solar system, here’s what the 33% rule means for you: Calculate your roof’s total square footage, then multiply by 0.33 to determine your threshold. For example, a 1,000 square foot roof allows approximately 330 square feet of solar panels before stricter requirements kick in. Exceeding this limit doesn’t prohibit installation, but it triggers additional permitting steps including expanded ridge setbacks (often 3-6 feet from the ridge instead of 18 inches), wider firefighter pathways (typically 3-4 foot corridors), and possible structural engineering reviews.
The rule directly impacts three key aspects of your solar project: permitting complexity, system design constraints, and overall installation costs. Staying within the 33% threshold typically results in faster permit approvals and lower compliance costs. Exceeding it requires meeting enhanced National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and International Residential Code (IRC) standards, adding weeks to timelines and potentially hundreds to thousands in additional engineering and design fees.
Why does this matter for your solar planning? Understanding the 33% rule upfront allows you to optimize your system design strategically. You can maximize energy production within the allowed area by selecting high-efficiency panels (20-22% efficiency ratings instead of standard 15-18%), incorporate battery storage to extend limited generation capacity, or supplement with ground-mounted arrays. Making informed decisions about the 33% rule during initial planning prevents costly permit rejections, project delays, and retrofit requirements that arise from non-compliant installations.
This guide explains exactly how the 33% rule works, when it applies, and how to design compliant solar systems that meet your energy goals while satisfying local fire and building codes.

What Is the 33% Rule in Solar Panel Installation?
Many jurisdictions enforce requirements where rooftop photovoltaic (PV) systems covering more than approximately 33% of a roof’s plan-view area must meet enhanced building and fire-safety standards. According to National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) documentation, installations exceeding 33% roof coverage require expanded roof-ridge vent clearances or enhanced firefighter access corridors.
In practical terms, a 1,000 ft² rooftop permits approximately 330 ft² (roughly 33%) of solar panel installation before stricter pathway and clearance regulations take effect. Exceeding this limit requires expanded ridge setbacks, wider access corridors, or comprehensive structural and fire-engineering assessments.
What Makes the 33% Rule Necessary: Fire Access, Codes, and Roof Integrity
Fire Department Access & Ventilation
Fire regulations mandate clear rooftop pathways enabling firefighters to ventilate smoke, access attics, and navigate safely during emergencies. Extensive panel coverage increases obstruction risks. Building authorities use the 33% threshold to determine when additional clearance becomes mandatory. Homeowners should also be aware that HOA regulations can impact solar permit approvals in addition to fire code requirements.
Structural Load & Roof Integrity
Arrays exceeding 33% of roof area can modify wind-uplift dynamics or snow-load distribution patterns. Before installing solar panels, you need to determine if your roof can support the additional weight. Local structural regulations may require detailed engineering analysis once this threshold is crossed.
Installer Design Simplicity
The 33% guideline offers homeowners and installers a straightforward benchmark: installations below this threshold undergo simpler permitting processes; those above face increased scrutiny or higher costs.
How It’s Applied in Residential PV Systems
The regulation typically unfolds during rooftop solar design and permitting as follows:
- Calculate total usable roof plan area (flat projection)
- Determine proposed array area (module dimensions × quantity)
- Array covering ≤ 33% of roof area → standard permitting procedures apply
- Array covering > 33% → enhanced setbacks, pathways, potential engineering review required
California residential permit guidelines illustrate this: panel coverage below 33% allows reduced ridge setbacks; coverage exceeding this threshold mandates larger setbacks. Understanding AHJ solar requirements is essential for navigating these regulations effectively.
Solar Permit Solutions
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Impact on System Sizing & Design
The 33% regulation directly influences maximum system size before triggering additional requirements or costs. Consider this example:
A 1,200 ft² roof with 400 ft² of panel coverage (≈ 33.3%) approaches the threshold. Staying within the safe zone might require limiting installation to approximately 390 ft² of panels, reducing total array size or requiring higher-efficiency module selection. According to the Department of Energy’s homeowners guide, careful system sizing is crucial for optimizing both performance and compliance.
Limited array capacity can still support effective energy management when paired with battery storage solutions to capture excess solar or grid power and maintain critical load backup. Modern systems must also comply with 2023 NEC rapid shutdown requirements for enhanced safety.
Design trade-offs
- Select higher-efficiency panels to maximize power generation within area constraints
- Supplement rooftop arrays with ground-mounted or carport installations where feasible
- Implement battery storage systems to optimize energy usage despite area limitations

How Battery Storage Fits In
When rooftop systems face 33% rule constraints, battery-based storage becomes strategically important. Whether you’re considering a DIY LiFePO4 battery pack or professional installation, energy storage offers critical benefits:
- Area-limited solar generation makes storing produced energy more valuable
- Battery storage captures excess solar production, off-peak grid power, or provides outage backup
- Limited panel coverage makes stored energy critical for essential loads (lighting, refrigeration, communications, heating)
For homeowners facing permitting constraints, combining modest solar coverage (within 33% limits) with robust battery systems delivers high functionality and cost-effectiveness. Learn more about energy storage systems and safety requirements from NFPA resources.
Comparing Solar Installations: Meeting vs. Exceeding the 33% Threshold
Conclusion
The 33% rule represents a critical planning consideration for residential solar installations, balancing energy production goals with fire safety and structural integrity requirements. While this regulation may initially appear restrictive, understanding and working within these guidelines ensures smoother permitting and inspection processes, faster project approvals, and compliant installations that protect both your investment and your home.
For homeowners pursuing solar energy, the key takeaway is strategic planning. Calculate your roof’s total area early in the design phase and work with qualified solar design professionals who understand local code requirements. If your energy needs demand more generation capacity than the 33% threshold allows, explore alternative solutions: higher-efficiency panels maximize power output within constrained areas, while ground-mounted or carport arrays can supplement rooftop installations without triggering additional roof coverage requirements.
Battery storage systems become particularly valuable when working within 33% rule constraints. By capturing and storing the energy your limited array produces, you extend the utility of every watt generated and maintain resilience during outages or low-production periods. This integrated approach, optimized rooftop solar paired with robust energy storage, often delivers better long-term performance and cost-effectiveness than simply maximizing panel coverage. For cost considerations, check out how much a home solar system costs in 2025.
Before finalizing your solar installation plans, verify the specific requirements with your local Authority Having Jurisdiction. Code provisions vary significantly across regions, and what applies in one area may differ substantially in another. Resources like Energy Star’s rooftop solar guide and state-specific residential solar programs provide additional compliance information. Taking the time to understand and comply with local regulations, including the 33% rule where applicable, positions your project for success from permit application through final inspection and decades of reliable solar energy production.
FAQs
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Frequently Asked Questions
This is not a federal mandate. It appears in numerous local fire and building codes (including NFPA guidance) and varies by jurisdiction. Understanding the law of solar energy helps clarify these regional differences. Always verify requirements with your local Authority Having Jurisdiction (AHJ) for specific thresholds.
No. Exceeding this threshold triggers additional requirements (clearances, pathways, setbacks, structural reviews). You can exceed it—but anticipate extra costs or design modifications. Whether considering professional installation versus DIY approaches, understanding these requirements is essential.
Yes, integrating battery storage maximizes the effectiveness of a smaller rooftop array and provides backup or off-grid capabilities without expanding roof coverage. If you're exploring DIY options, learn about building your own home solar power system and the essential tools needed for self-installation.
Permit approvals can be delayed or denied. Worst-case scenarios require costly and time-consuming retrofit corrections. Working with experienced providers like Solar Permit Solutions ensures compliance from the start. Additionally, understanding end-of-life solar panel regulations ensures long-term compliance throughout your system's lifecycle.
When rooftop solar faces area constraints, pairing with high-capacity battery storage enables you to capture available generation and utilize it during outages or low-production periods. Properly sizing fuses or circuit breakers for your solar system becomes essential for resilience planning. Utility programs like PG&E's solar getting started resources and IID's rooftop solar information offer additional support for integrating battery systems effectively.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
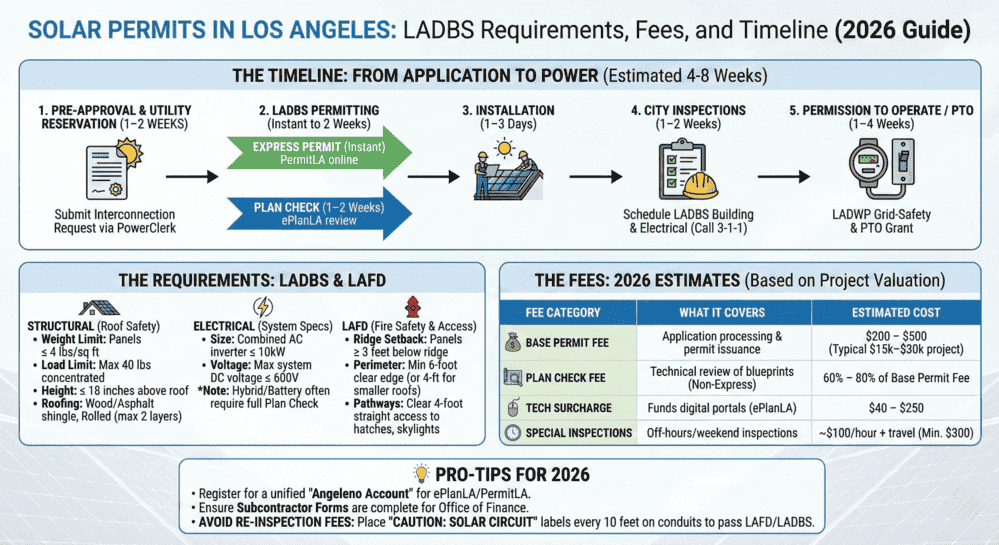
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...
