Solar utility inspection requirements mandate that all solar installations undergo government and utility company inspections before grid connection. Property owners need three primary permits: electrical permits for code compliance, structural permits for load-bearing verification, and solar photovoltaic permits for system specifications.
Residential installations cost $200-$500 for permitting, while utility-scale projects require $1,000+ and 6-12 months for approval.
The inspection process occurs in two phases. Pre-installation inspections verify electrical system capacity and structural integrity to support solar panel weight.
Post-installation inspections confirm building code compliance and safety regulations before utility companies grant permission to operate (PTO). Utility-scale installations face additional requirements including environmental impact assessments, grid interconnection studies, and substation equipment evaluations.
Most solar installers handle permitting logistics as part of their service package. Permit requirements vary by location, installation type (rooftop versus ground-mounted), and system size (residential, commercial, or utility-scale).
States like Colorado cap residential permitting at $500 and commercial at $1,000, while California limits residential to $450. The Solar Automated Permit Processing (SolarAPP+) initiative streamlines approvals for certified installers, saving over 33,000 hours of permitting staff time and reducing project timelines by approximately 31% compared to traditional permitting processes.
Understanding Government Authorization For Solar Installation
Solar installation requires obtaining permits from local government authorities for legal authorization. Property owners typically need to secure an electrical permit, a structural permit, and a dedicated solar photovoltaic (PV) permit. These applications require detailed specifications about proposed solar equipment and system design.
Required solar permits vary based on location and the type and size of the solar energy system being installed.
Geographic Variations In Permit Applications
Permitting requirements differ across states and municipalities based on local codes, zoning laws, and solar installation legislation. For instance, electrical permits ensure compliance with state-mandated codes, while fire departments may require specific clearance areas around solar arrays for emergency roof access.
Solar permitting requirements can vary between neighboring properties within the same municipality. Properties in historical districts may require approval from local historical commissions before solar panel installation. Homeowners association properties typically require HOA approval before panel placement.
How System Scale Affects Permit Complexity
Solar permitting requirements scale with the size and type of installation being deployed. Large commercial solar systems require more extensive permitting compared to small residential installations.
Utility-scale solar installations face the most time-intensive and costly permitting processes due to additional regulatory requirements. These large-scale installations occupy significant land area and manage substantial power loads, triggering additional regulations that demand more documentation and extended approval cycles.
Permit requirements also differ between rooftop and ground-mounted installations. Large ground-mounted solar projects may require land use reviews while potentially avoiding building or structural permits required for rooftop systems.
Local zoning laws establish different regulations for ground-mounted installations that impact permitting, including setback distances from property lines and maximum array heights.

Pre-Installation And Post-Installation Compliance Verification
Solar energy systems require inspections both before and after installation to ensure safety and code compliance. Pre-installation inspections verify that existing electrical systems can accommodate solar integration.
For rooftop solar panel systems, structural engineers assess roof integrity to confirm it can support the additional weight of solar panels and racking equipment.
Post-installation, local government building departments conduct final inspections before granting system approval. Inspectors verify that installations meet all building codes and safety regulations.
This inspection must occur before system activation, as utility companies require documented local government approval before solar interconnection to the grid.
Large-Scale Project Evaluation Standards
Utility-scale solar installations face more rigorous inspection requirements due to their size and grid impact. These large-scale projects undergo comprehensive safety evaluations, environmental impact assessments, and grid interconnection studies.
Inspectors examine structural foundations, electrical infrastructure, substation equipment, and power transmission components to ensure reliable operation at scale.
The utility company conducts its own inspection as the final step of the solar interconnection process. After completing this utility inspection, property owners receive permission to operate (PTO), authorizing solar energy system activation and grid connection.
Budget Expectations For Authorization And Compliance
Permitting costs vary widely based on system size and location requirements. Most residential solar panel installations incur permitting and inspection costs of several hundred dollars.
Some states impose regulatory caps on government permitting fees. Colorado limits residential solar permitting to $500 and commercial projects to $1,000, while California caps residential permits at $450 and commercial permits at $1,000.
Many solar installations include permitting costs within turnkey pricing. When solar companies charge comprehensive installation prices, they typically incorporate labor, equipment, interconnection, permitting, and inspection costs.
Property owners can request itemized breakdowns of permitting and inspection expenses or verify fees directly with local government offices.

Solar Permit Solutions
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
Accelerating Approval Timelines With Modern Solutions
The solar permitting and inspection process requires significant time investment that increases overall project costs. To simplify permit acquisition and reduce solar installation expenses, the Solar Energy Industries Association and the Solar Foundation launched Solar Automated Permit Processing (SolarAPP+).
The SolarAPP+ initiative implements several key streamlining elements, including expanded online permitting systems, automated permit approvals for certified installers of smaller solar projects, and standardized equipment requirements for PV systems.
Successful implementation of this streamlined process has already approved over 32,800 projects and saved more than 33,000 hours of permitting staff time, with projects experiencing approximately 31% faster approval timelines compared to traditional permitting processes.
Partner With Knowledgeable Installation Professionals
Selecting the right installer requires evaluating their local installation experience. Solar companies with skilled project managers and extensive regional experience understand permit and inspection requirements specific to system types, local governments, and state regulations.
Solar Permit Solutions connects property owners with experienced solar installers who navigate permitting and inspection processes efficiently. Working with knowledgeable installation professionals ensures smooth project approval and faster system activation timelines.
Conclusion
Navigating solar utility inspection requirements and permitting processes represents a critical phase in any solar installation project. Understanding the specific permits required for different system types, from residential rooftop arrays to large utility-scale installations, helps property owners anticipate timeline requirements and budget appropriately.
While the permitting and inspection process may seem complex, experienced solar installers handle these regulatory requirements as part of their comprehensive service offerings.
The evolution of streamlined permitting systems like SolarAPP+ continues to reduce administrative burdens and accelerate project timelines. Property owners benefit most when partnering with knowledgeable installation professionals who understand local jurisdiction requirements, utility company standards, and inspection protocols specific to their region.
Proper preparation and documentation ensure that solar energy systems meet all safety codes and regulatory standards, enabling faster approval and grid connection. For more insights on solar permitting best practices, visit our solar blog.
FAQs
Some jurisdictions may combine these into a single solar permit, while others require separate applications for each. Property owners should consult with their solar installer to determine exact permit requirements for their location.
Utility-scale projects face substantially longer timelines, often requiring 6-12 months or more due to environmental assessments, land use reviews, and extensive interconnection studies. Final utility inspection and permission to operate usually occurs within 1-2 weeks after installation completion.
Utility-scale inspections also involve multiple regulatory agencies and extensive documentation to ensure reliable operation at scale and grid stability.
DIY permitting requires significant time investment, knowledge of local codes, and ability to prepare detailed electrical and structural plans that meet regulatory standards.
Reputable installers typically resolve these issues quickly at no additional cost to property owners. The system cannot be activated or connected to the grid until it passes final inspection and receives permission to operate from the utility company.
Skip the Permit Headaches
We design plan sets that pass inspection the first time. Code-compliant, PE-stamped, accepted by AHJs nationwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Residential solar installations typically require three main permit types: an electrical permit to verify compliance with electrical codes, a structural or building permit to ensure roof integrity can support panel weight, and a dedicated solar photovoltaic permit specific to solar systems. Some jurisdictions may combine these into a single solar permit, while others require separate applications for each. Property owners should consult with their solar installer to determine exact permit requirements for their location.
The solar permitting and inspection timeline varies significantly by jurisdiction and system size. Residential installations typically complete permitting within 2-4 weeks, though some municipalities offer same-day or next-day approvals for standard systems. Utility-scale projects face substantially longer timelines, often requiring 6-12 months or more due to environmental assessments, land use reviews, and extensive interconnection studies. Final utility inspection and permission to operate usually occurs within 1-2 weeks after installation completion.
Yes, utility-scale solar installations undergo significantly more rigorous inspection processes compared to residential systems. These large-scale projects require comprehensive safety evaluations, environmental impact assessments, grid interconnection studies, and examination of substation equipment and power transmission components. Utility-scale inspections also involve multiple regulatory agencies and extensive documentation to ensure reliable operation at scale and grid stability.
While property owners can technically handle solar permitting independently, most choose to work with professional installers who manage this process. Solar companies have established relationships with local building departments, understand jurisdiction-specific requirements, and know how to prepare compliant permit applications. DIY permitting requires significant time investment, knowledge of local codes, and ability to prepare detailed electrical and structural plans that meet regulatory standards.
If a solar installation fails inspection, the installer must address all identified deficiencies before requesting a re-inspection. Common failure reasons include improper electrical connections, inadequate equipment grounding, code violations, or structural concerns. Reputable installers typically resolve these issues quickly at no additional cost to property owners. The system cannot be activated or connected to the grid until it passes final inspection and receives permission to operate from the utility company.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
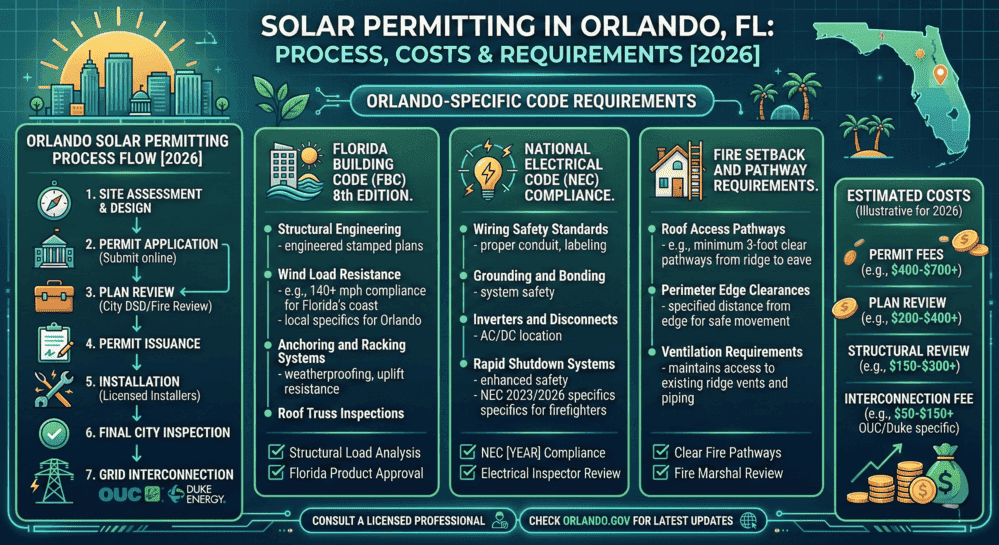
Solar Permitting in Orlando, FL: A Complete Guide for Homeowners & Installers
Solar permitting in Orlando, FL, requires a building permit and an electrical pe...
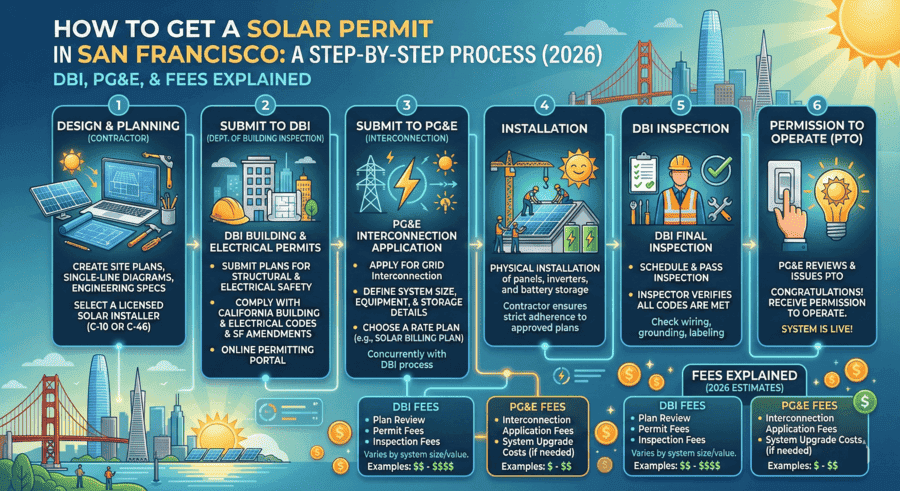
How To Get A Solar Permit In San Francisco: DBI, PG&E And Fees Explained (2026)
San Francisco solar permits require two separate approvals before your system ca...
Bifacial Solar Panel Installation And Permitting Guide
Bifacial solar panels generate 10 to 30 percent more energy than traditional mon...
