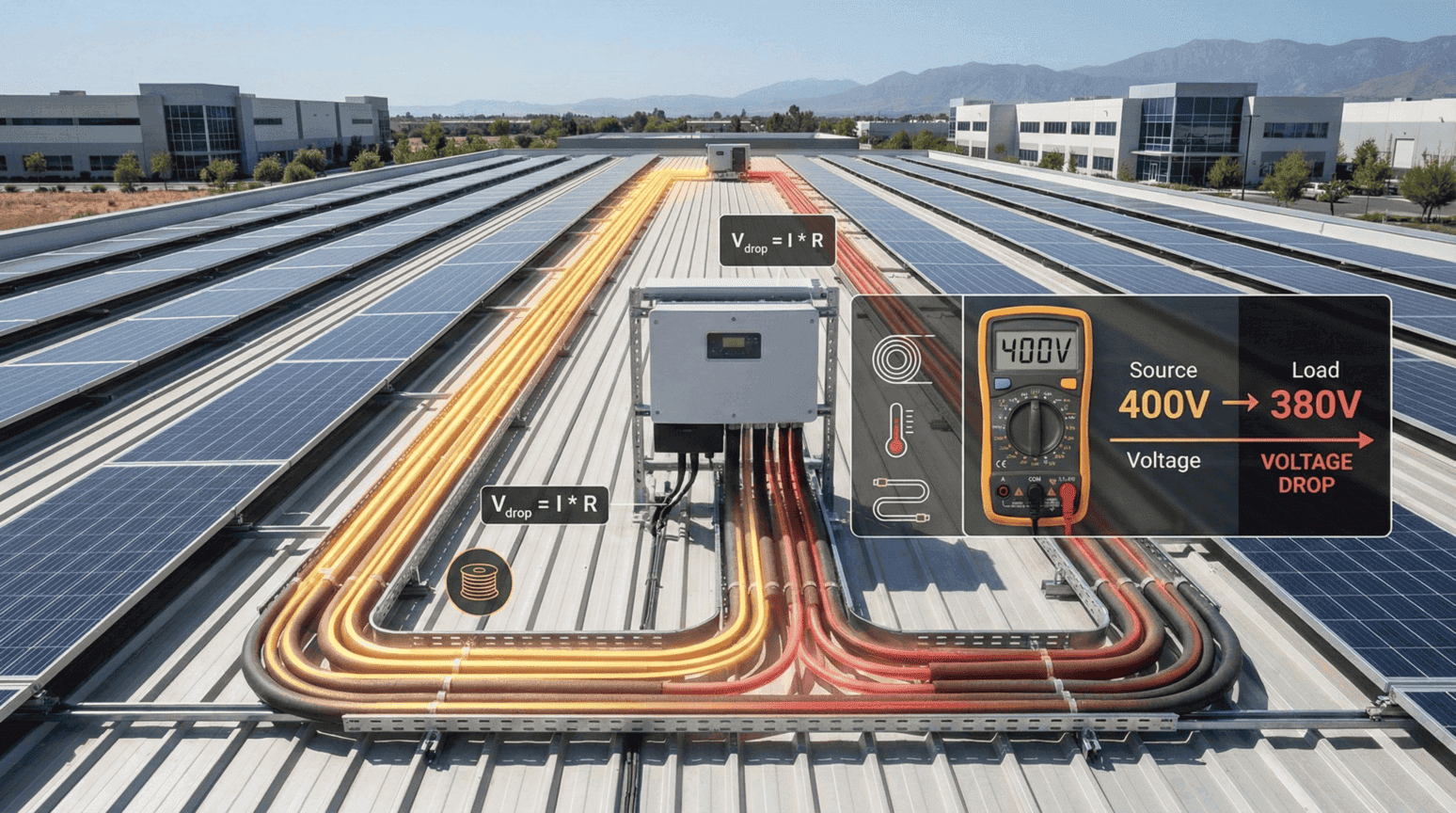
Voltage drop in solar systems is the reduction in electrical voltage that occurs as current flows through conductors due to resistance, typically measured as a percentage of the total system voltage. The National Electrical Code recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for individual circuits and 5% combined for optimal solar system performance.
Voltage drop is calculated using the formula Vd = I × R (voltage drop equals current times resistance) and can be minimized by using properly sized wire gauges, reducing conductor length, installing high-quality connectors, and managing temperature. Excessive voltage drop reduces solar system efficiency, decreases power output, can damage inverters and charge controllers, and creates safety hazards like overheating.
To calculate voltage drop accurately, you need the conductor’s resistance (R = (ρ × L) / A), current load in amps, wire material resistivity, conductor length, and cross-sectional area, with most solar professionals targeting 1-2% voltage drop for maximum energy production and system longevity.
Voltage drop represents a crucial factor in solar energy systems, directly affecting performance, efficiency, and operational safety. This comprehensive guide examines the fundamentals of voltage drop, its underlying causes and consequences, effective mitigation strategies, and its importance in solar installations.

What is Voltage Drop?
Voltage drop describes the decrease in electrical voltage that occurs along a conductor’s length, including wires and cables, caused by electrical resistance. This phenomenon happens when electric current flows through a conductor and encounters internal resistance, resulting in a voltage reduction between the power source and the connected load.
Causes of Voltage Drop in Solar Systems
Multiple factors trigger voltage drop in solar energy installations:
Wire Resistance: Conductor resistance stands as the principal element affecting voltage drop. Extended wire lengths or conductors with reduced cross-sectional dimensions exhibit increased resistance, producing more significant voltage reduction. Understanding solar wire and cable specifications helps in selecting appropriate conductors for your system.
Connector Resistance: Improperly installed or oxidized connectors elevate resistance levels, amplifying voltage drop. DC connector issues can create significant performance and safety problems in PV systems.
Temperature: Elevated temperatures raise conductor resistance, resulting in increased voltage drop. Temperature ratings are critical when selecting conductors for solar applications.
Current Load: Greater current demands generate more substantial voltage drop, especially in installations featuring extended wire distances. Proper circuit breaker and fuse sizing helps manage current loads effectively.

Effects of Voltage Drop
Voltage drop produces multiple detrimental consequences in solar energy systems:
Reduced Efficiency: Voltage reduction diminishes system efficiency, causing decreased power generation and compromised energy collection from solar arrays. This directly impacts the long-term performance of solar panels and overall system returns.
Equipment Damage: Extreme voltage drop can harm delicate electronic equipment, including inverters and charge controllers, shortening their operational lifespan and dependability. Understanding inverter grid integration is essential for maintaining system reliability.
Safety Hazards: Voltage drop generates safety concerns, such as conductor and connector overheating, creating potential fire dangers. Arc fault protection requirements address these critical safety considerations.
Solar Permit Solutions
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Mitigating Voltage Drop
Various approaches can minimize voltage drop in solar energy installations:
Proper Wire Sizing: Select conductors with appropriate gauge specifications according to current requirements and distance to reduce resistance and voltage reduction. Choosing the right wire size is fundamental to system design.
Reducing Wire Length: Shortening conductor runs between system components decreases voltage drop. Effective wire management and conduit practices optimize conductor routing in solar installations.
Using High-Quality Connectors: Utilize premium connectors and maintain proper installation practices to minimize resistance and voltage reduction. MC4 connector best practices ensure reliable connections throughout your system.
Temperature Management: Apply temperature control methods, including heat-resistant conductors and sufficient airflow, to lower voltage drop.

Voltage Drop Calculation
Voltage drop calculations utilize Ohm’s Law, which establishes that voltage (V) equals current (I) times resistance (R). The voltage drop (Vd) formula is:
Vd = I × R
Where:
- Vd represents the voltage drop (in volts)
- I represents the current (in amps)
- R represents the resistance (in ohms)
To determine voltage drop, you must establish the conductor’s resistance and the current passing through it. Calculate conductor resistance using this formula:
R = (ρ × L) / A
Where:
- R represents the resistance (in ohms)
- ρ (rho) represents the material’s resistivity (in ohm-cmil/ft or ohm-m)
- L represents the conductor’s length (in feet or meters)
- A represents the conductor’s cross-sectional area (in circular mils or square meters)
After obtaining resistance and current values, apply the formula Vd = I × R to determine the voltage drop across the conductor. Use an Ohm’s Law calculator for quick verification of your calculations.
Note that voltage drop calculations fluctuate based on variables including conductor composition, temperature conditions, and installation parameters. Understanding electrical fundamentals for solar projects ensures accurate system design. Furthermore, voltage drop calculations must adhere to NEC 2023 solar code requirements to guarantee safety and optimal performance.
Significance of Voltage Drop in Solar Installations
Voltage drop serves as an essential consideration in solar installations because of its immediate influence on system performance, efficiency, and safety. Whether designing residential solar systems, commercial installations, or off-grid applications, thorough comprehension and proper voltage drop management prove vital for maximizing performance and extending the operational life of solar energy systems.
Conclusion
Voltage drop constitutes a critical element to address in solar energy systems, influencing performance, efficiency, and safety parameters. Through understanding voltage drop’s causes and effects and executing proper mitigation techniques, solar professionals can guarantee optimal system performance and reliability. As global renewable electricity adoption expands, managing voltage drop grows increasingly vital in designing and implementing efficient solar installations. For expert assistance with voltage drop calculations and system design, contact Solar Permit Solutions or explore our comprehensive solar design services.
FAQs
Need Solar Permit Plans?
Professional, permit-ready solar plan sets delivered fast. Residential and commercial projects across all 50 states.
Frequently Asked Questions
The National Electrical Code (NEC) recommends keeping voltage drop below 3% for individual circuits and a combined maximum of 5% for both feeder and branch circuits in solar installations. However, many solar professionals aim for even lower voltage drop percentages, typically between 1-2%, to maximize system efficiency and energy production. Maintaining voltage drop within these acceptable ranges ensures optimal performance while preventing equipment damage and safety hazards.
Wire gauge directly impacts voltage drop because it determines the conductor's cross-sectional area and resistance. Larger wire gauges (smaller AWG numbers) have greater cross-sectional areas and lower resistance, resulting in reduced voltage drop. For example, using 10 AWG wire instead of 14 AWG wire for the same circuit length and current load will significantly decrease voltage drop. Proper wire gauge selection based on distance and current requirements is essential for minimizing voltage losses in solar systems.
Yes, excessive voltage drop can potentially damage solar inverters, charge controllers, and other sensitive electronic components. When voltage drop is too high, inverters may receive insufficient voltage to operate efficiently, causing them to work harder and generate excess heat. This can lead to premature component failure, reduced lifespan, and system shutdowns. Additionally, voltage drop can cause inverters to operate outside their optimal voltage range, triggering error codes and reducing overall system reliability. Understanding proper wiring to breaker boxes and electrical panel types helps prevent these issues.
To calculate voltage drop for your solar installation, use the formula: Vd = I × R, where Vd is voltage drop in volts, I is current in amps, and R is resistance in ohms. First, determine the conductor resistance using R = (ρ × L) / A, where ρ is the material's resistivity, L is the wire length (multiply by 2 for round-trip distance), and A is the cross-sectional area. Alternatively, you can use online voltage drop calculators specifically designed for solar applications by inputting wire gauge, length, current, and voltage to quickly determine voltage drop percentages.
Yes, temperature significantly affects voltage drop in solar systems. As conductor temperature increases, electrical resistance also increases, leading to greater voltage drop. This is particularly important in solar installations where wiring is often exposed to direct sunlight and elevated ambient temperatures. For every 10°C increase in temperature, conductor resistance typically increases by approximately 4%. This is why using temperature-rated conductors and implementing proper wire management techniques, such as adequate spacing and ventilation, are critical for minimizing temperature-related voltage drop in solar energy systems. Rapid shutdown compliance also requires careful consideration of temperature effects on system components.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
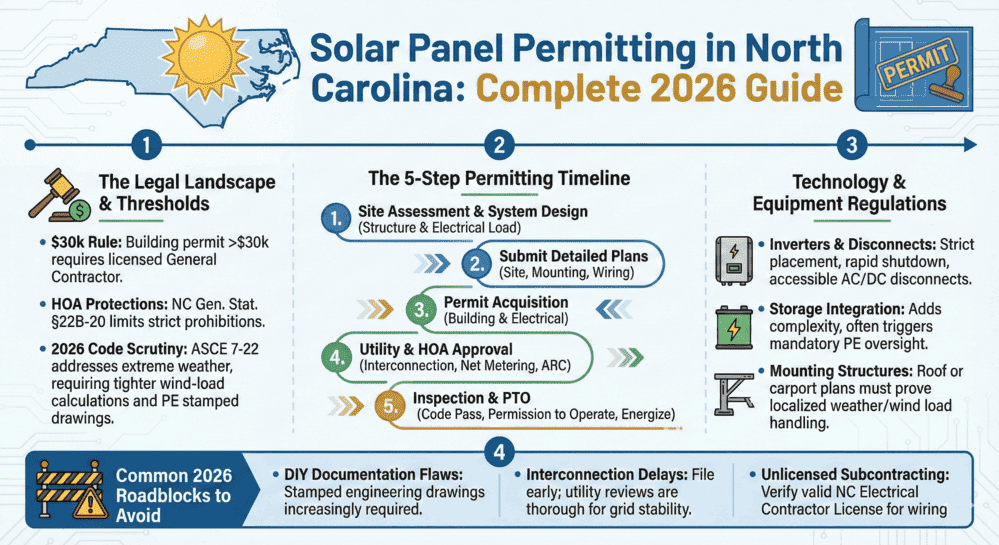
New 2026 North Carolina Solar Permit Guide: Duke Energy & Storage Rules
Learn North Carolina solar panel licensing and permitting requirements. Discover...

Section 25D Expiration: Homeowner Options In 2026
The Section 25D Residential Clean Energy Credit, which covered 30% of residentia...

Solar Permits In Arizona: Phoenix, Tucson, Maricopa County, And Mesa Requirements (2026 Guide)
Arizona solar permitting at a glance: Arizona HB2301 now requires every municipa...