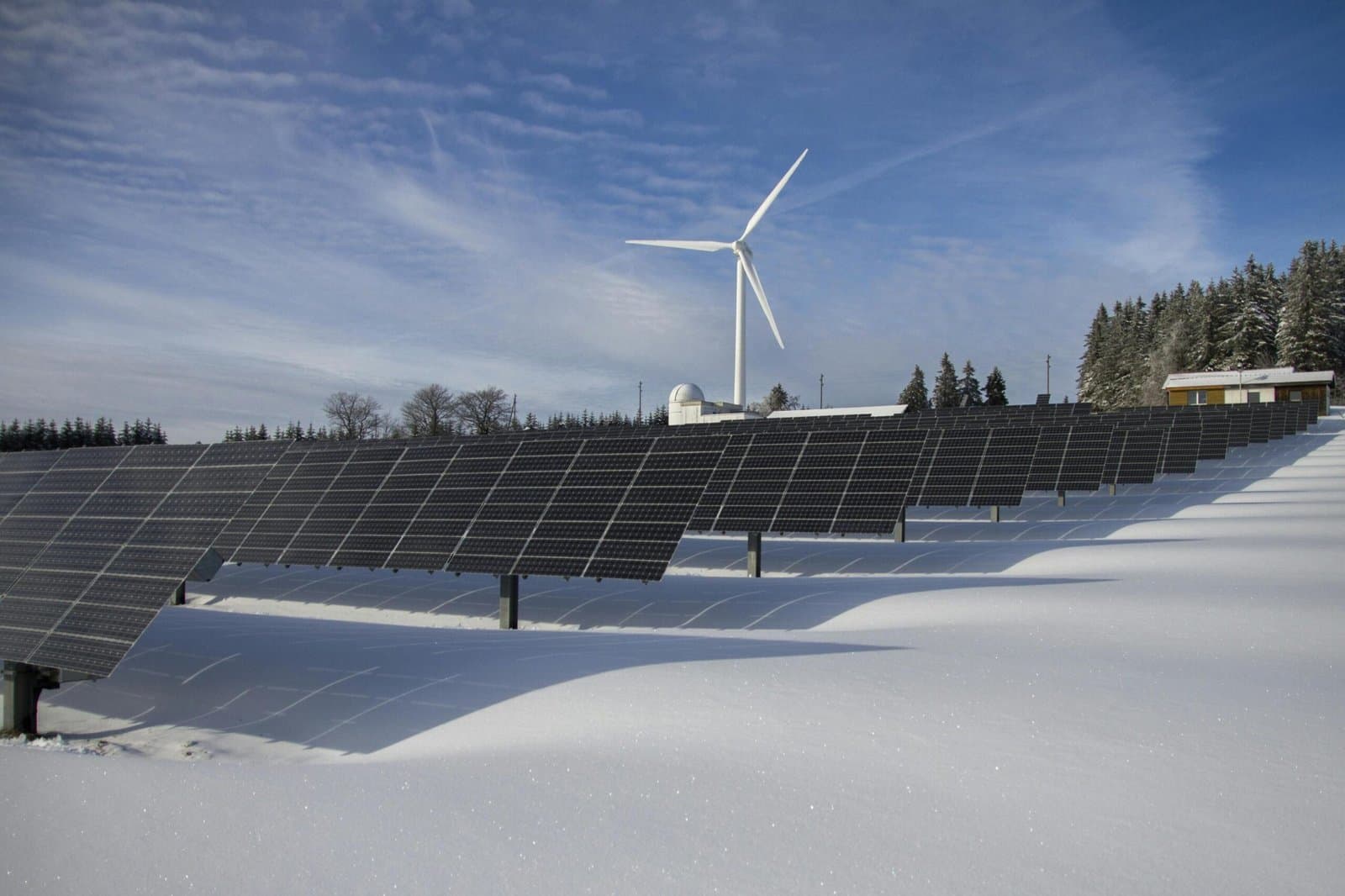
Yes, solar panels work effectively in snowy climates and can even perform better in cold temperatures. While snow accumulation temporarily reduces energy production, properly installed systems with steep panel angles (35-45 degrees) naturally shed snow, and reflected sunlight from snow-covered ground can boost overall output by 10-20%.
Key requirements for snowy climate solar installations include: Monocrystalline panels with snow load capacity of 20-50 pounds per square foot Mounting systems angled at latitude minus 15 degrees (steeper for heavy snowfall areas) Ground-mounted or tilted systems for easier snow shedding and maintenance access Snow guards to prevent dangerous ice sheets from sliding off roofs Regular monitoring systems to detect performance drops from snow coverage
Common challenges and solutions: Snow and ice buildup can block up to 100% of sunlight, but this is temporary. Remove light snow using soft-bristled brushes or specialized snow rakes from ground level. For heavy accumulation, heating systems or micro-inverters minimize individual panel impact. Most snow naturally melts within 1-3 days in temperatures above freezing.
Installation costs and ROI considerations: Snowy climate installations typically cost 10-15% more due to reinforced mounting systems and specialized equipment, but federal tax credits cover 30% of total costs. Winter energy production may decrease 20-40% during heavy snow months, but annual production often matches warmer climates due to increased efficiency in cold temperatures and extended summer daylight hours.
This comprehensive guide covers optimal panel selection, mounting system design, roof preparation, angle optimization, snow removal techniques, and year-round maintenance strategies to maximize your solar investment in winter conditions.

Navigating Winter Installation Obstacles
Setting up solar panels in snowy environments introduces unique hurdles that property owners must address. The primary concern involves managing snow and ice accumulation, which diminishes energy output and may cause equipment damage. Success requires thoughtful system design, strategic installation planning, and selecting appropriate hardware like snow guards and mounting frameworks engineered to shed frozen precipitation.
Snow and Ice Removal Strategies
Implement these approaches for managing winter buildup on your panels:
Deploy a soft-bristled broom: The simplest removal method involves gently sweeping accumulated snow using a broom with soft bristles to prevent panel damage.
Add heating elements: In areas experiencing severe winter conditions, installing heating systems to melt ice and snow proves beneficial. Options include electric heating pads and hot water circulation systems.
Utilize adjustable tilt mechanisms: These systems enable angle adjustments so panels face the sun directly and shed frozen precipitation more effectively, particularly valuable in heavy snowfall zones.
Employ specialized snow rakes: These purpose-built tools safely remove snow from panels without causing harm. Their gentle design allows operation from ground level.
Explore automated cleaning solutions: Certain manufacturers provide self-cleaning mechanisms that use water and mild cleaning agents to eliminate dirt, debris, and snow. These systems effectively maintain panel cleanliness and functionality.
Engineering Systems for Heavy Snow Tolerance
Creating a solar installation capable of withstanding substantial snow loads demands attention to multiple factors. Follow these guidelines to ensure your system handles winter weather:
Select appropriate equipment: When purchasing panels, inverters, and related components, prioritize products engineered for heavy snow loads. Seek items tested and certified for cold-climate operation.
Execute proper installation procedures: Correct installation is fundamental to snow load resistance. Verify that panels are firmly secured to mounting systems or roofing, and all electrical connections receive proper sealing and moisture protection.
Evaluate panel positioning: Panel angle influences snow accumulation patterns. In heavy snowfall zones, install panels at steeper angles to facilitate natural snow shedding.
Choose robust mounting hardware: Panels require secure attachment to roofs or ground structures. Select mounting systems specifically designed to support heavy snow loads.
Selecting Optimal Equipment for Cold Climates
Choosing suitable panels and mounting systems for snowy conditions is critical for maximizing energy production and preventing equipment damage. When evaluating panels, prioritize those with high snow load ratings that withstand heavy ice and snow accumulation. Monocrystalline panels typically deliver superior performance in cold, snowy weather compared to polycrystalline options. For mounting systems, select configurations with steep angles that allow frozen precipitation to slide off naturally. Pole-mounted systems also merit consideration, as they elevate panels above ground level, preventing snow accumulation at the base.
Top Panel Choices for Winter Performance
Consider these panel types when installing in cold climates:
Monocrystalline panels: Manufactured from single silicon crystals, these panels offer exceptional efficiency and durability. They excel in low temperatures and shed snow more readily than alternatives due to their smooth, uniform surfaces.
Polycrystalline panels: Constructed from multiple silicon crystals, these panels cost less than monocrystalline options. Though slightly less efficient, they still perform well in cold weather and manage heavy snow loads effectively.
Thin film panels: Built from photovoltaic material layers on flexible substrates, these panels sacrifice some efficiency for reduced weight and flexibility, advantageous qualities for snow-climate installations where these factors matter.
Bifacial panels: Engineered to capture sunlight from both sides, these panels capitalize on snow reflection in winter conditions. Their smooth surfaces also facilitate easier snow shedding.
Back-contact panels: With electrical contacts positioned on the rear, these panels reduce front-surface damage risk from snow and ice accumulation.
Solar Permit Solutions
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Mounting System Selection for Minimal Buildup
Selecting appropriate mounting hardware is essential for minimizing snow accumulation and preventing damage from heavy loads. Consider these options for snowy regions:
Ground-mount configurations: These systems typically allow easier maintenance access and can be positioned at steeper angles for better snow shedding. They’re also less susceptible to damage from frozen precipitation compared to roof installations.
Adjustable tilt systems: Mounting frameworks that permit panel tilting effectively shed snow and ice. Steep angles prevent accumulation and encourage sliding.
Gapped racking systems: Mounting frameworks with spacing between panels help prevent buildup. Gaps enable snow and ice to slide off more easily, reducing panel weight and preventing damage.
Ballasted systems: These use weights rather than roof penetrations to secure panels. Common in commercial solar applications, they’re effective in snowy conditions as they avoid roof damage and resist winter weather impacts.
Optimizing Winter Panel Angles
To maximize winter energy output, account for the sun’s lower trajectory during cold months. Follow these recommendations for optimal panel positioning:
Determine your latitude: Optimal angles vary by location. Use online tools or a compass to identify your latitude.
Apply the latitude formula: Generally, angle panels at your latitude minus 15 degrees. For instance, at 40 degrees latitude, position panels at 25 degrees (40-15=25). This maximizes winter sun exposure.
Factor in local conditions: While the latitude-minus-15 rule provides a baseline, consider local weather considerations. In heavy snowfall areas, steeper angles may be preferable for better snow shedding.
Consider solar tracking systems: For maximum winter output, explore solar trackers. These devices automatically adjust panel angles to follow the sun’s path throughout the day, significantly boosting winter performance when the sun travels lower across the sky.

Roof Preparation for Winter Installations
Preparing your roof for solar installation in snowy climates ensures safe, secure panel mounting. Start by inspecting your roof to confirm it’s structurally sound and can support panel weight plus snow accumulation. This may require structural reinforcement or repairing existing damage. Next, properly seal your roof to prevent leaks and ice dams that could damage panels and compromise roof integrity. Installing a snow guard system also helps prevent frozen precipitation from sliding off and potentially harming your panels.
Effective Roof Sealing Techniques
Proper roof sealing prevents leaks and ice dams during winter. Implement these steps for effective sealing:
Conduct thorough inspections: Before sealing, examine your roof for damage or wear. Check for missing or damaged shingles, flashing cracks, or other deterioration signs.
Address existing damage: Repair any issues discovered during inspection before sealing. Replace damaged shingles and fix flashing cracks or other material problems.
Ensure proper ventilation: Adequate ventilation prevents ice dam formation. Verify your roof has sufficient airflow to release warm attic air and stop ice dam development.
Install protective membranes: Ice and water shields are protective layers installed beneath shingles to prevent water infiltration. These are particularly crucial in heavy snowfall and ice dam zones.
Seal penetration points: Create watertight seals around all roof penetrations including vents and chimneys. Use quality sealants to prevent water intrusion at these locations.
Consider heating cables: In severe winter areas with ice dam problems, installing roof heating cables helps melt snow and prevent ice dam formation.
Snow Guard System Advantages
Installing snow guards on your roof delivers multiple benefits, especially in heavy snowfall regions. These devices prevent large, dangerous chunks of frozen precipitation from sliding off unexpectedly. Key benefits include:
Enhanced safety: Large ice and snow chunks pose significant hazards when falling unexpectedly. Snow guards retain frozen precipitation on the roof, allowing gradual melting or evaporation, protecting people and property.
Component protection: Sliding snow and ice can damage gutters, vents, and other roof elements. Snow guards prevent this damage, reducing expensive repair needs.
Lower maintenance requirements: When frozen precipitation slides off roofs, it creates ground-level messes requiring frequent cleanup. Snow guards reduce falling snow and ice volume, minimizing maintenance demands.
Improved efficiency: Snow and ice barriers between your roof and sun reduce sunlight reaching panels or HVAC units. Snow guards keep frozen precipitation in place, allowing roof-mounted equipment to operate more efficiently.

Winter System Maintenance
Maintaining your solar installation in snowy conditions ensures continued optimal energy output and equipment condition. The most critical task involves keeping panels clear of snow and ice buildup through manual removal with snow rakes or automated systems like heated mats or robots. Regular performance monitoring helps identify potential issues, such as declining energy production from damaged panels or inverter problems. Additionally, periodic cleaning removes dirt, debris, and melted snow residue that reduces energy output.
Snow and Ice Clearance Methods
Apply these techniques for maintaining clear panels:
Use specialized snow rakes: These tools are specifically designed for safe snow removal from panels without causing damage.
Install heating systems: Place heating elements beneath panels to melt accumulated snow and ice, especially helpful in heavy snowfall areas.
Select appropriate mounting: Choose wind and snow resistant mounting systems with steep angles that allow natural sliding.
Maintain tree trimming: Trees can drop branches or topple during heavy snowfall, risking panel damage. Keep trees trimmed and remove those threatening your panels.
Inspect for damage: After significant snowfall, examine panels for cracks, chips, or other damage potentially caused by falling ice or snow.
Monitoring System Benefits
Investing in solar monitoring systems provides numerous advantages for property owners with panel installations. Key benefits include:
Real-time tracking: Monitor panel performance continuously, viewing energy production, consumption, and grid feedback in real time.
Early problem detection: Identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems, such as production drops indicating faulty panels or inverter issues.
Enhanced efficiency: Discover opportunities to improve energy efficiency by identifying appliances or devices consuming excessive energy, enabling usage adjustments.
Maximized savings: Performance monitoring ensures optimal investment returns. Adjust energy usage to maximize savings and avoid utility bill overpayments.
Remote access: Many systems offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing performance checks from anywhere, anytime, particularly valuable for properties with absent owners.
Conclusion
Solar panels represent a viable and profitable energy solution even in the harshest winter climates. While snow and ice present legitimate challenges, modern solar technology and proper system design have effectively addressed these concerns. The key to success lies in selecting appropriate equipment, particularly monocrystalline panels with adequate snow load ratings and robust mounting systems engineered for winter conditions.
Installation planning proves critical for long-term performance. Steep panel angles between 35-45 degrees facilitate natural snow shedding, while ground-mounted configurations offer easier maintenance access during winter months. Property owners in heavy snowfall regions should prioritize structural considerations, ensuring both roof integrity and mounting systems can withstand combined loads from panels and accumulated precipitation. Understanding proper wire sizing and adhering to NEC installation requirements ensures safe, code-compliant installations that perform reliably throughout winter.
The economic case for winter solar installations remains compelling despite initial cost premiums. While system costs may increase 10-15% for snow-climate modifications, available federal tax incentives offset 30% of total expenses. More importantly, the performance advantages of cold temperatures often compensate for reduced winter production, with annual energy yields matching or exceeding warmer climate installations. The efficiency gains from lower operating temperatures, combined with extended summer daylight hours at higher latitudes, create surprisingly favorable conditions for solar energy generation.
Maintenance requirements, though more demanding than mild-climate installations, remain manageable with proper planning. Regular monitoring allows early detection of snow-related performance issues, while safe removal techniques preserve panel integrity. Property owners uncomfortable with rooftop work should engage professional assistance rather than risk injury or equipment damage. Safety must always remain the paramount concern when working around snow-covered panels and slippery roof surfaces.
Whether pursuing residential projects, commercial installations, or off-grid configurations, winter climate considerations should inform every phase of project development. Working with experienced installers who understand regional weather patterns and local building codes ensures optimal system performance. For comprehensive guidance on residential solar design tailored to cold climates, professional consultation addresses site-specific challenges. Those exploring off-grid solar system design face additional complexity in winter, requiring careful battery sizing and backup power planning. Advanced energy storage solutions, including LiFePO4 battery packs, provide reliable winter backup while withstanding cold temperature extremes better than traditional battery chemistries.
Understanding DIY solar insurance and liability risks becomes especially important in snowy climates where winter conditions increase maintenance hazards and potential property damage. Proper insurance coverage protects against unique winter risks including roof damage from ice dams, structural failures from snow loads, and personal injury during snow removal activities. The transition to solar energy in snowy climates requires commitment to proper design, quality equipment, and ongoing maintenance. However, thousands of successful installations across northern regions demonstrate that winter weather need not deter solar adoption. With appropriate preparation and realistic expectations, property owners in cold climates can harness solar power effectively while contributing to renewable energy goals.
For additional guidance and resources on winter solar installations, explore our comprehensive blog covering technical topics and best practices. Discover essential solar energy books to deepen your understanding of system design and winter optimization strategies. Professional solar services can navigate the complexities of cold-climate installations, ensuring your system delivers optimal performance year-round while meeting all safety and building code requirements.
FAQs
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, solar panels can work effectively in winter and snowy climates. In fact, solar panels often perform better in cold temperatures because excessive heat can reduce their efficiency. While snow accumulation can temporarily block sunlight, properly angled panels allow snow to slide off naturally. Additionally, snow on the ground can reflect sunlight onto your panels, potentially increasing energy production. The key is to ensure your system is designed with appropriate angles, quality equipment, and proper maintenance protocols to handle winter conditions.
The frequency of snow removal depends on your local weather conditions and panel angle. Panels installed at steep angles (typically 35 degrees or more) often shed snow naturally without intervention. For lighter snowfall, waiting for natural melting is usually sufficient. However, after heavy snowfall or when snow has compacted into ice, manual removal may be necessary to restore energy production. Monitor your system's performance regularly—if you notice a significant drop in energy output after a snowstorm, it's time to clear your panels. Always prioritize safety and consider hiring professionals for removal if you're uncomfortable working on your roof.
Quality solar panels are designed to withstand significant weight and are tested to handle snow loads typical for their intended climate zones. Most panels can support 20-50 pounds per square foot, which exceeds normal snow accumulation in most regions. However, proper installation is crucial—your mounting system and roof structure must also be engineered to handle combined weight from panels and snow. If you live in an area with exceptionally heavy snowfall, inform your installer during the design phase so they can select panels with higher snow load ratings and reinforce mounting systems accordingly.
While you can safely remove light snow yourself using proper techniques and tools, certain situations warrant professional assistance. Safe DIY removal involves using a soft-bristled brush or specialized solar panel snow rake from ground level—never climb onto a snow-covered roof, use metal tools, or apply hot water, which can crack panels. If your panels are difficult to reach, snow has turned to thick ice, or you're uncomfortable with the task, hiring professionals is the safer choice. Professional services have appropriate equipment, safety gear, and insurance to handle the job without risking injury or equipment damage.
Yes, several modifications and equipment choices optimize solar installations for snowy climates. First, select panels with high snow load capacity, preferably monocrystalline panels that shed snow more easily due to their smooth surface. Choose mounting systems that allow steep angles (35-45 degrees) for natural snow shedding. Consider ground-mounted systems for easier access and maintenance. Additional helpful equipment includes snow guards to prevent dangerous sliding, heating systems or cables to melt ice, micro-inverters to minimize shading impacts, and monitoring systems to track performance. Your installer should assess your specific climate conditions and recommend appropriate equipment during the design phase.
Ice dams can potentially affect your solar panel system and overall roof integrity. Ice dams form when heat escapes through your roof, melting snow that refreezes at the roof's edge, creating barriers that trap water. This trapped water can seep under shingles and damage your roof structure, potentially compromising your solar panel mounting system. To prevent ice dams, ensure proper attic insulation and ventilation, install ice and water shield membranes under shingles, and consider heating cables in problem areas. Properly sealed roof penetrations from solar installations are also essential to prevent water infiltration during ice dam events.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
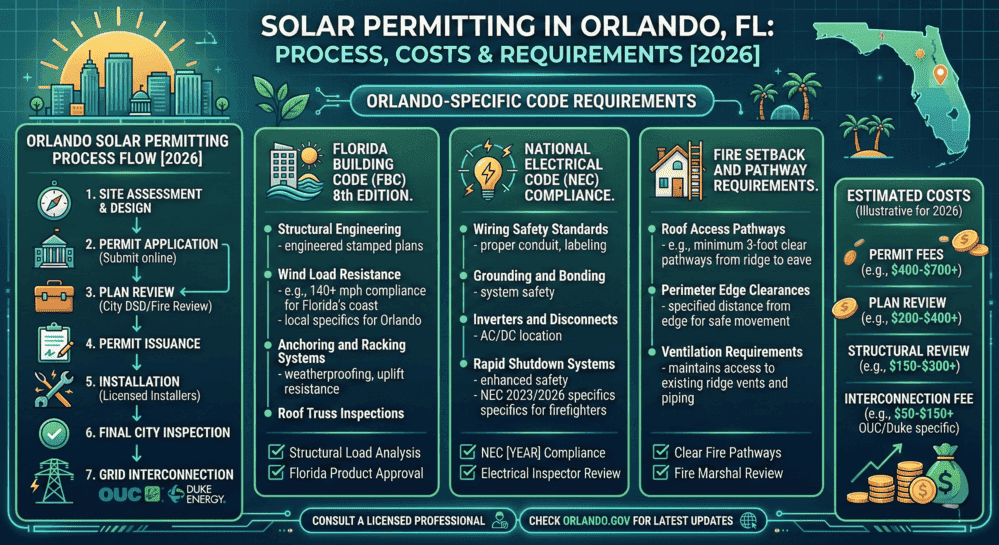
Solar Permitting in Orlando, FL: A Complete Guide for Homeowners & Installers
Solar permitting in Orlando, FL, requires a building permit and an electrical pe...
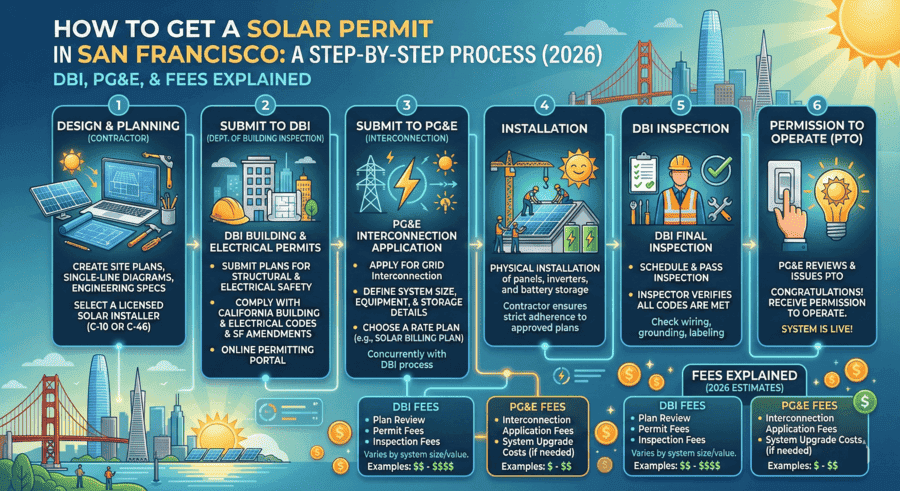
How To Get A Solar Permit In San Francisco: DBI, PG&E And Fees Explained (2026)
San Francisco solar permits require two separate approvals before your system ca...
Bifacial Solar Panel Installation And Permitting Guide
Bifacial solar panels generate 10 to 30 percent more energy than traditional mon...
