What Is Solar Permitting, and Why Does It Matter?
Solar permitting is the mandatory regulatory approval process required before installing photovoltaic systems on residential, commercial, or utility-scale properties. This multi-tiered authorization framework involves securing building permits, electrical permits, zoning approvals, and utility interconnection agreements from local, state, and federal authorities before solar panel installation can legally commence.
Timeline expectations: Residential solar permits typically take 2-12 weeks for approval, while commercial projects require 3-6 months, depending on jurisdiction complexity. Permit costs range from $200-$2,500 for residential installations and $1,000 to $15,000+ for commercial projects, representing approximately 1-3% of total installation expenses.
Why permitting exists: Authorization requirements ensure solar installations meet structural safety standards, electrical code compliance (NEC 2023), fire safety protocols, zoning ordinances, and grid interconnection safety requirements. These regulations protect property owners, utility infrastructure, and emergency responders while maintaining community aesthetic standards.
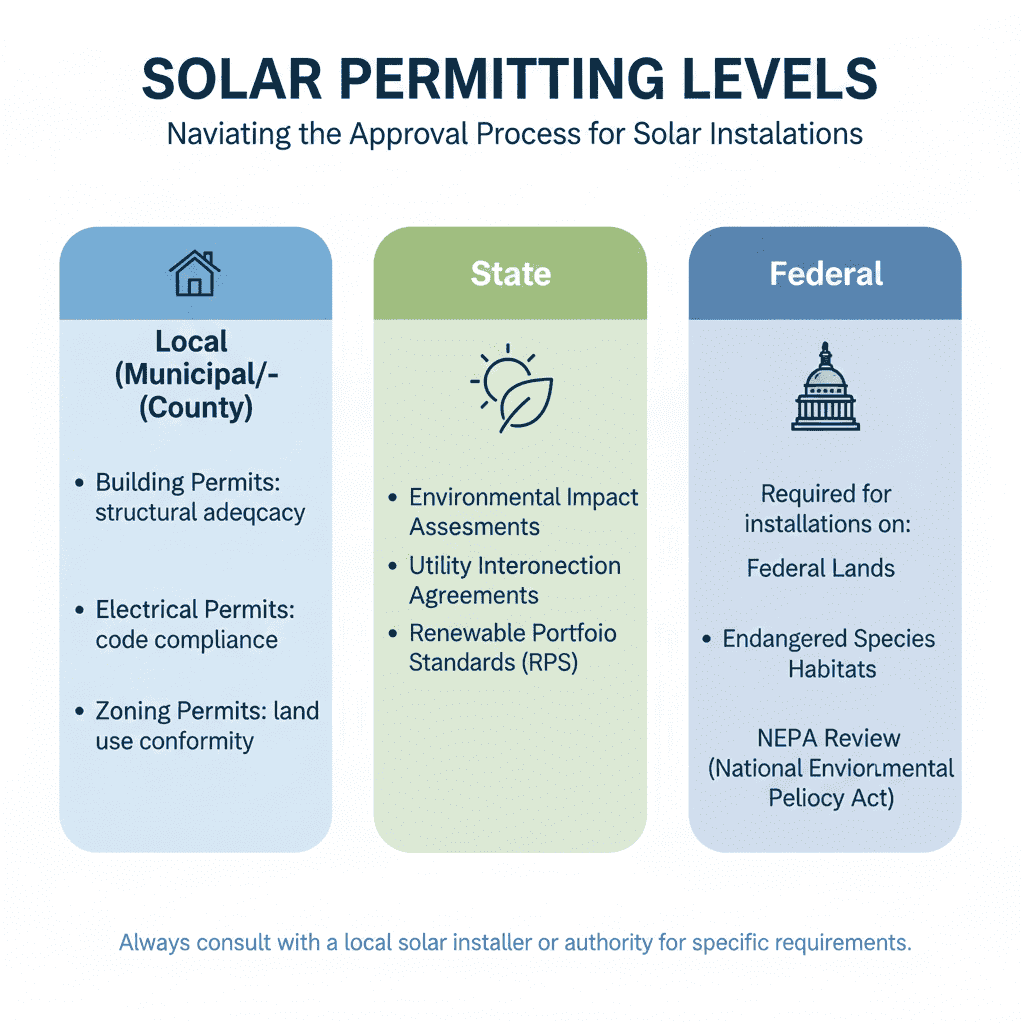
The three permitting levels:
- Local (Municipal/County): Building permits verify structural adequacy, electrical permits ensure code compliance, and zoning permits confirm land use conformity
- State: Environmental impact assessments, utility interconnection agreements, and Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) compliance
- Federal: Required only for installations on federal lands, projects affecting endangered species habitats, or developments requiring National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) review
Primary challenges: Installation professionals face fragmented regulatory frameworks varying across 50 states and thousands of municipalities, inconsistent documentation requirements, lengthy review cycles due to permitting office backlogs, utility interconnection delays, unexpected fee structures, and community opposition in historic or aesthetically regulated districts.
Industry impact: Permitting complications delay approximately 40-60% of solar projects beyond original timelines, adding $0.15-$0.50 per watt in soft costs. Streamlining authorization processes could reduce residential solar installation costs by 10-15% while accelerating deployment timelines by 30-50%, directly supporting renewable energy adoption targets and climate change mitigation objectives.
Who handles permits: Licensed solar installation companies typically manage permit acquisition as standard service inclusions, leveraging regulatory expertise and established authority relationships. Property owners pursuing DIY installations assume full permitting responsibility, requiring substantial technical knowledge of building codes, electrical standards, and local ordinance navigation.
This comprehensive guide examines solar permitting complexity across all governmental tiers, identifies common approval obstacles, provides actionable strategies for efficient authorization navigation, and explores industry advocacy efforts promoting regulatory streamlining for accelerated clean energy deployment.
Decoding Solar Permitting Complexity
Photovoltaic technology dominates the sustainable energy revolution as nations worldwide pivot from traditional power sources. Converting sunlight into electricity, while beneficial, consistently encounters bureaucratic friction and administrative bottlenecks.
Obtaining installation authorization for solar projects represents both crucial and convoluted aspects of the industry, demanding proficiency across multi-tiered government regulatory systems.
Mapping the Regulatory Framework and Approval Obstacles
Solar developments operate within fragmented legal structures spanning multiple government jurisdictions. Municipal authorities establish land use policies and construction standards dictating system placement, installation specifications, and community visual compatibility. These local rules attempt to balance renewable energy expansion and concerns including neighborhood aesthetics, real estate values, and development patterns.
At the state tier, projects typically must satisfy comprehensive environmental and energy legislation. Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) enacted by states require designated renewable energy percentages in power generation portfolios, directly shaping solar project pathways.
Environmental protection agencies at the state level may mandate ecological consequence assessments contingent on installation scale and geography, evaluating factors like ecosystem disruption or water resource demands.
National-level organizations, including FERC and EPA establish overarching solar policy and regulatory parameters. Federal authorization becomes necessary for installations on government property or projects carrying substantial cross-state ramifications, introducing additional complication tiers.

Breaking Down Permitting Across Governmental Tiers: Municipal, State, and Federal
Municipal Authorization:
Local permit acquisition and licensing constitute foundational installation phases. This tier demands zoning law adherence, authorization from city or county officials, and resident concern resolution. Municipal applications typically evaluate array footprint, property line distances, and neighborhood visual consequences. Public forums and stakeholder input sessions guarantee inclusive perspective consideration.
State Authorization:
State-level permit frameworks demonstrate significant variation influenced by energy policy direction, environmental statutes, and grid connection protocols. Certain states implement expedited approval pathways promoting solar deployment, though streamlining depth fluctuates. State permits may encompass ecosystem impact analyses, water consumption reviews, and specialized code adherence.
Federal Authorization:
Federal oversight extends to installations involving national interests or consequences. This encompasses government land developments, projects potentially impacting endangered habitats or species, or initiatives requiring transmission system integration.
Federal permit navigation presents heightened difficulty, mandating exhaustive environmental documentation, indigenous community consultation, and NEPA conformity.
Solar authorization intricacy highlights requirements for meticulous preparation, comprehensive regulation mastery, and skilled stakeholder coordination. Processes traverse numerous government examination layers, each introducing distinct obstacles and evaluation criteria.
Industry professionals, policy architects, and community leaders must forge collaborative approaches through permitting complexity, accelerating solar expansion, and making sustainable development contributions.
Installation Professional Obstacles During Permitting
Solar sector growth has accelerated dramatically over the previous ten years as residential and commercial property owners deploy photovoltaic systems for sustainable power generation. Notwithstanding this momentum, authorization processes impose substantial obstacles on installation professionals, materially affecting project schedules, budgets, and operational performance.
This segment investigates prevalent challenges confronting solar installers throughout permitting while dissecting the delays, expenditures, and stipulations impeding project finalization.
Recognizing Standard Permitting Phase Complications
Fragmented Regulatory Environment: Installation authorization requirements present intricate variations across governmental boundaries. Professionals must interpret building standards, land use restrictions, fire prevention mandates, and environmental stipulations operating at municipal, state, and federal dimensions. Mastering these frameworks requires specialized knowledge and exhaustive detail management.
Grid Integration and Utility Coordination: Connecting photovoltaic systems to established electrical infrastructure typically necessitates utility company collaboration. Grid integration processes consume substantial time while requiring adherence to company-specific procedures, technical benchmarks, and protection standards.
Structural Validation and Engineering: Building codes frequently mandate load-bearing evaluations and engineering certifications, ensuring safe solar panel incorporation into existing structures. Rooftop alterations or ground array installations may activate these stipulations, generating schedule extensions and budget increases.
Heritage and Visual Compliance: Installations within historic preservation zones or aesthetically regulated districts must satisfy appearance requirements protecting architectural heritage. Reconciling clean energy objectives with cultural preservation generates persistent friction.
Community Resistance: Local opposition regarding panel visibility, property valuation concerns, or shadow casting disputes may prolong evaluation phases or trigger outright rejections.
Obstacles Affecting Project Completion Schedules
Extended Evaluation Cycles: Permitting departments routinely manage overwhelming caseloads, producing delays throughout assessment and clearance stages. Installation professionals frequently endure multi-week or multi-month waiting periods before authorization receipt.
Non-Uniform Requirement Standards: Divergent permitting criteria across jurisdictions breed confusion and waste resources. Professionals must reconfigure designs and paperwork to match individual jurisdiction specifications.
Surprise Information Demands: During evaluations, authorities may mandate supplementary data or design revisions. These demands can dramatically elongate authorization timelines.
Multi-Layered Fee Systems: Authorization involves compounding charges, including submission fees, design review assessments, and inspection costs. Accumulated expenses erode installation profitability margins.
Utility Review Schedules: Grid connection requires utility approval operating on independent timelines, injecting additional delay possibilities.
Diverse permitting complications confronting solar professionals impact schedules, budgets, and operational effectiveness. Managing fragmented regulations, balancing stakeholder concerns, and accommodating contradictory standards form core authorization process dimensions.
Installation professionals typically combine technical expertise, strategic communication, and tactical planning to overcome these barriers. Resolving authorization challenges proves critical for solar sector advancement as sustainable energy demand intensifies.
Building Productive Municipal and Utility Partnerships
Establishing effective relationships with local government entities and power companies proves fundamental for successful construction, development, or infrastructure expansion initiatives. These alliances secure regulatory conformity and guarantee critical service delivery efficiency.
Creating municipal and utility partnerships while mastering zoning frameworks and grid connection protocols demands strategic foresight, transparent dialogue, and thorough regional knowledge.
Cultivating Government and Utility Company Connections
Developing robust municipal government and utility relationships proves vital for solar installation project success. These collaborations advance renewable energy proliferation while enabling efficient photovoltaic integration into regional power networks.
Mastering effective organizational collaboration becomes paramount as worldwide momentum toward sustainable energy accelerates. Implement these actionable tactics for constructing intelligent, interconnected communities as a solar professional:
Proactive Outreach: Initiate relationship cultivation immediately. Establish contact with municipal and utility leadership before project launches. Present company credentials, strategic objectives, and solar technology advantages. Proactive engagement cultivates supportive collaboration frameworks.
Knowledge Transfer: Government and utility personnel may possess incomplete solar technology comprehension. Deliver educational workshops or briefings detailing system mechanics, community advantages, and emission reduction impacts. This approach fosters cooperation while dispelling misconceptions.
Continuous Dialogue: Sustain uninterrupted communication pathways throughout project lifecycles. Consistent progress updates, schedule notifications, and infrastructure impact communications demonstrate transparency and dedication.
Concern Resolution: Municipalities and utilities may raise installation-related concerns spanning aesthetic consequences to grid stability. Practice active listening and deliver evidence-based responses. Addressing apprehensions demonstrates collaborative problem-solving capabilities and establishes mutual understanding.
Regulatory Mastery: Comprehend local statutes and permit protocols governing solar developments. Guarantee project conformity with zoning ordinances, construction codes, and utility-specific mandates. Trust-building through compliance demonstration expedites approval pathways.
Community Value Proposition: Emphasize solar energy’s local benefits. Showcase energy autonomy enhancement potential, economic stimulus opportunities, and employment creation prospects. This illustrates program alignment with environmental targets and regional economic vitality.
Tailored Approaches: Acknowledge municipal and utility organizational differences. Customize recommendations addressing specific community and utility priorities and challenges. Generic strategies fail to resonate with diverse stakeholder groups.
Credibility Demonstration: Position yourself as a competent, dependable solar energy collaborator. Supply examples, testimonials, and documentation from prior successful implementations. This reinforces confidence and exhibits quality work dedication.
Mastering Zoning and Interconnection Protocol Navigation
Successfully traversing zoning statutes and utility integration procedures proves essential for project realization, particularly regarding solar installations. Zoning limitations demand comprehensive local regulation understanding, ensuring systems satisfy community safety and visual expectations. Early planning agency engagement permits modifications satisfying project goals while maintaining zoning conformity.
Utility interconnection encompasses integrating photovoltaic installations into power grids through intensive utility company coordination. This requires technical specification adherence, safety protocol observance, and load calculation compliance. Securing mandatory interconnection authorizations demands utility-specific procedure familiarity. Backup strategies help mitigate delay and complication risks.
Successfully navigating these frameworks requires proactive investigation approaches, transparent communication practices, and adaptive flexibility. Guaranteeing solar installations advance renewable objectives while seamlessly integrating with existing environments and infrastructure enables sustainable energy futures.
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Contractor? We Design Your Plans.
Outsource your permit plan sets to our team. PE-stamped, code-compliant, fast turnaround so you can focus on installation.
Implementing Solar Sector Excellence Standards
Embracing excellence standards proves essential in the evolving solar industry for sustaining operational fluidity, consistent expansion, and regulatory compliance amid shifting mandates. Critical success components include deploying efficient, uniform documentation for authorization applications and maintaining currency with evolving solar permitting requirement modifications.
Concentrating on these elements enables solar enterprises to boost operational performance, minimize delays, and catalyze renewable energy proliferation.
Deploying Streamlined and Uniform Application Documentation
Boosting Reliability and Precision: Pursuing diverse solar system authorizations presents challenges. Deploying standardized documentation guarantees consistent information presentation, minimizing mistake and gap risks causing delays.
Digital Platform and Automation Integration: Employing digital platforms for authorization application documentation delivers substantial benefits. Automation heightens precision and accelerates submissions, diminishing manual workload. Digital submission also strengthens communication among regulatory bodies, inspectors, and installation professionals.
Checklist and Template Development: Establishing thorough checklists and templates for authorization packages helps professionals streamline workflows. These instruments guarantee complete documentation presence, curtailing regulatory correspondence requirements.
Regulatory Collaboration: Partnering with permitting agencies and understanding their expectations and preferences produces superior application readiness. Communication channel establishment promotes cooperation and quickens clearance procedures.
Maintaining Currency on Permitting Regulation Evolution
Remaining informed regarding solar permitting regulation modifications and amendments proves vital in the constantly shifting renewable landscape. Industry participants must proactively engage regulatory evolution, ensuring compliance and operational effectiveness.
Consistent regional, state, and federal regulatory agency monitoring, industry publication subscriptions, and webinar participation maintain awareness of changing requirements. Designating specialized compliance personnel or teams interpreting and disseminating modifications throughout organizations proves essential. Continuous personnel training and education on emerging requirements cultivates compliance culture.
Trade association collaboration and forum engagement enable knowledge exchange and excellence standard sharing, amplifying awareness. Solar enterprises can effectively handle permitting obstacles, circumvent risks, and adapt to regulatory evolution through vigilance and flexibility.
Championing Permitting Simplification Initiatives
Solar sector expansion has proven remarkable across recent decades, positioning the industry as pivotal in worldwide sustainable energy transformation. Despite solar technology’s numerous strengths, administrative obstacles and protracted authorization procedures can restrict deployment. Industry advocacy proves instrumental in advancing regulatory reforms supporting authorization streamlining to combat these challenges.
Advocacy encompasses collaboration with solar coalitions and legislative authorities developing efficient procedures, expanding solar adoption, and advancing environmental sustainability.
Advocacy’s Impact on Legislative Transformation
Industry advocacy substantially influences legislative modifications affecting solar deployment rates. It empowers sector participants, including manufacturers, installation professionals, and consumers expressing concerns regarding cumbersome authorization frameworks.
Advocates can convince policymakers to recognize the necessity of streamlining and standardization by spotlighting solar technology’s economic, environmental, and social advantages.
Advocacy transcends mere bureaucratic grievances; it enables constructive regulator and legislator engagement. Delivering meticulously researched evidence and implementation examples demonstrating simplified authorization’s beneficial impacts on employment generation, regional economies, and carbon reduction constitutes effective advocacy foundations.
Reducing solar deployment barriers enables industry champions to effectively communicate benefit potential, cultivating expanded public support for policy evolution.
Partnering with Solar Organizations and Government Leaders for Enhanced Processes
Effective expedited solar authorization advocacy requires cooperation. Solar organizations unite diverse participants as cohesive platforms, magnifying collective influence. These entities provide venues for exchanging installation-related excellence standards, evidence-based insights, and achievement narratives. They additionally coordinate efforts engaging national, regional, and municipal political leadership.
Industry champions can shape legislation and regulations advancing accelerated, efficient authorization frameworks through legislative engagement. Well-informed advocacy assists policymakers in comprehending solar enterprise and consumer obstacles, enabling regulation development prioritizing renewable adoption.
Champions and legislators can jointly craft legislation diminishing administrative friction, harmonizing requirements, and instituting concrete authorization approval deadlines.
Solar organization and lawmaker collaboration can additionally yield training programs and resource development for regional regulatory personnel. These initiatives bridge knowledge deficits, educating local officials regarding solar advantages and approval acceleration imperatives.
Advancing simplified solar authorization represents a significant undertaking requiring solar industry participant, association, and legislator cooperation. Advocacy importance resides in legislative change influence capability, eliminating solar development obstacles and yielding efficient authorization frameworks.
Champions can facilitate smoother sustainable energy transitions, establishing foundations for prosperous, environmentally responsible futures through teamwork encouragement, information exchange, and evidence-driven argumentation.
Addressing solar authorization challenges proves critically important for renewable adoption advancement. Simplifying regulatory procedures and accelerating authorization empowers professionals, stimulates sustainable energy deployment, and contributes to climate change mitigation.
Government bodies, industry participants, and communities must unite to simplify authorization, reduce expenditures, and enhance solar system accessibility. Embracing innovative methodologies and effective policy frameworks establishes conditions for prosperous, environmentally conscious solar-powered futures.
Conclusion
Navigating solar permitting requirements represents one of the most significant operational challenges facing the renewable energy industry today. Authorization frameworks spanning municipal, state, and federal jurisdictions create complex compliance landscapes that installation professionals must master for project success. Understanding these multi-tiered regulatory systems, from local zoning ordinances to federal environmental reviews, proves essential for efficient solar deployment.
The path forward demands collaborative action across multiple fronts. Installation professionals must adopt standardized documentation practices, maintain regulatory currency, and cultivate productive relationships with government entities and utility providers. Simultaneously, industry advocacy efforts must continue pressing policymakers to harmonize conflicting requirements, reduce administrative barriers, and establish predictable approval timelines.
Streamlining solar authorization processes delivers benefits extending far beyond individual projects. Simplified permitting accelerates renewable energy adoption, reduces installation costs, creates employment opportunities, and advances climate change mitigation objectives. Communities gain enhanced energy independence, while municipalities benefit from expanded tax bases and economic development.
Technology adoption and regulatory modernization offer tremendous potential for transforming permitting landscapes. Digital submission platforms, automated compliance checking systems, and inter-agency coordination tools can dramatically compress approval timelines. States and municipalities implementing best practices demonstrate that efficient permitting remains achievable without compromising safety standards or environmental protections.
The solar industry stands at a critical juncture. Meeting aggressive renewable energy targets requires removing bureaucratic friction impeding deployment. Installation professionals, government officials, utility companies, and advocacy organizations must intensify collaboration efforts to construct permitting frameworks supporting rapid, responsible solar expansion. The transition to sustainable energy futures depends on transforming authorization processes from obstacles into enablers of clean power proliferation.
FAQs
Who is responsible for obtaining solar permits – the homeowner or the installer?
Licensed solar installation companies typically handle permit acquisition as standard service components included in project contracts. Professional installers possess regulatory expertise, established relationships with permitting authorities, and experience navigating local requirements efficiently. This arrangement benefits property owners by eliminating technical complexity and ensuring compliance with constantly evolving codes. Installers prepare engineering drawings, structural calculations, electrical diagrams, and interconnection applications meeting jurisdiction-specific standards. However, property owners retain ultimate responsibility for permit compliance and must sign applications as legal property representatives. Homeowners pursuing DIY solar installations assume full permit responsibility, including researching requirements, preparing technical documentation, scheduling inspections, and ensuring code compliance. This approach demands substantial technical knowledge and time investment. When contracting professional installation, verify the agreement explicitly states permit acquisition responsibilities, associated costs, and timeline expectations. Reputable installers provide permit status updates and handle inspection coordination throughout the approval process.
Solar Contractor? We Design Your Plans.
Outsource your permit plan sets to our team. PE-stamped, code-compliant, fast turnaround so you can focus on installation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Solar permitting timelines vary significantly based on jurisdiction complexity and project scale. Residential installations in streamlined municipalities typically require 2-4 weeks for permit approval, while more complex jurisdictions may extend timelines to 8-12 weeks. Commercial and utility-scale projects often face 3-6 month permitting periods due to additional environmental reviews, structural engineering requirements, and stakeholder consultation processes. Federal land projects or installations requiring Environmental Impact Statements can take 12-24 months. Factors affecting timeline include permit office workload, application completeness, utility interconnection review schedules, and whether projects trigger additional assessments like historical preservation reviews or habitat evaluations. Installing professionals can accelerate timelines by submitting comprehensive documentation upfront, engaging authorities early, and maintaining proactive communication throughout review cycles.
Solar installations typically require multiple authorization types across different governmental tiers. At the municipal level, expect building permits verifying structural adequacy and electrical permits ensuring code-compliant wiring and system integration. Zoning permits may be necessary confirming land use compliance and setback requirement adherence. Fire department approvals often apply, particularly for commercial installations, addressing emergency access and firefighter safety protocols. State-level requirements may include electrical contractor licensing, environmental permits for large-scale ground installations, and utility interconnection agreements authorizing grid connection. Homeowners associations, where applicable, require design review approval for aesthetic compliance. Historic district installations need preservation commission authorization. Federal permits apply only for installations on government property or projects affecting protected species and habitats. Requirements vary substantially by location, making local permit office consultation essential before project commencement.
Licensed solar installation companies typically handle permit acquisition as standard service components included in project contracts. Professional installers possess regulatory expertise, established relationships with permitting authorities, and experience navigating local requirements efficiently. This arrangement benefits property owners by eliminating technical complexity and ensuring compliance with constantly evolving codes. Installers prepare engineering drawings, structural calculations, electrical diagrams, and interconnection applications meeting jurisdiction-specific standards. However, property owners retain ultimate responsibility for permit compliance and must sign applications as legal property representatives. Homeowners pursuing DIY solar installations assume full permit responsibility, including researching requirements, preparing technical documentation, scheduling inspections, and ensuring code compliance. This approach demands substantial technical knowledge and time investment. When contracting professional installation, verify the agreement explicitly states permit acquisition responsibilities, associated costs, and timeline expectations. Reputable installers provide permit status updates and handle inspection coordination throughout the approval process.
Solar permit fees demonstrate substantial variation across jurisdictions, typically ranging from $200-$2,500 for residential installations and $1,000-$15,000+ for commercial projects. Municipal building permit fees commonly calculate as flat rates ($200-$800) or percentages of project valuation (0.5%-2% of installation cost). Electrical permit fees typically range $100-$500 for residential systems. Plan review charges, covering engineering evaluation time, add $150-$1,000 depending on system complexity. Utility interconnection application fees span $100-$500, with some utilities charging additional interconnection studies for larger systems ($500-$3,000). Inspection fees may apply as separate charges ($100-$300 per inspection) or include in base permit costs. Some jurisdictions impose impact fees or renewable energy surcharges. Total permitting costs typically represent 1%-3% of overall residential installation expenses. Many states and municipalities have implemented permit fee caps or streamlined processes reducing costs for standardized residential installations. Contact local building departments for jurisdiction-specific fee schedules and inquire about available permit fee waivers or rebates for renewable energy projects.
Installing solar systems without proper authorization violates building codes and constitutes illegal construction across virtually all United States jurisdictions. Consequences prove severe and multifaceted. Building departments discovering unpermitted installations issue stop-work orders halting projects immediately and impose violation fines ranging $500-$10,000+ daily until compliance achievement. Property owners face mandatory system removal requirements at their expense, forfeiting entire installation investments. Unpermitted installations void equipment warranties and installer workmanship guarantees. Homeowners insurance policies may deny coverage for unpermitted work, leaving property owners personally liable for fire damage, electrical failures, or injury incidents. Unpermitted systems disqualify properties from federal Investment Tax Credit claims and state renewable energy incentive programs, eliminating thousands in potential savings. Real estate transactions encounter complications as title companies flag unpermitted construction, requiring retroactive permitting, extensive inspections, or system removal before sale completion. Banks may refuse mortgages or equity loans on properties with code violations. Utility companies typically refuse grid interconnection for unpermitted systems, eliminating net metering benefits. The permit process exists protecting property owners, ensure structural safety, electrical code compliance, and fire safety standards. Always secure proper authorization before installation commencement.
Solar permit applications face rejection for numerous technical and administrative reasons. Incomplete documentation represents the primary rejection cause, including missing electrical diagrams, inadequate structural calculations, or absent engineering stamps. Zoning violations occur when proposed installations breach setback requirements, exceed height restrictions, or locate in prohibited zones like historic districts without proper variances. Structural inadequacy concerns arise when roof load calculations fail demonstrating adequate capacity for panel weight, particularly on older structures or those with existing condition issues. Electrical code non-compliance includes improper conductor sizing, inadequate overcurrent protection, missing rapid shutdown systems, or incorrect grounding specifications. Fire code violations involve insufficient access pathways, inadequate spacing from roof edges, or missing firefighter access routes. Aesthetic non-compliance in regulated communities includes visible conduit, inappropriate mounting positions, or designs conflicting with architectural review board standards. Utility interconnection issues emerge from incorrect inverter specifications, missing anti-islanding protection, or inadequate utility notification procedures. Environmental concerns trigger rejections for installations potentially affecting protected habitats, wetlands, or endangered species. Avoid rejections by engaging licensed professionals, submitting comprehensive documentation, verifying zoning compliance before design finalization, and consulting permitting authorities during planning phases addressing jurisdiction-specific requirements proactively.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...
Solar Permits in Los Angeles: LADBS Requirements, Fees, and Timeline (2026 Guide)
Quick Answer: Solar permits in Los Angeles are issued by LADBS and require LAFD ...