Yes, you need a permit to install solar panels in California. All residential and commercial solar installations require building and electrical permits to ensure compliance with safety codes and local regulations. Here’s what you need to know:
Quick Facts:
- Cost: $100 to $600 for residential permits (most pay $200-$500)
- Timeline: 1 to 8 weeks for approval (or same-day with SolarAPP+)
- Required Permits: Building permit, electrical permit, and potentially zoning, fire safety, or battery storage permits
- Validity Period: 180 days to 1 year before expiration
- Mandatory For: All solar installations, whether rooftop, ground-mounted, residential, or commercial
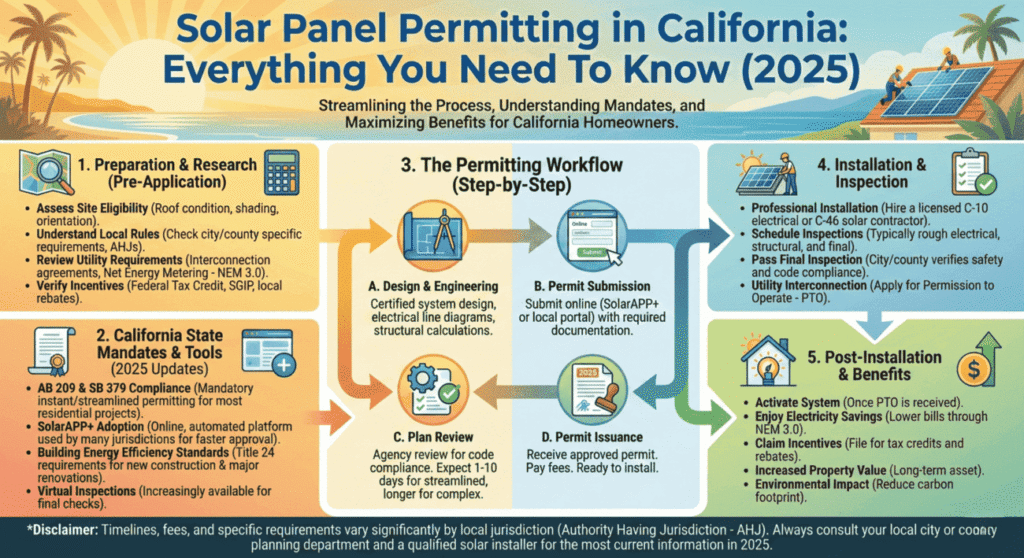
The permitting process follows six steps: system design, application submission, review and approval, installation, inspection, and Permission to Operate (PTO) from your utility company. California’s streamlined permitting initiatives, including SolarAPP+ and the California Solar Permitting Guidebook, have simplified the process in many jurisdictions, though specific requirements vary by city and county.
Whether you’re a homeowner planning a residential solar system or a business pursuing commercial solar deployment, understanding California’s 2025 permit requirements prevents costly delays, ensures safety compliance, and protects your investment. This comprehensive guide breaks down every aspect of the solar permitting process, from required documents and costs to timelines and common challenges.
California leads the charge in renewable energy adoption, positioning solar power as a cornerstone strategy for cutting carbon footprints and meeting environmental targets. Whether you’re pursuing a residential or commercial solar energy system, securing the proper permits stands as a critical first step. These permits guarantee your solar installation meets local safety protocols, adheres to building standards, and complies with zoning ordinances. While California has advanced solar deployment significantly, the permitting framework addresses the diverse nature of installation projects, verifying each system delivers safety, stability, and optimal energy performance.
The state’s dedication to clean energy has simplified the permit acquisition process across numerous jurisdictions, though specific requirements fluctuate between municipalities and counties. A properly executed solar installation satisfies both property owner objectives and regulatory safety benchmarks. Understanding the permitting pathway ensures your renewable energy system functions reliably and securely over its lifetime.
Required Solar Permit Categories in California
Installing a solar energy system in California triggers various permit requirements based on your project’s specifications. Building permits verify the structure can adequately bear the solar panel load, particularly crucial for rooftop installations where weight distribution and mounting techniques demand safety evaluation. Electrical permits confirm all electrical components meet National Electrical Code (NEC) compliance standards and undergo proper installation procedures. Zoning permits become necessary for certain projects, especially large-scale systems or installations that could influence community aesthetics or structural characteristics.
Fire safety permits are increasingly mandatory, particularly throughout wildfire-prone regions, guaranteeing solar arrays conform to fire prevention regulations. Encroachment permits may apply when installations interface with public infrastructure or municipal property. These distinct permit types work collectively to safeguard public welfare and maintain regulatory adherence at state and local levels.
California Solar: Governing Laws & Regulatory Framework (2025)
California maintains a comprehensive regulatory structure overseeing solar energy system deployment. Primary legislation includes the California Building Standards Code (Title 24), which establishes precise guidelines for both residential and commercial solar projects, covering structural specifications, electrical safety protocols, and energy performance standards. The California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) administers the Net Energy Metering (NEM) program, enabling property owners to earn credits for excess solar generation fed into the utility grid.
Additional regulations from the California Energy Commission (CEC) define renewable energy benchmarks and efficiency objectives that influence permitting decisions. Notably, AB 2188 (2022) simplified permit procedures for small-scale residential systems, eliminating bureaucratic obstacles for straightforward installations. Municipal authorities frequently implement supplementary requirements, including height restrictions or specialized construction standards, making it vital to research your jurisdiction’s specific rules to prevent compliance issues and project setbacks.
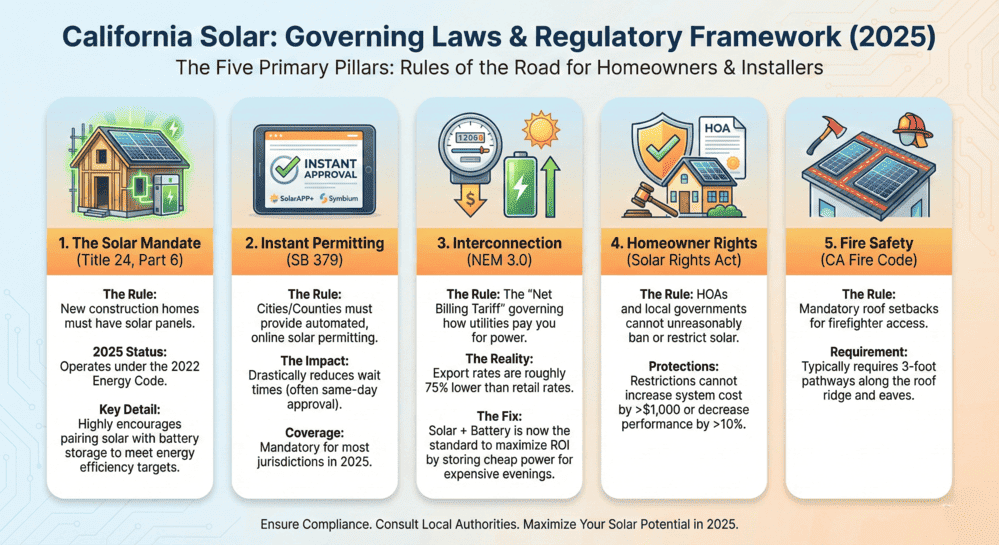
Quick Reference Summary
| Law/Regulation | Core Requirement | 2025 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Mandate (Title 24, Part 6) | New construction homes must include solar PV | Operating under 2022 code; 2025 code (with battery mandate) takes effect Jan 1, 2026 |
| Instant Permitting (SB 379) | Cities/counties must provide automated online solar permitting | All non-exempt jurisdictions should be compliant |
| Net Billing Tariff (NEM 3.0) | Export compensation based on avoided cost rates | ~75% lower export rates make battery storage essential |
| Solar Rights Act (Civil Code 714) | HOAs cannot unreasonably restrict solar installations | Restrictions limited to $1,000 cost increase or 10% efficiency reduction |
| Fire Safety (CRC R324) | Mandatory roof setbacks and pathways for firefighter access | Setbacks vary by array coverage; rapid shutdown required |
1. The California Solar Mandate (Title 24, Part 6)
California became the first state to mandate solar on new construction. Under the California Building Standards Code (Title 24), specifically Part 6 (Energy Code), all new residential builds, including single-family homes (SFH), low-rise multifamily buildings (up to 3 stories), and Accessory Dwelling Units (ADUs), must include a solar PV system sized to offset the home’s projected annual electrical usage.
Key Requirements:
- System sizing is calculated based on conditioned floor area and climate zone
- The solar mandate has applied to new residential construction since January 1, 2020
- Commercial buildings, high-rise residential, and schools were added to the mandate in 2023
2025 Code Transition: The 2022 Energy Code remains in effect through December 31, 2025. The 2025 Energy Code takes effect January 1, 2026 and introduces significant changes:
| Code Version | Battery Storage Requirement | Effective Period |
|---|---|---|
| 2022 Code | Incentivized (25% PV reduction with 7.5kWh+ battery) | Jan 1, 2023 – Dec 31, 2025 |
| 2025 Code | Mandatory for buildings with required PV | Jan 1, 2026 forward |
Exemptions:
- Homes with excessive roof shading or insufficient solar access
- Properties where roof area cannot accommodate minimum system size
- Seasonal properties lacking basic utilities for year-round occupancy
- Homes that participate in qualifying community solar programs as an alternative
2. The Instant Permit Law (Senate Bill 379)
Passed to eliminate the “solar bottleneck,” SB 379 (Wiener, 2022) requires most California cities and counties to implement an automated, online permitting platform for residential solar and energy storage systems. The platform must verify code compliance and issue permits in real time.
How It Works: Instead of waiting weeks for a plan check, installers enter system specifications into an approved portal (such as SolarAPP+ or Symbium). If the design meets code requirements, the permit is issued instantly, often within minutes rather than weeks.
Compliance Deadlines (All Passed):
| Jurisdiction Type | Population Threshold | Compliance Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| Large cities | 50,000+ | September 30, 2023 |
| Large counties | 150,000+ | September 30, 2023 |
| Smaller cities | 5,000 – 50,000 | September 30, 2024 |
| Small cities | Under 5,000 | Exempt |
| Small counties | Under 150,000 | Exempt |
Platform Options:
- SolarAPP+ – Free platform developed by NREL and the U.S. Department of Energy
- Symbium – Alternative automated permitting platform
- Custom platforms – Jurisdiction-developed systems meeting SB 379 requirements
2025 Status: By 2025, virtually all non-exempt jurisdictions should be compliant. If your local building department still requires paper plans and multi-week reviews for a standard residential retrofit, they may be in violation of state law. You can verify your jurisdiction’s compliance status on the CEC’s SB 379 Dashboard.
3. Net Billing Tariff (NEM 3.0)
The most significant shift in California’s solar financial landscape is NEM 3.0, officially called the Net Billing Tariff (NBT), which took effect April 15, 2023. This policy applies to customers of the three investor-owned utilities: PG&E, SCE, and SDG&E.
The Fundamental Change: Under NEM 2.0, homeowners sold excess power to the grid at retail rates (typically $0.30–$0.45/kWh). Under NEM 3.0, export compensation is based on “avoided cost” rates calculated through the Avoided Cost Calculator (ACC), which averages approximately 75% less than retail rates.
Export Rate Structure:
| Factor | Detail |
|---|---|
| Rate Basis | Avoided Cost Calculator (ACC), not retail rates |
| Rate Variations | 576 different rate combinations (by hour, day type, and month) |
| Typical Midday Rate | $0.04–$0.08/kWh (when solar production peaks) |
| Peak Evening Rate | Up to $2.00–$3.50/kWh (4–9 PM, summer months) |
| Average Reduction | ~75% lower than NEM 2.0 retail-rate compensation |
The Strategic Response: This framework makes battery storage essential for maximizing ROI. The goal is no longer to export power during midday (when rates are lowest), but to:
- Store excess daytime production in batteries
- Use stored energy during expensive evening peak hours (4–9 PM)
- Export strategically during high-value windows when rates can exceed retail
Battery Attachment Rates: Since NEM 3.0 took effect, battery attachment rates have surged from approximately 11% to over 50% of new installations, with some installers reporting 60–90% attachment rates.
Grandfathering & Lock-In:
- NEM 1.0/2.0 customers retain their rates for 20 years from interconnection date
- NEM 3.0 customers lock in ACC export rates for 9 years from Permission to Operate (PTO)
- PG&E and SCE customers receive ACC Plus adders (extra export compensation) that decrease 20% annually through 2028
- Adding battery storage to an existing NEM 2.0 system does not trigger a switch to NEM 3.0
Who NEM 3.0 Does NOT Apply To:
- LADWP customers (Los Angeles Department of Water and Power)
- SMUD customers (Sacramento Municipal Utility District)
- Other municipal utility customers operating under separate net metering rules
4. The Solar Rights Act (Civil Code 714)
The Solar Rights Act is the homeowner’s legal shield. Codified in California Civil Code Sections 714 and 714.1, it prevents Homeowners Associations (HOAs) and local governments from enforcing restrictions that effectively prohibit or unreasonably restrict solar energy system installations.
Core Protection: Any covenant, restriction, or HOA rule that “effectively prohibits or restricts” solar installation is void and unenforceable under California law.
What Counts as “Reasonable”: An HOA may impose restrictions only if they meet both of the following thresholds:
| Restriction Type | Maximum Allowable Impact |
|---|---|
| Cost Increase | No more than $1,000 added to system cost |
| Efficiency Reduction | No more than 10% decrease in system output |
Example: An HOA can request that panels be moved to a less visible roof slope, but only if that relocation doesn’t add more than $1,000 to the project cost or reduce energy production by more than 10%. If either threshold is exceeded, the restriction is legally unenforceable.
Timeline Protection: HOAs have only 45 calendar days to approve or deny a solar installation application. If the HOA fails to respond within this window, the application is automatically deemed approved.
Condo & Common Area Protections (Civil Code 714.1 and §4600):
- HOAs cannot require a membership vote to approve solar installations on common area roofs where the owner resides
- Solar installations are explicitly exempt from the typical 67% member approval requirement for exclusive use of common areas
- Condo owners can install solar on their rooftop, or an adjacent garage or carport assigned to them, without HOA prohibition
What HOAs CAN Require:
- Proof of liability insurance (but coverage amounts must be reasonable)
- Licensed contractor installation
- Compliance with building codes and permit requirements
- Reasonable aesthetic guidelines that don’t exceed the $1,000/10% thresholds
5. Fire Safety & Setbacks (California Residential Code R324)
Safety compliance is non-negotiable. The California Residential Code (CRC) Section R324 dictates how solar panels must be laid out to ensure firefighters can access the roof for ventilation operations during a fire emergency.
Pathway Requirements: Clear pathways allow firefighters to move across the roof and access ventilation points.
| Requirement | Specification |
|---|---|
| Minimum pathway width | 36 inches (914 mm) |
| Number of pathways | At least two pathways on separate roof planes, from eave to ridge |
| Location | At least one pathway on the street or driveway side of the roof |
| Surface | Over areas capable of supporting firefighter weight |
Ridge Setback Requirements: The required setback from the roof ridge varies based on how much of the roof is covered by the solar array:
| Array Coverage | Required Ridge Setback (Both Sides) |
|---|---|
| ≤33% of roof area | 18 inches minimum |
| >33% of roof area | 36 inches minimum |
| With NFPA 13D Sprinkler System: | |
| ≤66% of roof area | 18 inches minimum |
| >66% of roof area | 36 inches minimum |
Exemptions:
- Flat roofs (slope of 2:12 or less) are exempt from setback and pathway requirements
- Detached non-habitable structures (garages, carports, solar trellises, shade structures) are exempt from roof access requirements
- Fire code officials may waive requirements where they determine rooftop operations will not be employed
Array Size Limits:
- Maximum array dimensions: 150 feet × 150 feet in either axis
- Larger installations must include smoke ventilation pathways between array sections
Rapid Shutdown Requirements (NEC 690.12): All grid-tied solar systems must include rapid shutdown capability to de-energize array conductors in an emergency:
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
| Initiation | Rapid shutdown must activate within 30 seconds of initiator activation |
| Controlled conductors | All conductors more than 3 feet from the array must be reduced to 30V or less within 30 seconds |
| Array conductors | Conductors within the array boundary must be reduced to 80V or less within 30 seconds |
| Technology | Typically achieved through module-level power electronics (MLPEs), either microinverters or DC optimizers with rapid shutdown capability |
Labeling Requirements:
- Reflective, weather-resistant warning labels required on all DC conduit, junction boxes, disconnects, and combiner boxes
- Labels must read “WARNING: PHOTOVOLTAIC POWER SOURCE” in white letters (minimum 3/8″ height) on red background
- Main service disconnect must have clearly visible PV system warning label
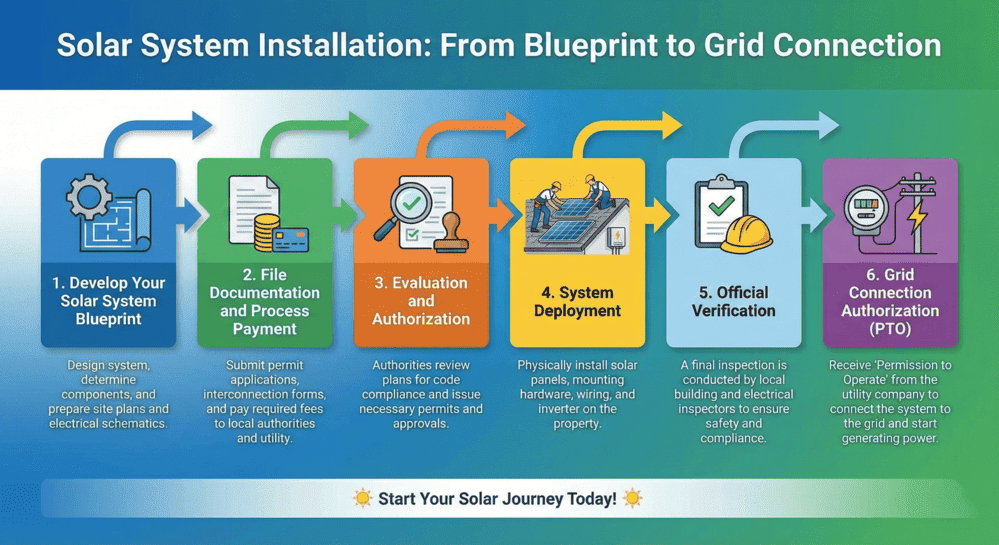
Solar Installation Permit Acquisition Steps
Obtaining authorization for solar energy system installation follows a structured progression. Initially, your installer conducts a comprehensive property assessment, evaluating roof direction, pitch angle, and structural capacity. Next, the installer develops complete plan sets featuring structural engineering drawings, electrical schematics, and system configuration details. These documents undergo submission to your local building authority or municipal department for evaluation.
Reviewing officials verify plan compliance with applicable building standards, electrical requirements, and relevant ordinances. Many municipalities now offer accelerated review tracks for residential solar applications, expediting approval timelines. Upon successful plan review, the jurisdiction grants permit authorization, clearing the path for installation commencement. Post-installation, a final compliance inspection confirms adherence to all local code provisions. Passing this inspection authorizes grid interconnection and system activation.
Breaking Down Each Phase for Complete Clarity
Step 1: Develop Your Solar System Blueprint
Beginning the permit process requires creating a comprehensive design for your solar panel array. This phase involves partnering with a licensed solar contractor who evaluates your property or rooftop and develops an installation strategy. Your design must align with local construction standards, California’s Title 24 regulations, and electrical code requirements.
Critical Factors:
- Structural capacity: Your rooftop must handle the solar panel weight without compromise.
- Power requirements: System sizing should correspond to your household or business energy usage.
- Safety regulations: California enforces rigorous fire safety standards for solar deployments, particularly regarding equipment positioning and clearance spacing.
Step 2: File Documentation and Process Payment
After finalizing your system blueprint, your contractor submits required paperwork to the municipal building authority for examination. Standard application packages contain:
- Engineering drawings: Confirming the roof structure can securely accommodate the panels.
- Electrical schematics: Outlining wiring configurations, inverter specifications, and additional electrical elements.
- Processing costs: Permit expenses fluctuate by location but generally fall between $100 and $500.
Most jurisdictions provide preliminary feedback within several weeks. Nevertheless, variables such as project complexity or seasonal application volume may extend response times.
Step 3: Evaluation and Authorization
Local officials examine your permit submission, verifying conformity with municipal, state, and federal requirements. This evaluation period spans from one day (when utilizing expedited platforms like SolarAPP+) to multiple weeks for intricate projects.
Throughout this phase, authorities may request supplementary documentation or design adjustments to meet particular code provisions. Though this might appear challenging, responding quickly to official inquiries prevents timeline extensions. For complex projects, consider professional permit expediting services to streamline the approval process.
Step 4: System Deployment
Following permit approval, installation work commences. Your licensed contractor mounts solar panels, inverter equipment, and other essential hardware. Installation typically requires 1 to 3 days, varying with system scale and project intricacy.
Throughout this phase, your contractor guarantees every component follows approved specifications while maintaining rigorous safety standards. For those interested in DIY solar installations, understanding permitting requirements becomes even more critical.
Step 5: Official Verification
Post-installation, your solar array undergoes one or multiple inspections conducted by local building officials. These examinations are essential for confirming the installation satisfies all safety protocols and construction code mandates.
Step 6: Grid Connection Authorization (PTO)
After your system clears inspection requirements, the concluding phase involves securing Permission to Operate (PTO) from your utility provider. This authorization enables you to interconnect your solar installation with the electrical grid and begin power generation. Understanding supply-side and load-side interconnection options helps ensure proper grid connection. Note that utility companies may conduct their own system evaluation or review process.
At this stage, your solar array becomes operational, allowing you to harness the advantages of clean, sustainable energy production according to international renewable energy standards.
Solar Permit Approval Timeframes
Solar permit processing durations across California fluctuate depending on installation scale, project complexity, and jurisdictional procedures. Typically, residential solar system permitting spans one to eight weeks. Straightforward, smaller installations generally progress faster through approval channels due to reduced technical complexity, whereas larger or intricate projects demand extended evaluation periods. Municipalities implementing streamlined authorization protocols often accelerate application processing, with certain jurisdictions providing fast-track reviews for compact residential arrays.
Local building department workload backlogs can substantially prolong approval schedules. Projects incorporating new construction elements or major structural alterations frequently encounter additional waiting periods stemming from heightened documentation requirements or multiple approval stages. Beyond permit issuance, installation execution and inspection verification consume further time. Recognizing these timeline variables and initiating the permit process promptly helps property owners prevent setbacks in activating their solar energy systems.
State Regulations vs Municipal Requirements
California operates under a dual-layer regulatory framework combining statewide mandates with local governance provisions for solar permitting. State legislation, including the California Solar Mandate, obligates all newly constructed residential properties to incorporate solar panels while establishing foundational safety and energy efficiency benchmarks. Concurrently, individual municipalities and counties enforce their distinct building standards, zoning ordinances, and supplementary criteria affecting solar developments.
Local authorities may institute height limitations, architectural design standards, or specialized fire safety protocols, particularly throughout wildfire-susceptible zones. While state policy promotes solar deployment, municipal jurisdictions retain authority over permit review and project-specific approval decisions. Comprehending local permitting regulations before project initiation proves critical for ensuring compliance. Certain cities extend expedited permitting options for small residential installations, whereas others maintain more stringent qualification criteria. Successfully navigating both state and municipal regulatory layers remains fundamental to achieving seamless solar installation outcomes.
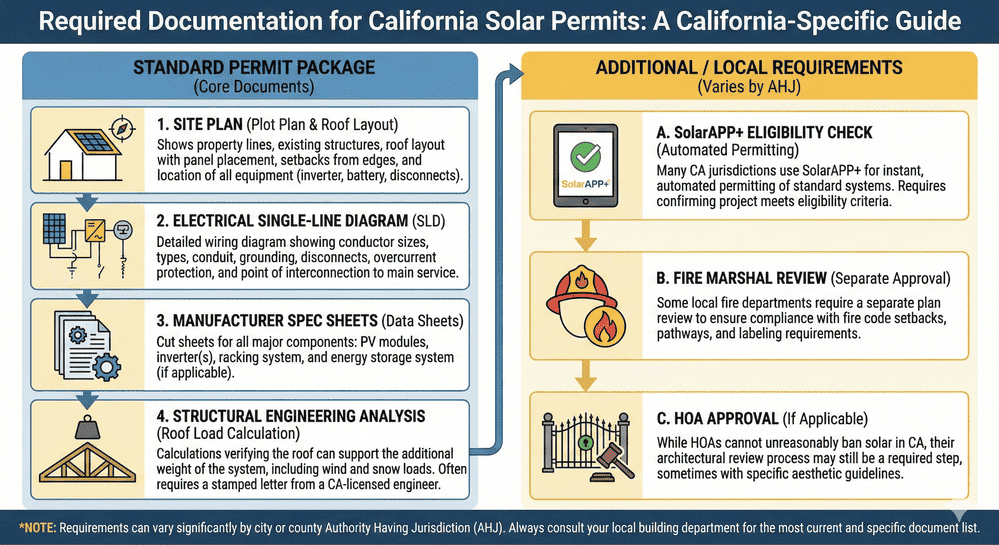
Required Documentation for California Solar Permits
Securing a solar permit in California necessitates submitting specific documentation to verify adherence to municipal building standards, safety protocols, and energy compliance regulations. These materials enable local officials to evaluate installation proposals and confirm system safety and performance:
1. Permit Application Package: This submission contains vital property details, solar system specifications, and owner information. Jurisdictions accept applications through online portals or physical office submission.
2. Property Layout Diagram: A comprehensive property map indicating solar panel placement on rooftop or ground locations. Required elements include roof measurements, panel positioning, and potential obstacles like chimneys, ventilation structures, or vegetation that could impact deployment.
3. Rooftop Schematic: A roof blueprint featuring dimensional specifications and proposed solar array locations. This enables inspectors to confirm rooftop suitability for the planned installation.
4. Electrical System Blueprints: A technical diagram illustrating how solar panels integrate with the building’s electrical infrastructure. Documentation must specify inverter positioning, wire routing, and protective devices, including circuit breakers. Learn more about supply-side connections for proper electrical integration.
5. Structural Load Assessment: An evaluation from a certified engineer validating the roof’s capacity to bear solar panel weight plus mounting hardware. This verification proves particularly critical for aging or unconventional structures.
6. Equipment Technical Documentation: Manufacturer-supplied information for solar panels, inverters, and ancillary system components. Contents include product models, performance metrics, and warranty coverage for each element.
7. Energy Standards Verification Documentation confirming system compliance with California’s energy performance requirements, including Title 24 provisions. Contractors or energy specialists typically prepare these forms, demonstrating the installation achieves efficiency objectives aligned with Energy Star guidelines.
8. Processing Fee Confirmation: Evidence of solar permit fee payment, which fluctuates based on jurisdiction and installation capacity. This charge covers application processing expenses and mandatory inspection services.
9. Site Photography: Visual documentation of the property, focusing on rooftop areas designated for panel installation. These images assist inspectors in evaluating roof condition and identifying potential installation obstacles or challenges.
10. Inspection Protocol Summary: An outline of inspection procedures, including scheduling logistics and assessment scope (such as structural integrity, electrical connections, and panel mounting). Applicants may need to furnish supplementary materials or provide property access for inspection activities.
This documentation collection guarantees safe and proper solar system integration into building structures and electrical networks while accelerating permit approval. Specific requirements differ among local jurisdictions, making it essential to consult your municipal permitting office for precise guidelines. For comprehensive support, explore our solar design services.
Solar Permitting Cost Structure
Securing a solar permit in California involves expenses that fluctuate considerably based on installation magnitude and technical complexity. Residential solar projects typically encounter permit costs between $100 and $500, though larger systems or those requiring supplementary authorizations or inspections may exceed this range. Commercial solar deployments generally face elevated permitting expenses due to project scale and intricacy.
Additional charges may apply for plan examination, inspection services, and electrical grid interconnection. Jurisdictions impose varying fee structures influenced by geographic location and regional living expenses. For instance, metropolitan or higher-income areas often maintain steeper fee schedules. Property owners should also factor in potential charges associated with energy storage or battery installations, as these components frequently necessitate separate permits and verification procedures.
Homeowners must incorporate these expenses into their solar project budget to prevent unexpected financial obligations. Certain circumstances allow fee waivers or reductions for low-income households or nonprofit entities. To learn about federal incentives, visit the Department of Energy’s solar tax credit guide.
California Solar Permit Fee Breakdown
Local jurisdictions throughout California establish solar permitting fees that vary based on project scope and geographic positioning. Smaller residential installations commonly encounter permitting charges ranging from $200 to $600. Larger commercial arrays or projects incorporating additional infrastructure like energy storage face higher cost thresholds.
Permit expenses typically comprise multiple elements: building authorization fees, electrical permit charges, and costs tied to inspection or administrative procedures. Particular municipalities or counties levy plan review charges, creating an additional expense homeowners must anticipate. Furthermore, utility providers may assess interconnection fees for grid connection, contributing to total installation costs.
California residents can contact their local permitting offices to obtain itemized cost breakdowns specific to their jurisdiction. Some authorities provide fee reductions or exemptions for low-income residents, promoting solar energy accessibility in underserved neighborhoods.
Post-Installation Verification Requirements
Following solar system deployment, inspections verify compliance with safety protocols and regulatory standards. Inspectors evaluate electrical connections, structural soundness, and overall safety measures. The verification process confirms system adherence to local building codes and alignment with approved permit plans.
Should inspectors identify issues such as improper wiring or missing safety components, installers must rectify problems before reinspection. Upon passing inspection, the solar system receives grid connection authorization and can commence energy production. Significant deficiencies may result in inspection failure, requiring additional work or modifications before approval.
Post-installation inspections prove essential for confirming proper solar system operation and safety compliance, protecting both property and occupants. For sustainable building practices, consult Green Building Advisor resources.
Net Metering and Grid Connection Process
California’s Net Energy Metering (NEM) program enables homeowners and businesses with solar installations to earn credits for surplus electricity returned to the grid. This mechanism helps solar adopters offset electricity consumption expenses. Accessing net metering benefits requires completing a utility interconnection process, which involves submitting applications to local utility providers for grid connection authorization.
Utilities examine system specifications to verify technical standard compliance and confirm grid safety compatibility. Interconnection represents a critical permitting component, allowing solar systems to function as renewable energy sources contributing to statewide power supply. California utility companies may charge interconnection processing fees, though these costs remain relatively modest.
Solar customers must comprehend both net metering costs and benefits to ensure financially viable installations. For technical guidance on renewable energy systems, refer to IEEE renewable energy resources.
Permit Validity and Extension Procedures
California solar permits maintain validity periods spanning 180 days to one year. Projects incomplete within designated timeframes face permit expiration. Expired permits require renewal applications or reissuance, potentially involving updated plan submissions or supplementary documentation.
Extended time lapses may necessitate site reinspection to verify current code and standard compliance. Renewal needs arise from various circumstances, including construction schedule delays or project modifications. Homeowners and contractors should monitor permit expiration dates to prevent unnecessary complications.
Local permitting authorities may grant extensions under certain conditions, requiring appropriate paperwork submission. Maintaining proactive timeline awareness and understanding expiration and renewal regulations helps avoid installation process disruptions.
Battery Storage System Permitting
Growing solar energy adoption drives increasing interest in solar battery storage systems for excess power retention. California frequently mandates separate permits for these systems due to complexity and specific safety standard requirements. Battery storage installations fall under electrical and fire safety code governance, ensuring proper and secure implementation.
Local jurisdictions maintain specific battery system guidelines that vary regionally. Wildfire-prone areas may impose additional requirements for fire-resistant materials and battery spacing specifications. Solar storage permit acquisition typically involves submitting separate applications detailing battery specifications, capacity, and installation methodology.
Local authorities may conduct post-installation inspections verifying safety regulation compliance. With expanding energy storage integration into solar projects, understanding permitting procedures for these systems prevents project delays. For off-grid solar system design with battery storage, specialized permitting knowledge becomes essential.
Solar Permitting Obstacles
Despite California’s substantial progress promoting solar energy, the permitting process encounters persistent challenges. Common difficulties include local regulation complexity and inconsistency. Individual cities or counties maintain slightly divergent requirements, complicating navigation for homeowners or businesses.
Certain regions experience extended permit approval waiting periods due to bureaucratic backlogs, delaying solar installations. Larger commercial projects face heightened permitting complexity, demanding extensive documentation, detailed planning, and multiple inspections. Additionally, utility interconnection challenges and safety regulation compliance create further delays.
Permit acquisition costs, particularly for energy storage projects, may become prohibitively expensive for some property owners. Despite these obstacles, California maintains its solar energy adoption leadership through continued commitment to reducing barriers and promoting solar power as a clean energy solution, contributing to global renewable energy goals.
Process Optimization Initiatives
California has implemented multiple measures to streamline permitting procedures and encourage broader solar energy adoption. Notable developments include expedited permitting protocols for small residential systems, reducing approval timelines and simplifying homeowner solar installation initiation.
Many jurisdictions utilize the California Solar Permitting Guidebook, providing standardized procedures for municipalities and counties, ensuring statewide permitting consistency. Online permitting platform implementation has simplified application submission and permit progress tracking for residents. These modifications have reduced delays and simplified paperwork requirements for solar projects.
State-level initiatives, including the SB 700 (2017) legislation, mandate simplified permitting for certain small-scale systems, including battery storage installations. Through continued innovation and procedural streamlining, California aims to enhance solar power accessibility for all residents, aligning with American Solar Energy Society standards.
Conclusion
While California’s solar permitting process involves complexity, it fulfills crucial roles ensuring safety, compliance, and efficiency for solar energy systems. Without proper permitting, solar installations might fail to meet building codes or electrical safety standards, creating risks for property owners and broader communities.
Adhering to permitting procedures ensures California solar energy systems receive correct and safe installation, aligning with state renewable energy objectives and EPA green power initiatives. The state’s ongoing efforts to streamline permitting procedures will enhance solar power accessibility and affordability, benefiting homeowners, businesses, and environmental sustainability through this clean energy source. Despite existing challenges, navigating the permitting process remains vital for anyone contributing to California’s renewable energy future.
Need expert assistance with your solar permit application? Visit Solar Permit Solutions for professional support, contact our team directly, or explore our comprehensive blog resources for more guidance on California solar permitting.
FAQs
Do I need a permit to install solar panels in California?
Yes, obtaining a permit is mandatory for all solar panel installations in California, whether residential or commercial. Permits ensure your solar system complies with local building codes, electrical safety standards, and zoning regulations. Most installations require both a building permit (verifying structural capacity) and an electrical permit (confirming proper wiring and component installation). Attempting to install solar panels without proper permits can result in fines, forced system removal, insurance coverage denial, and potential safety hazards. Working with a licensed solar contractor helps navigate the permitting requirements specific to your jurisdiction.
How long does the solar permitting process take in California?
The solar permitting timeline in California typically ranges from one to eight weeks for residential systems, though this varies significantly by jurisdiction and project complexity. Smaller, straightforward installations generally receive faster approval, while larger or more complex projects require extended review periods. Jurisdictions implementing expedited processes like SolarAPP+ can issue permits within hours or days. However, local building department backlogs, incomplete documentation, or projects involving new construction or structural modifications may extend timelines considerably. Starting the permit application process early and submitting complete, accurate documentation helps minimize delays.
What are the typical costs for solar permits in California?
Solar permit costs in California vary by jurisdiction and project scale. Residential installations typically encounter fees ranging from $100 to $600, with most falling between $200 and $500. Commercial projects generally face higher costs due to increased complexity and scale. Permit expenses usually include multiple components: building permit fees, electrical permit fees, plan review charges, and inspection costs. Additional fees may apply for energy storage systems or utility grid interconnection. Some jurisdictions offer fee reductions or waivers for low-income residents or nonprofit organizations. Contact your local permitting authority for specific fee schedules in your area.
What happens if my solar permit expires before installation is complete?
California solar permits maintain validity periods ranging from 180 days to one year, depending on the jurisdiction. If your project remains incomplete within this timeframe, the permit expires and requires renewal or reissuance. Renewal typically involves submitting updated plans or documentation, and extended time lapses may necessitate site reinspection to verify current code compliance. Permit expiration can result from construction delays, project modifications, or scheduling complications. Monitoring expiration dates closely and communicating with your contractor helps prevent unnecessary complications. Some jurisdictions grant extensions through appropriate paperwork submission, though approval is not guaranteed.
Do I need a separate permit for solar battery storage systems?
Yes, solar battery storage systems in California frequently require separate permits due to their complexity and specific safety requirements. Battery installations fall under both electrical and fire safety code regulations, with requirements varying by jurisdiction. Wildfire-prone regions may impose additional mandates for fire-resistant materials and specific battery spacing. The battery storage permitting process involves submitting separate applications detailing battery type, capacity, and installation methodology. Post-installation inspections verify safety regulation compliance. As energy storage integration expands, understanding these distinct permitting requirements prevents project delays and ensures proper system installation.