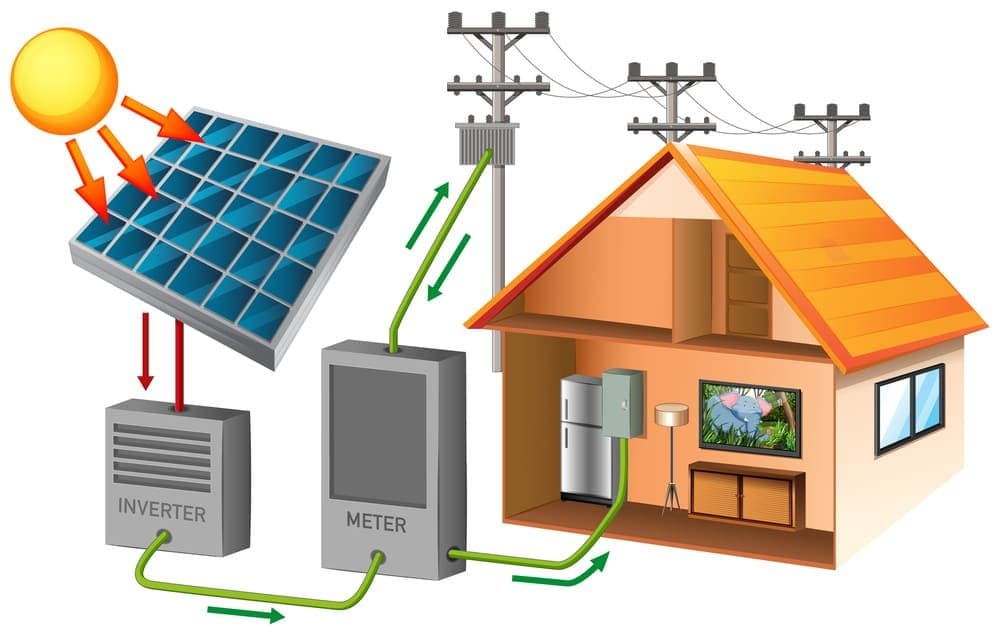
A grid-tied solar system is a photovoltaic installation that connects directly to your local utility grid, allowing you to generate solar electricity while maintaining 24/7 power reliability without expensive battery storage. In 2025, these systems cost between $2.50-$4.00 per watt installed, deliver 6-10 year payback periods with the 30% federal tax credit, and produce savings of $30,000-$50,000 over 25 years for the average homeowner.
Grid-tied systems dominate 90% of residential solar installations because they eliminate the $10,000-$30,000 cost of battery backup while still reducing electricity bills by 80-100% through net metering programs. When your solar panels produce more electricity than you consume, the excess flows back to the utility grid and credits your account, essentially using the grid as free energy storage. During nighttime or cloudy periods, you draw power from the grid seamlessly, paying only for your net electricity usage.
This comprehensive 2025 guide explains how grid-tied solar systems work, breaks down installation costs and ROI calculations, compares grid-tied versus off-grid and hybrid alternatives, and provides step-by-step guidance on sizing, permitting, and maintaining your system. You’ll discover why modern 450W monocrystalline panels with string inverters or microinverters offer the optimal balance of performance and affordability, how to navigate federal and state incentive programs, and when adding battery backup makes financial sense for your specific situation.
Whether you’re exploring solar for the first time or ready to request installation quotes, understanding grid-tied systems helps you make informed decisions that maximize your investment returns while contributing to energy independence and environmental sustainability, according to the EPA’s green power markets.
Essential Takeaways
Discover why grid-tied solar leads the industry: current 2025 installation costs between $2.50-$4.00 per watt, combined with a 30% federal tax incentive available until 2032, position grid-tied systems as the most cost-effective choice. Expect payback timeframes of 6-10 years and maximize your investment returns, all without the expense of battery storage.
Understand net metering as your financial cornerstone: Exporting surplus solar energy to the grid in exchange for bill credits creates the economic foundation that makes grid-tied systems practical.
Take action now: confirm your utility provider’s net metering guidelines, as regulatory adjustments continue to reshape these programs across numerous states.
Experience minimal maintenance with maximum output: Today’s monocrystalline panels deliver 450W+ capacity as the industry standard, while sophisticated monitoring platforms track real-time performance metrics. Commit to a low-upkeep solution that generates reliable electricity for 25+ years with annual degradation staying below 0.5%.
Prepare for tomorrow with built-in flexibility: expand your grid-tied system seamlessly or integrate battery backup when circumstances shift. Invest in an adaptable infrastructure ready to support electric vehicle charging, property expansions, or changing utility pricing models over the long term.
What is a grid-tied solar system?
Grid-tied solar systems, also referenced as grid-connected or on-grid photovoltaic setups, establish a direct link to the public electricity network. This integration enables your solar array to function alongside your utility provider’s power distribution, delivering a unified energy solution.
What defines grid-tied configurations is their capacity to function without battery storage requirements. When your solar panels generate surplus electricity beyond your consumption needs, that excess energy feeds back into the utility grid via net metering. On the flip side, when your panels produce insufficient power (during nighttime hours or overcast conditions), you pull electricity from the grid exactly as you did before going solar.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid vs. Hybrid Systems
Comparing solar system categories reveals why grid-tied installations capture the largest market share:
Grid-Tied Systems: Link to utility infrastructure, eliminate battery requirements, deliver the lowest initial investment, depend on grid electricity during power interruptions
Off-Grid Systems: Operate independently, demand battery storage plus backup generator equipment, carry the highest upfront expenses, and maintain functionality during blackouts. Learn more about off-grid solar system design for remote installations.
Hybrid Systems: Connect to utility grid while incorporating battery backup, require moderate to substantial initial costs, supply emergency power when outages occur
Solar Permit Solutions
Affordable Solar Permit Plans
Don't let permit costs slow your project. Professional plan sets at competitive prices — all 50 states, fast turnaround.
Grid-Tied Solar System Operation
Grasping grid-tied solar operation means tracking energy’s journey from sunlight to practical electricity powering your property.
Sequential Operation Process
Solar Energy Capture: Photovoltaic modules transform sunlight into direct current (DC) power
DC to AC Conversion: Grid-tie inverters change DC electricity to alternating current (AC) compatible with your property’s electrical infrastructure. Mastering electrical fundamentals is crucial for proper solar system design.
Power Distribution: AC electricity routes to your building’s electrical panel and energizes your devices
Excess Power Export: Surplus generation flows backward through your utility meter into the grid
Grid Power Import: During periods of insufficient solar output, electricity flows from the utility network to your property
Net Metering Explained
Net metering establishes the billing structure that makes grid-tied solar economically compelling. Your utility meter advances when drawing grid power and reverses when sending solar electricity back. Each billing cycle charges you solely for your net energy usage.
Practical Example: Consider a month where your solar array generates 1,000 kWh while you use 800 kWh. You’ll earn credit for the additional 200 kWh. Apply this credit against upcoming electricity consumption, effectively banking your excess solar output within the grid.
Daily Operation Patterns
Grid-tied configurations function distinctly across daily cycles:
Peak Generation Window (10 AM to 4 PM): Maximum solar generation typically surpasses household demand, resulting in net grid export
Transition Periods (Morning/Evening): Moderate solar output may partially cover property electricity requirements
Nocturnal Hours: Zero solar generation means complete reliance on grid electricity
Protective Systems and Safety Features
Grid-tied inverters incorporate essential safety protocols mandated by electrical standards:
Anti-Islanding Safeguards: Automatically terminates solar generation during grid failures, ensuring utility worker safety
Ground Fault Detection: Identifies wiring faults and deactivates the system preventing fire hazards
Arc Fault Detection: Recognizes hazardous electrical arcing and isolates the configuration
Rapid Shutdown: Decreases DC voltage to safe thresholds within 30 seconds upon activation per NEC 690.56(C) requirements
Essential Parts and Tools
A standard grid-tied solar configuration combines multiple critical components that work collectively to transform sunlight into practical electricity.
Solar Panels
Contemporary residential solar modules for grid-connected setups predominantly utilize monocrystalline silicon technology, as polycrystalline options have been discontinued by major producers:
Monocrystalline Panels: Achieve 20-25% efficiency, represent the premium choice, deliver superior low-light performance, currently define the industry benchmark
Polycrystalline Panels: Reach 15-20% efficiency, essentially outdated by 2025, no longer manufactured by leading brands
Bifacial Panels: Capture energy from front and rear surfaces, boost output by 10-20% under ideal conditions
Today’s residential panels typically deliver 400-500 watts, with 450W modules establishing themselves as the 2025 baseline.
Grid-Tie Inverters
Your inverter serves as your grid-tied system’s core component, and selecting the appropriate type influences performance quality, monitoring capabilities, and upkeep requirements:
String Inverters
- Single central unit manages multiple panels
- Presents the lowest initial investment
- Overall system output constrained by poorest-performing panel
- Optimal for shade-free, consistent installations
Microinverters
- Dedicated inverter attached to each panel
- Maximizes energy extraction from every module
- Enables panel-level tracking and optimization
- Requires higher upfront investment but delivers superior long-term results
Power Optimizers
- DC optimization units paired with central string inverter
- Panel-specific optimization at reduced cost versus microinverters
- Provides balanced solution between performance and expense
Monitoring Systems
Current grid-tied installations feature extensive monitoring functionalities:
Production Monitoring: Track energy generation across daily, monthly, and yearly timeframes
Performance Analysis: Detect underperforming modules or system complications
Financial Tracking: Observe savings accumulation and investment returns
Mobile Apps: Access real-time system status and receive smartphone notifications
Electrical Components
Professional grid-connected installations demand several electrical elements. Understanding solar three-line diagrams helps visualize system connections:
AC Disconnect Switch: Enables utility personnel to isolate the solar configuration
Production Meter: Quantifies total solar electricity output
Net Meter: Bidirectional device tracking energy import and export flows
Grounding Equipment: Maintains electrical safety and regulatory compliance
DC and AC Wiring: Premium-grade cables designed for outdoor solar environments
Mounting Systems
Reliable mounting proves essential for system performance and durability:
Roof-Mounted Systems: Most prevalent approach, leverages existing roof framework, minimizes ground space usage
Ground-Mounted Systems: Simplifies maintenance accessibility, permits optimal panel angles, demands available property area
Pole-Mounted Systems: Elevated placement, advantageous for snowy regions or shade-prone locations

Advantages and Disadvantages
Like all technologies, grid-tied solar configurations present both strengths and constraints that prospective buyers must evaluate.
Advantages of Grid-Tied Solar Systems
Cost-Effectiveness
Grid-tied setups deliver the most affordable upfront commitment among solar alternatives by eliminating expensive battery storage requirements. Average cost reductions compared to off-grid configurations span $15,000 to $30,000 for standard residential projects.
Net Metering Benefits
Utility net metering initiatives enable you to earn credits for surplus solar generation. Within states offering advantageous net metering frameworks, property owners can eliminate 90-100% of electricity expenses with correctly sized installations.
Environmental Impact
A standard 6kW grid-connected solar array prevents roughly 7,500 pounds of CO2 emissions each year, matching the impact of planting 85 trees or reducing vehicle miles by 8,000 annually, according to renewable energy research.
Low Maintenance Requirements
Grid-tied configurations contain fewer parts than battery-dependent systems, producing reduced maintenance expenses and enhanced reliability. Most installations need only yearly inspections and periodic cleaning.
Scalability
Grid-connected systems accommodate straightforward expansion through additional panels and inverter capacity, enabling property owners to begin modestly and enlarge their setup progressively.
Disadvantages and Limitations
No Power During Outages
The fundamental constraint of standard grid-connected systems involves their failure to supply power during utility interruptions. Anti-islanding safety mandates terminate solar generation when grid power fails, leaving you without electricity despite sunny conditions.
Utility Dependency
Grid-tied configurations depend on utility infrastructure and regulatory frameworks. Modifications to net metering regulations, interconnection charges, or electricity pricing can influence system financial performance.
Time-of-Use Rate Challenges
Within regions employing time-of-use electricity pricing, maximum solar generation frequently coincides with low-rate windows, while highest consumption occurs during premium-rate periods, diminishing total savings.
Limited Energy Independence
Though grid-tied systems cut electricity costs, they don’t deliver genuine energy autonomy since you maintain connection to and reliance upon the utility network.

Installation Process and Requirements
Installing a grid-connected solar configuration encompasses multiple phases, spanning initial planning through final utility connection. Professional solar design services ensure optimal system performance and regulatory compliance.
Professional vs. DIY Installation
Although DIY solar packages exist, professional installation receives strong recommendations for grid-tied setups due to:
Electrical Code Compliance: Licensed installers comprehend local electrical regulations and safety protocols
Permit Acquisition: Certified contractors can secure permits and manage inspection processes
Warranty Protection: Numerous component warranties mandate professional installation
Insurance Coverage: Professional installation may satisfy homeowner’s insurance requirements
DIY Considerations: Choosing DIY installation demands electrical proficiency, appropriate permits, and successful local inspection completion. DIY approaches can reduce labor expenses by $3,000-$8,000 but require substantial time commitment and technical knowledge. Review our DIY home solar guide for detailed instructions.
Permitting and Inspection Requirements
Grid-connected solar projects necessitate multiple permits and inspection approvals according to solar permitting best practices:
Building Permit: Mandated by local building authority, typically ranges $200-$800
Electrical Permit: Required for electrical modifications, generally $100-$500
Structural Review: May be necessary for roof-mounted configurations, particularly on aging properties
HOA Approval: Homeowner associations might impose specific guidelines or limitations
Electrical Inspection: Local inspector confirms code compliance before grid connection
Utility Interconnection Process
Linking your configuration to the utility network involves these phases. Understanding solar interconnection options helps streamline the approval process:
Interconnection Application: Submit documentation with system details and electrical schematics
Utility Review: Power company assesses system compatibility with regional grid infrastructure
Net Metering Agreement: Execute contract establishing compensation for surplus solar generation
Meter Installation: Utility deploys bidirectional net meter (when not already present)
Permission to Operate: Utility issues final authorization to activate the system
Timeline and Typical Costs
The full installation sequence generally requires 1-3 months. Learn about solar permit timelines to plan your project effectively:
Design and Permitting: 2-6 weeks
Equipment Procurement: 1-4 weeks
Installation: 1-3 days
Inspection and Interconnection: 1-4 weeks
2025 Installation Costs:
- Professional installation: $2.50-$4.00 per watt
- Permits and inspections: $500-$2,000
- Utility interconnection: $0-$500
Safety Considerations and Code Compliance
Grid-connected solar projects must satisfy multiple safety regulations:
National Electrical Code (NEC): Establishes electrical safety mandates
Local Building Codes: Address structural integrity and fire safety requirements
Utility Requirements: Specify interconnection protocols and safety benchmarks
UL Standards: Equipment certification criteria for safety and operational excellence
Financial Considerations
Grasping the complete financial landscape enables you to make educated decisions about grid-tied solar investments.
System Costs Breakdown (2025 Pricing)
Current marketplace pricing for grid-connected solar configurations has dropped substantially over the previous decade:
Equipment Costs (per watt)
- Solar panels: $0.60-$1.20
- Inverters: $0.25-$0.50
- Mounting hardware: $0.15-$0.30
- Electrical components: $0.10-$0.25
Total System Costs
For a standard 6kW residential setup:
- Equipment only: $6,600-$13,500
- Professional installation: $15,000-$30,000
- After federal tax credit: $10,500-$21,000
Federal Tax Credits and State Incentives
Federal Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The federal ITC delivers a 30% tax credit for solar projects through 2032, as detailed in the homeowner’s guide to federal tax credits:
- 2025-2032: 30% tax credit
- 2033: 26% tax credit
- 2034: 22% tax credit
- 2035 and beyond: 10% for commercial, 0% for residential
State and Local Incentives
Numerous states extend additional benefits:
- State tax credits: Extra 10-25% in select states
- Rebate programs: Immediate cash rebates of $500-$2,000 per kW
- Performance payments: Continuous payments tied to system generation
- Property tax exemptions: Solar projects don’t elevate property tax assessments
Investment Returns and Breakeven Analysis
Grid-connected solar configurations typically recover costs through electricity savings:
Sample ROI Calculation
6kW system in California:
- System cost after incentives: $12,000
- Annual electricity savings: $1,800
- Simple payback period: 6.7 years
- 25-year savings: $33,000
- Internal rate of return: 12-15%
Financing Options
Multiple financing pathways make solar attainable for more property owners:
Cash Purchase: Maximum returns, instant ownership, complete incentive advantages
Solar Loans: $0 down alternatives available, retain ownership and incentives
Solar Leases: Zero upfront expenses, but restricted savings and no incentives
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs): Pay for solar electricity at predetermined rate
Long-Term Savings Projections
Grid-connected solar systems generate decades of financial benefits:
Years 1-10: Recover initial investment through electricity cost reductions
Years 11-25: Direct profit from ongoing electricity generation
Beyond 25 years: Sustained savings with progressively declining output
Sizing Your Grid-Tied System
Appropriate system sizing guarantees optimal performance and maximum financial returns from your grid-connected solar investment.
Energy Consumption Analysis
Begin by examining your electricity usage behaviors:
- Review 12 months of utility statements to comprehend seasonal fluctuations
- Calculate average monthly kWh consumption and pinpoint peak usage periods
- Consider future modifications like electric vehicles, pool equipment, or property expansions
- Evaluate time-of-use behaviors if your utility implements variable pricing
Sizing Guidelines:
- 100% offset: System generates annual electricity matching consumption
- 80-90% offset: Advised for most property owners to prevent over-generation
- 120%+ offset: Consider when planning electric vehicle or significant electric appliances
Roof Space and Orientation Factors
Physical limitations influence system dimensions and efficiency:
Roof Space Requirements
- Standard 450W panel: 22 square feet
- 1kW system: ~50 square feet
- 6kW system: ~300 square feet
- Account for setbacks, barriers, and maintenance pathways
Optimal Orientation and Tilt
- Best orientation: South-facing (180° azimuth)
- Acceptable orientations: Southeast to southwest (135° to 225° azimuth)
- Optimal tilt: Equal to latitude (30-40° for most US regions)
- Acceptable tilt range: 15-45° with minimal production decline
Location-Based Solar Energy Assessment
Solar resources fluctuate considerably by geography, as documented by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory:
- High solar resource areas: Southwest US (5.5-7.0 kWh/kW/day)
- Moderate solar resource areas: Most of continental US (4.0-5.5 kWh/kW/day)
- Lower solar resource areas: Pacific Northwest, Northeast (3.5-4.5 kWh/kW/day)
Array Sizing Computation Method
Use this sequential approach to determine your system capacity:
- Annual consumption: Total 12 months of kWh usage
- Daily average: Annual consumption divided by 365 days
- Local solar hours: Research peak sun hours for your region
- System size (kW): Daily kWh divided by peak sun hours divided by 0.85 (system efficiency factor)
- Number of panels: System size (watts) divided by panel wattage
Example Calculation:
- Annual consumption: 10,800 kWh
- Daily average: 29.6 kWh
- Local peak sun hours: 5.2
- Required system size: 29.6 divided by 5.2 divided by 0.85 = 6.7 kW
- Number of 450W panels: 6,700 divided by 450 = 15 panels

Upkeep and Performance Tracking
Grid-connected solar configurations demand minimal maintenance but gain from consistent monitoring and periodic upkeep.
Periodic Maintenance Essentials
Most grid-tied setups need only fundamental maintenance:
Annual Tasks
- Visual inspection: Check for damaged modules, loose connections, or debris accumulation
- Performance review: Compare actual vs. projected production
- Inverter check: Confirm proper operation and absence of error codes
- Electrical connections: Verify all connections stay secure and corrosion-free
Seasonal Tasks
- Panel cleaning: Eliminate dust, foliage, or snow as necessary
- Vegetation management: Trim trees or shrubs creating shade
- Weather damage assessment: Examine after extreme weather incidents
Optimal Performance Tracking Methods
Strategic monitoring helps detect issues before they affect production:
Key Performance Metrics
- Daily production (kWh): Compare to weather conditions and historical records
- System efficiency: Actual vs. theoretical generation
- Individual panel performance: Identify underperforming modules (microinverter configurations)
- Monthly/annual trends: Monitor long-term performance decline
Monitoring Tools
- Brand-specific applications: Inverter producers offer proprietary monitoring software
- Independent platforms: Manufacturer-agnostic monitoring systems supporting various equipment brands
- Utility measurement devices: Fundamental generation documentation
- Household energy trackers: Wide-ranging energy consumption evaluation
Typical Problem Diagnosis
Identify and resolve common grid-tied solar challenges:
Reduced Production
- Shading: New barriers blocking sunlight
- Soiling: Dust, dirt, or debris on modules
- Equipment failure: Inverter or module malfunction
- Grid issues: Utility voltage complications affecting inverter function
System Deactivation
- Grid outage: Anti-islanding protection activating
- Inverter fault: Safety shutdown due to electrical fault
- Temperature extremes: High-temperature shutdown protection
- Ground fault: Electrical protection systems activating
Protecting Your Warranty Coverage:
Understanding warranty terms secures your solar investment and provides lasting peace of mind.
What’s Covered Under Warranty
- Solar modules: 25-year power production guarantee, 10-12 year equipment defect coverage
- Power inverters: 10-25 year warranty varying by type and brand
- Racking systems: 10-20 year protection on mounting structures and hardware
- Installation labor: 2-10 year workmanship guarantee from your contractor
Smart Warranty Management
- Register immediately: Sign up your equipment with manufacturers right after installation completes
- Keep detailed records: Save all performance data and maintenance receipts
- Report problems quickly: File warranty claims as soon as issues arise to protect your rights
- Know transfer rules: Learn how warranties transfer if you sell your home
Future Considerations
Anticipating future developments guarantees your grid-connected array remains beneficial and modifiable across its multi-decade service period.
Integrating Energy Storage Solutions
Many homeowners begin with basic grid-connected setups and then later incorporate battery storage capabilities:
Upgrade Pathways
- Alternating current-coupled batteries: Compatible with existing grid-tied power conversion infrastructure
- Direct current-coupled systems: Might require inverter upgrade for seamless functionality
- Dual-purpose inverters: Consider storage-ready conversion equipment during initial setup phase
Storage Integration Advantages
- Continuous electricity access during utility disruptions
- Time-based rate schedule maximization
- Greater energy self-sufficiency
- Reserve power capacity for priority electrical loads
2025 Storage Pricing: Lithium-based battery systems range $1,000-$1,200 per kWh installed capacity, with typical home emergency power setups costing $10,000-$30,000.
Scalability Options
Grid-tied configurations commonly support augmentation to address evolving power demands. Understanding solar supply-side connections enables efficient system expansion:
Scaling Evaluation Factors
- Roof surface capacity: Supplementary space for expanded module deployment
- Inverter headroom: Existing conversion equipment may support added photovoltaic units
- Circuit limitations: Service panel and utility interconnection boundaries
- Regulatory constraints: Compensation program caps or connection restrictions
Typical Growth Catalysts
- EV charging requirements
- Building expansions or major renovations
- Aquatic recreation equipment addition
- Rising home-office energy demands
Technological Evolution and Enhancement Pathways
Photovoltaic innovation progresses continuously, unlocking future upgrade possibilities according to the International Energy Agency’s renewable energy outlook:
Next-Generation Technologies
- Advanced efficiency modules: Photovoltaic cells exceeding 25% efficiency transitioning to standard offerings
- Bifacial photovoltaic systems: Harnessing sunlight from dual surfaces to boost power output
- Advanced conversion equipment: Grid stabilization functions paired with enhanced tracking capabilities
- Artificial intelligence integration: Machine learning systems optimizing operational performance
Connected Home Integration
- Seamless connection with residential energy control systems following Energy Star guidelines
- EV charging automation and coordination
- Automated appliance scheduling aligned with solar generation cycles
- Active participation in utility demand management programs
Utility Network Evolution Effects
Power grid transformation directly impacts grid-tied photovoltaic systems:
Intelligent Network Advantages
- Improved dependability: Rapid fault detection and power recovery processes
- Flexible rate structures: Real-time energy pricing responding to grid demand patterns
- Support capabilities: Solar arrays contributing voltage regulation and frequency balancing
- Aggregated energy resources: Combined distributed generation forming collective power sources
Regulatory Landscape
- Compensation program revisions
- Temporal pricing architecture
- Modernization expense recovery mechanisms
- Decentralized generation incorporation standards supported by the American Solar Energy Society
Conclusion
Grid-tied solar systems represent the smartest pathway for property owners seeking to harness renewable energy while maintaining reliable power access and maximizing financial returns. With 2025 installation costs ranging $2.50-$4.00 per watt and federal tax incentives delivering 30% savings through 2032, these systems achieve payback periods of just 6-10 years while generating electricity for 25+ years.
Take decisive action by evaluating your property’s solar potential, confirming your utility’s net metering policies, and obtaining quotes from certified installers. The combination of declining equipment costs, favorable incentive programs, and proven technology makes 2025 an optimal time to transition to grid-connected solar power. For streamlined project management, consider using solar permit expediting services to accelerate approval timelines.
Remember that grid-tied systems offer unmatched flexibility. Start with a modest installation from commercial solar design specialists and expand as your energy needs grow, or retrofit battery backup when circumstances demand emergency power capabilities. Your investment today positions you for decades of reduced electricity expenses, environmental benefits supported by the World Bank’s energy initiatives, and energy security as utility rates continue climbing and grid modernization advances.
Begin your solar journey by analyzing your annual electricity consumption, assessing your roof’s solar potential, and connecting with experienced solar professionals through Solar Permit Solutions who can design a system tailored to your specific requirements and financial goals. Visit our blog for additional insights and resources, or contact us for personalized project assistance.
FAQs
Affordable Solar Permit Plans
Don't let permit costs slow your project. Professional plan sets at competitive prices — all 50 states, fast turnaround.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, standard grid-tied solar configurations automatically shut down during utility outages due to anti-islanding safety protocols. This critical safety mechanism protects utility workers repairing power lines from unexpected electrical hazards. Your system stops generating electricity when grid power fails, even during sunny conditions. However, you can add battery backup storage to your grid-tied system, creating a hybrid configuration that provides emergency power to critical circuits during outages while maintaining grid connection benefits during normal operation.
Savings vary based on your location, electricity rates, system size, and net metering policies. A typical 6kW residential system in areas with favorable conditions generates $1,500-$2,500 in annual electricity savings. Over 25 years, expect total savings of $30,000-$50,000 after accounting for your initial investment. Properties in states with high electricity rates and strong net metering programs achieve the highest returns. Calculate your specific savings by analyzing your current electricity costs, local solar irradiance levels, available incentives, and utility compensation rates for excess generation.
Surplus electricity flows backward through your utility meter into the grid via net metering. Your meter tracks both electricity consumed from the grid and excess energy exported to the grid. Most utilities credit your account for exported electricity at retail or wholesale rates, depending on your state's net metering regulations. These credits typically roll forward month-to-month, allowing you to bank excess summer production to offset higher winter consumption. Verify your utility's specific net metering terms, as policies vary significantly across different service territories and continue evolving through regulatory changes.
Determine your system size by analyzing 12 months of utility bills to calculate annual consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Divide your annual usage by 365 to find daily average consumption, then divide by your location's peak sun hours and a 0.85 efficiency factor. For example, if you consume 10,800 kWh annually in an area with 5.2 peak sun hours, you need approximately 6.7 kW: (10,800 divided by 365 divided by 5.2 divided by 0.85). Most homeowners target 80-90% offset to avoid overproduction, though you might size larger when planning electric vehicle adoption or property expansions.
Grid-tied configurations demand minimal ongoing maintenance compared to battery-based systems. Perform annual visual inspections checking for damaged panels, loose connections, or debris accumulation. Review system performance monthly using monitoring apps to identify production issues early. Clean panels 1-2 times yearly in dusty climates or after severe weather events. Rainfall naturally cleans panels in most regions. Trim vegetation causing shade and verify inverter operation remains error-free. Professional maintenance services typically cost $150-$300 annually and include comprehensive system checks, performance optimization, and electrical connection verification. Most systems operate reliably for 25+ years with this basic maintenance schedule.
SPS Editorial Team
Solar Permit Solutions
Solar Permit Solutions provides professional solar permit design services for residential, commercial, and off-grid installations across all 50 states. Our team ensures permit-ready plan sets delivered fast.
Related Articles
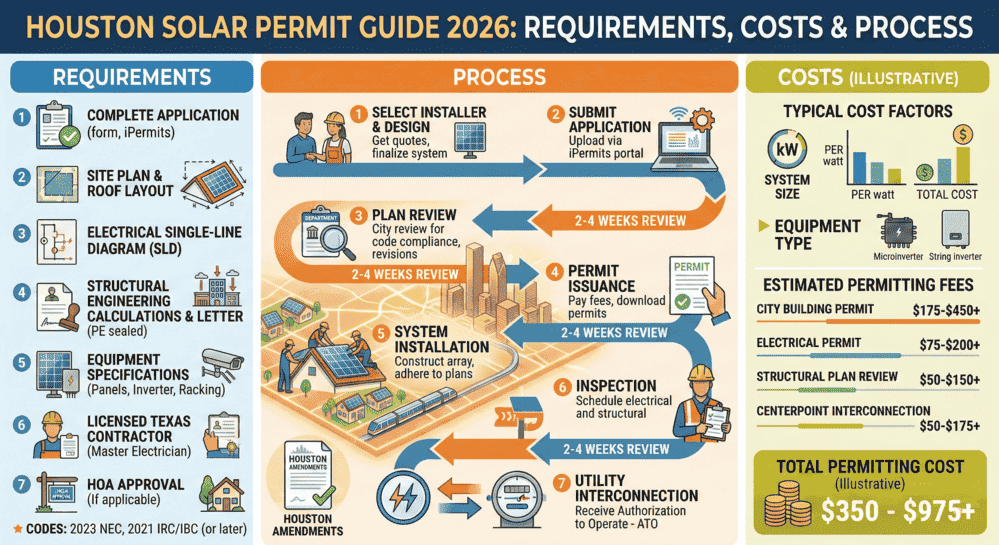
Houston Solar Permit Guide 2026: Requirements, Costs & Process
Quick Answer: In Houston, TX, solar PV installations require a building permit (...
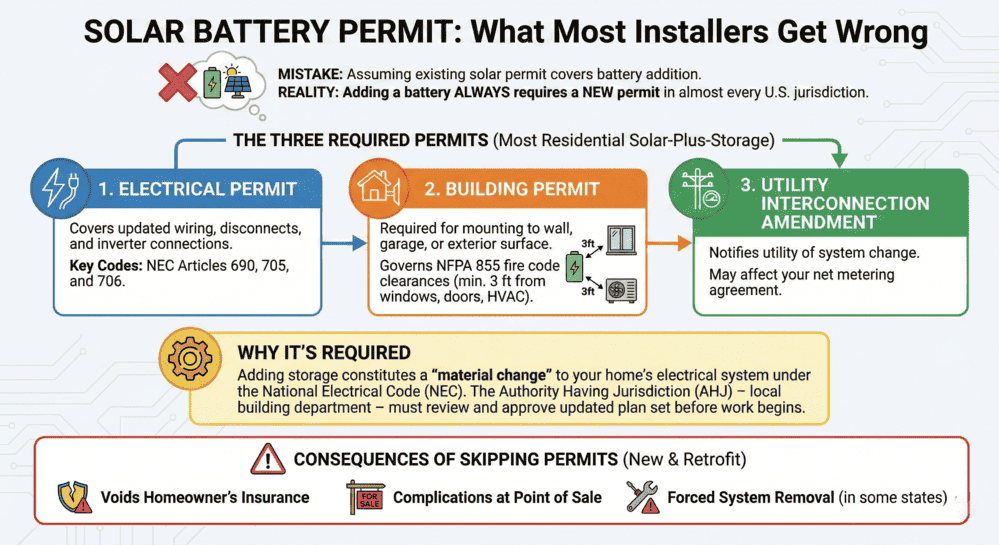
Solar Battery Permit: What Most Installers Get Wrong
Adding a battery to a solar system requires a new permit in almost every U.S. ju...
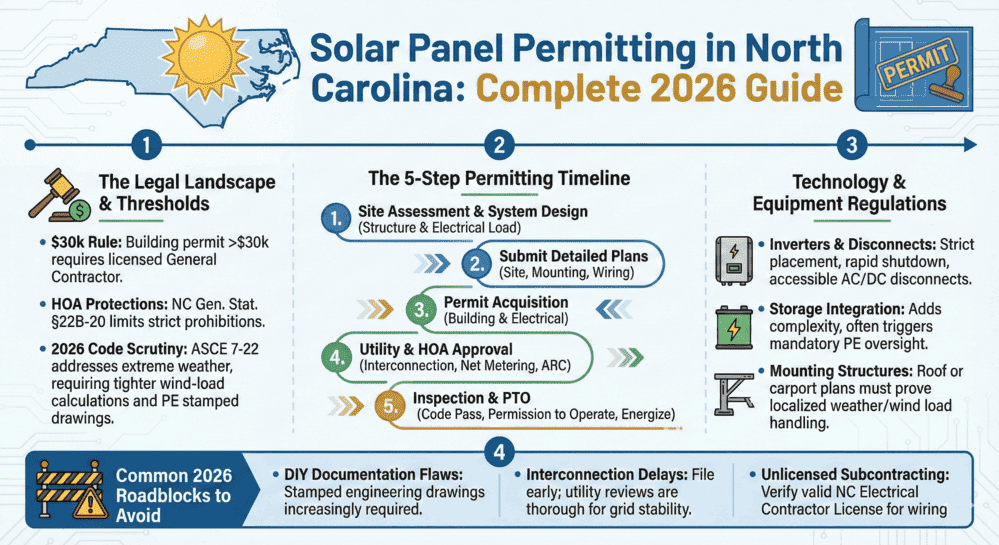
New 2026 North Carolina Solar Permit Guide: Duke Energy & Storage Rules
Learn North Carolina solar panel licensing and permitting requirements. Discover...