A solar equipment specification sheet is a technical document that provides detailed information about a solar panel’s electrical performance, physical dimensions, operating parameters, and safety certifications. These documents help solar installers, engineers, and designers properly size photovoltaic systems, ensure compliance with electrical codes, and predict energy output under various environmental conditions.
Reading solar panel spec sheets requires understanding key metrics including maximum power point (Pmax), voltage ratings, current specifications, efficiency percentages, temperature coefficients, and mechanical load ratings. The specification sheet reveals how panels perform across different temperatures (typically negative 40 to positive 85 degrees Celsius), their power tolerance ranges, and structural capacity for wind and snow loads measured in Pascals.
This guide explains how to interpret every critical specification on solar panel datasheets, from electrical data like open circuit voltage (Voc) and short circuit current (Isc) to warranty terms and industry certifications. Understanding these specifications ensures accurate system design and optimal panel selection for specific project requirements.

Decoding Solar Panel Specification Documents
Solar specification sheets can appear overwhelming at first glance due to specialized terminology and technical jargon. However, understanding these documents becomes manageable once the key terms and expected values are identified. Solar Permit Solutions helps professionals navigate these technical requirements efficiently.
What Is The Maximum Power Rating?
The maximum power point, abbreviated as Pmax or MPP rating, represents the most critical value on a specification sheet.
Maximum power point combines voltage and current to produce the highest wattage output. It represents the optimal balance between volts and amps for peak performance.
When current decreases and voltage increases, the system moves away from the maximum power point, reducing overall efficiency. Understanding electrical fundamentals is crucial for interpreting these power relationships.
Solar panels typically carry ratings between 250 and 400 watts. Higher wattage values indicate greater system efficiency and fewer required modules.
Why Voltage Matters In PV System Design
Voltage represents another crucial specification factor, particularly when planning residential solar design projects.
When designing a system with 12 panels in a string, voltage must remain below specific thresholds for optimal operation. The Department of Energy’s technical specifications provide detailed guidance on voltage requirements.
Systems should be sized to avoid exceeding 600 volts per string. Beyond this threshold, panel performance degrades significantly.
Performance Efficiency Metrics
Efficiency ratings require careful consideration from installers, engineers, and designers. Solar panel efficiency typically ranges from 15% to 20%, with premium panels reaching 23%. These ratings continue improving as cell technology advances.
Specification sheets also document the assumptions used to establish operating parameters. California’s solar equipment lists maintain updated efficiency standards for approved panels.
Temperature ranges typically span from negative 40 degrees Celsius to 85 degrees Celsius, found under Operating Condition and Mechanical Data sections.
Panels generally perform better in colder temperatures compared to warmer conditions.
Climate Impact On Module Performance
Weather conditions significantly impact solar panel efficiency. Module temperature ranges generally fall between negative 20 degrees Celsius and positive 85 degrees Celsius in most regions. Areas experiencing extreme temperatures require special attention to panel temperature tolerances.
Operating cell temperature provides another important metric. Different panels generate varying amounts of heat during operation. This value indicates how modules respond to different sunlight intensity levels.
Current ratings also demand attention. Under electrical data headings, specification sheets provide rated current values. DC connector risks illustrate why exceeding current ratings can be dangerous.
Exceeding the rated current can permanently damage the panel. Maximum current depends on the specific panel model and the number of parallel strings in the system configuration.
Structural Load Specifications For Harsh Environments
Regions experiencing extreme weather conditions, particularly those prone to high winds or heavy snow, require attention to mechanical or static load ratings. Commercial solar design often demands higher structural specifications.
Front side ratings focus on snow load capacity, while back side ratings address wind load resistance. The New York State solar specifications outline detailed load requirements for various climate zones.
Load figures appear in Pascals, which measure pressure. Higher Pascal values indicate stronger, more durable panels.

Key Information Found In PV Module Data Sheets
Physical Properties And Dimensions
Specification sheets should include comprehensive information about material characteristics, covering vital details regarding size and dimensions of solar panels. These measurements are essential when preparing solar permit applications.
Critical Electrical Data Points
Electrical specifications contain numerous technical terms and metrics. This section includes data on important specifications such as Pmax and temperature testing parameters. Several key electrical specifications appear within solar panel specification sheets.
Nominal Operating Cell Temperature (NOCT)
The expected operating temperature of a solar cell determines the output it provides. Nominal Operating Cell Temperature (NOCT) represents the temperature reached by a solar panel under four standard environmental conditions:
- Sunlight hitting the solar panel equals 800 watts per square meter
- Wind velocity equals 1 meter per second
- Air temperature equals 20 degrees Celsius (68 degrees Fahrenheit)
- Panel angle equals 45 degrees from horizon
NOCT significantly impacts solar panel performance and must be factored into solar system planning and optimization. The University of Alaska’s solar manual provides comprehensive temperature analysis guidelines.
Temperature Coefficient (Percent Per Degree Celsius)
Silicon in PV cells becomes less efficient when heated. A solar panel’s temperature coefficient demonstrates the relationship between PV output and panel temperature, represented as the overall percentage decrease in power for each degree of temperature increase.
Maximum Power Point (MPP)
The Maximum Power Point represents when a solar panel achieves maximum power output. MPP changes slightly with temperature and sunlight intensity variations.
Maximum Power Point Voltage (Vmp)
This value represents the available voltage of a connected panel operating at maximum capacity under standard testing conditions. Most manufacturers rate their panels around 70 to 80 percent of the Open Circuit Voltage (VOC). Understanding these voltage parameters is critical for supply side connections.
Maximum Power Point Current (Imp)
Maximum Power Point Current (Imp) represents the current (amperage) a solar panel produces at maximum power output. This is the target current when the panel connects to a charge controller under standard test conditions. Imp varies with sunlight intensity hitting the panel.
Open Circuit Voltage (Voc)
Open Circuit Voltage (Voc) represents the maximum voltage a solar panel can produce without a load. Voc is measured at the unconnected terminals of a solar panel to verify or test the panel during installation. Proper documentation in three line diagrams requires accurate Voc values.
Short Circuit Current (Isc)
Short Circuit Current (Isc) measures the current produced when the positive and negative terminals of a solar panel connect to each other. Isc shows the highest current a solar panel can deliver without self-damage and determines how many amps a panel can safely handle when connected to a load. The University of Maryland’s wiring guide explains proper fusing based on Isc values.
Power Tolerance
Power tolerance measures how much power a solar panel can produce below or beyond its rated capacity. For example, a 100 watt panel with negative 4 percent to positive 4 percent power tolerance could produce 96 to 106 watts in real-world conditions.
Module Efficiency (Percent)
A solar panel’s module efficiency measures how much sunlight hitting the panel converts to electricity. Higher module efficiency means fewer panels are needed to achieve desired output. This factor significantly influences off-grid system design requirements.
Quality Assurance Standards
Quality solar panels undergo rigorous testing under various environmental stressors to ensure quality and safety. Solar panel certifications are printed on specification sheets. Common solar panel testing and certification standards are established by testing organizations. The Arizona Extension’s solar guide details certification requirements.
Product Warranty Details
Solar specification sheets also mention warranty information. Most panels include 25-year warranties. Some manufacturers offer a 90 percent warranty for 10 years, with decreasing percentages as panels age. Premium panels typically feature better warranty terms. The solar PV guidelines provide comprehensive warranty evaluation criteria.
Taking Action With Your Specification Sheet
This guide provides a foundation for reviewing solar specification sheets. Testing a solar software platform represents the logical next step, simplifying the process of ensuring a viable system setup. Professional services can help streamline this verification process.
Solar Permit Solutions
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Conclusion
Understanding solar equipment specification sheets is fundamental to successful PV system design and installation. These technical documents provide the critical data needed to properly size systems, ensure safety compliance, and optimize energy production for specific environmental conditions.
Mastering the key metrics like maximum power point, voltage thresholds, efficiency ratings, and temperature coefficients enables informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. Whether evaluating panels for residential installations or commercial-scale solar farms, the ability to interpret specification sheets directly impacts system performance and longevity. The Department of Defense specifications demonstrate how specification standards apply across different sectors.
As solar technology continues advancing, staying current with specification terminology and industry standards remains essential. Taking time to thoroughly review and understand these documents before installation prevents costly mistakes and ensures optimal system configuration. Knowing what happens without permits emphasizes the importance of proper documentation. With the knowledge gained from reading specification sheets effectively, solar professionals can confidently select the right equipment for each unique project requirement. Contact our team for expert assistance with specification review and system design.
FAQs
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Frequently Asked Questions
The maximum power point (Pmax) rating is typically the most critical specification to evaluate. This value indicates the optimal combination of voltage and current that produces the highest wattage output. Pmax directly determines how much energy the panel can generate under standard test conditions and helps calculate the total number of panels needed for a system. However, other specifications like voltage limits, efficiency ratings, and temperature coefficients should also be considered for comprehensive system design.
Temperature significantly impacts solar panel output, which is why specification sheets include temperature coefficients and NOCT ratings. As solar panels heat up, their efficiency decreases, typically shown as a percentage loss per degree Celsius increase. Specification sheets provide temperature ranges (usually negative 40 to positive 85 degrees Celsius) and indicate how panels perform across different climate conditions. Panels generally operate more efficiently in cooler temperatures, making temperature data essential for accurate performance predictions in various geographic locations.
Power tolerance indicates the acceptable variance in a panel's actual power output compared to its rated capacity. For instance, a panel rated at 300 watts with a plus or minus 3 percent tolerance could produce anywhere from 291 to 309 watts under real-world conditions. This specification accounts for manufacturing variations and helps set realistic expectations for system performance. Panels with tighter tolerance ranges (lower percentage variance) generally indicate higher manufacturing quality and more predictable output.
Mechanical load ratings, measured in Pascals, indicate how much physical stress a panel can withstand from environmental forces. Front side ratings specify snow load capacity, while back side ratings address wind resistance. These specifications are crucial for regions experiencing extreme weather conditions like heavy snowfall or high winds. Higher Pascal values mean stronger, more durable panels that can survive harsh conditions without structural failure. Ignoring these ratings can lead to panel damage, system failure, and safety hazards.
Open circuit voltage (Voc) represents the maximum voltage a panel produces with no load connected, while maximum power point voltage (Vmp) is the operating voltage when the panel generates maximum power under standard conditions. Voc is typically measured during installation to verify panel function at the unconnected terminals. Vmp, usually rated at 70 to 80 percent of Voc, represents the actual working voltage when the panel connects to a charge controller or inverter. Both values are essential for proper system sizing and ensuring voltage stays within safe operational limits.
Manufacturers typically update specification sheets whenever they release new panel models or make significant changes to existing products. This can occur annually or every few years depending on technological advancements and manufacturing improvements. As cell technology evolves, efficiency ratings increase and specifications change accordingly. Always verify that specification sheets correspond to the exact panel model and production batch being installed, as even minor model variations can have different performance characteristics. Checking for the most current version ensures accurate system design and performance expectations.
Reputable solar panels should display certifications from recognized testing organizations. Common certifications verify that panels have undergone rigorous testing under various environmental stressors including temperature cycling, humidity exposure, and mechanical stress. Panels lacking proper certifications may not meet safety standards or perform reliably over their expected lifespan.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
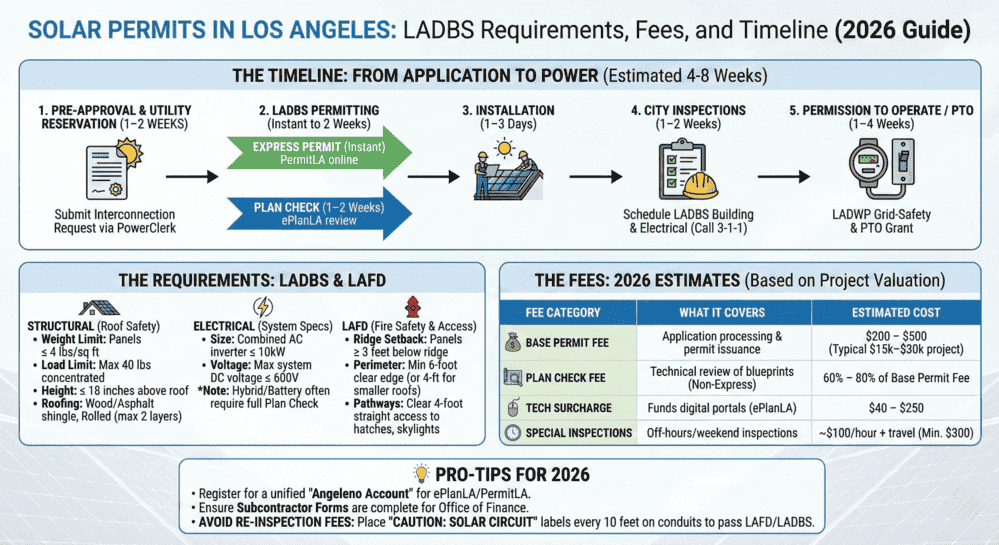
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...
